Willem Einthoven - Inventor of the First Practical Ecg, Timeline and Personal Life
Willem Einthoven's Personal Details
Willem Einthoven was a renowned Dutch physiologist who received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1924 for inventing the first practical electrocardiogram
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | May 21, 1860 |
| Died on | September 29, 1927 |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Famous | Inventors & Discoverers, General Practitioners, Inventor of the First Practical Ecg |
| Known as | Dr. Willem Einthoven |
| Universities |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Semarang |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Taurus |
| Born in | Semarang |
| Famous as | Inventor of the first practical ECG |
| Died at Age | 67 |
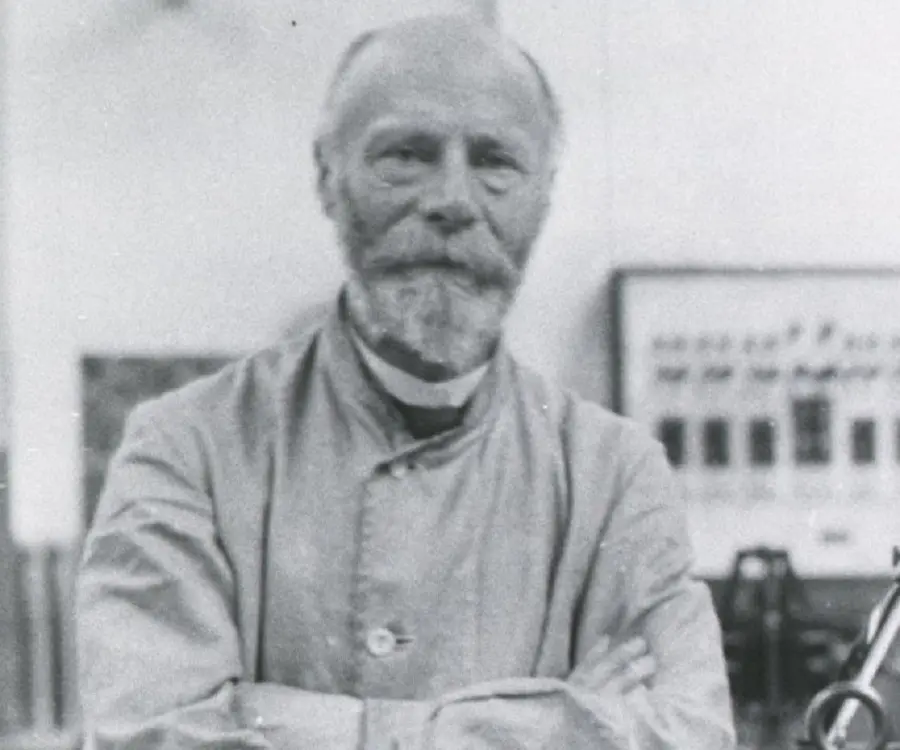
Willem Einthoven's photo
Who is Willem Einthoven?
Willem Einthoven was a renowned Dutch physiologist who received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1924 for inventing the first practical electrocardiogram. He was born in Dutch East Indies but the family returned to Netherlands after his father’s premature death and settled at Utrecht, where he was first admitted to the Hogere Burgerschoo and then to the University of Utrecht. Ultimately, he secured a medical degree from the University of Utrecht and began his career as an assistant to a renowned ophthalmologist at the famous eye-hospital “Gasthuis voor Ooglidders”. Later he shifted to the University of Leiden as Professor of Physiology and remained there until his death. Towards the end of the nineteenth century he embarked on a new project, which would ultimately make him famous. Sometime now, he was asked to accurately register the heart sound of human being; but the tool available at that time was not adequate for that purpose. So after few years of hard work, he devised his own string galvanometer, which could measure the heartbeats and record them graphically. Though a little bulky, it was the first practical electrocardiogram, which later became an essential tool for doctors dealing with varied types of heart diseases. Much later he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for this invention.
// Famous Inventors & Discoverers
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Thomas Newcomen
Thomas Newcomen was a British inventor who developed the world’s first steam engine. Browse through this biography to learn in details about his life, career, works and timeline.
Erno Rubik
The famous inventor and educationist, Erno Rubik is known world-wide for his invention the ‘Rubik’s Cube’. To know more about the childhood, profile, timeline and career of this famous architect-inventor read on.
Childhood & Early Years
Willem Einthoven was born on May 21, 1860, in Semarang on the island of Java, Indonesia, then known as Dutch East Indies. His father, Jacob Einthoven, born and educated in Netherlands, was an army medical officer posted there. He later became parish doctor in Semarang.
Willem’s mother, Louise M.M.C. de Vogel, was the daughter of the then Director of Finance in the Indies. He was the third child and the eldest son his parent’s six children.
Willem lost his father at the age of six. Four years later his mother decided to shift to Netherland and subsequently settled down at Utrecht with her six children.
Willem graduated from the secondary school in 1878 and then entered the University of Utrecht as a medical student. Initially it was expected that he would follow his father’s foot step and become a doctor; but soon he began to show an outstanding talent in research work.
Career
After Einthoven gained his ‘candidaat’ diploma, which was equivalent to the B.Sc. degree, he joined a renowned eye-hospital, Gasthuis voor Ooglidders. There he started working as an assistant to distinguished ophthalmologist H. Snellen Sr.
Sometime now, he broke his wrist. The accident kindled his interest in anatomy. Before long he published his first major paper titled ‘Quelques remarques sur le mécanisme de l'articulation du coude’ (Some remarks on the elbow joint) under the guidance of anatomist W. Koster. It attracted a widespread attention.
He next studied under physiologist F.C. Donders and in 1885 published his second paper entitled ‘Stereoscopie door kleurverschil’ (Stereoscopy by means of colour variation). It served as his doctoral thesis.
On July 4, 1885, Einthoven received his medical doctoral degree from the University of Utrecht. In the same year, he was appointed as the Professor of Physiology at the University of Leiden. However, he took up the position in January 1886, after he had qualified as a general practitioner.
At Leiden, Einthoven continued with his research work. In 1892, he published his first important paper titled ‘Über die Wirkung der Bronchialmuskeln nach einer neuen Methode untersucht, und über Asthma nervosum’ (On the function of the bronchial muscles investigated by a new method, and on nervous asthma) from there.
At the same time, he began working on optics and remained devoted to the topic throughout his life. In 1898, he published another paper titled ‘Eine einfache physiologische Erklärung für verschiedene geometrisch-optische Täuschungen’ (A simple physiological explanation for various geometric-optical illusions).
However much before that, in 1889, Einthoven had witnessed Augustus Desiré Waller registering the current of the heart as deduced from the body surface with the help of a capillary electrometer at the First International Congress of Physiologists. It interested young Einthoven a great deal.
Einthoven’s great opportunity came when he was assigned the task of accurately registering the heart sounds. Since capillary electrometer, used for measuring the heart beats, was not suitable for diagnostic purpose, he began working in that direction.
He first began to investigate the theoretical principles of capillary electrometer and then devised ways to correct the mathematical errors in the photographically registered results, which generally occurred due to the inertia of the gadget.
In 1901, after intense research he invented a prototype of string galvanometer, which did not involve any kind of mathematical calculation. However, the instrument needed to be more sophisticated and precise if it were to be used for medical purpose.
He then went on to refine the instrument and at the same time continued his work on optics. In 1902, he published his second important paper, titled Die Accommodation des menschlichen Auges" (The accommodation of the human eye) on the topic.
Finally in 1903, after a hard labor, Einthoven developed the first string galvanometer, later known as the Einthoven galvanometer. The device could measure the changes of electrical potential caused by contractions of the heart muscle and record them graphically.
The instrument he designed was bulky, but could be used as effectively in medical science as in other types of technical research. Einthoven now began to study electrocardiographic features of different types of cardio vascular diseases and collaborated with P. Battaerd to study heart sounds.
At the same time, he worked with W. A. Jolly to carry on research into retina current. In 1908, Einthoven published his third most important paper on optics titled ‘The form and magnitude of the electric response of the eye to stimulation by light at various intensities’.
Also from 1908 to 1913, Einthoven studied the patterns of normal heart sounds so that deviations could be recognized and interpreted instantly. He also continued to work on electrode arrangements and in 1912 developed the concept of imaginary inverted equilateral triangle centered on the chest, today known as Einthoven’s Triangle.
In fact, many of the terminologies used in electrocardiography even today have originated from Einthoven. For example, he had assigned the letters P, Q, R, S and T to the various deflections; they are being used even today.
Einthoven spent his later years working on acoustic and capacity studies. It led to development of string phonograph in 1923. He continued working till his death publishing number of important papers from the University of Leiden.
Major Works
Einthoven is best remembered for his invention of string galvanometer, which was the first practical electrocardiograph suitable for medical use. Although one such machine had been recorded in 1887 it could not produce any quantifiable result.
Contrarily, Einthoven’s invention could detect and record even the minutest electric currents produced by human heart. In addition to that the string galvanometer is widely used in the study of the periphery and sympathetic nerves.
Awards & Achievements
Willem Einthoven was awarded with the 1924 Nobel Prize in Medicine ‘for his discovery of the mechanism of the electrocardiogram’.
In 1902, Einthoven became a Member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1886, Einthoven married his first cousin Frédérique Jeanne Louise de Vogel. She was the sister of Dr. W.Th. de Vogel, former Director of Public Health Service in the Dutch East Indies. The couple had four children; Augusta, Louise, Willem and Johanna.
Among them, Willem was the Director of the Radio Laboratory in Bandung, Java. He was also a reputed electro-technical engineer. Around 1912, he along with his father developed the first vacuum model of the string galvanometer and used it for wireless communication. Johanna was a physician.
Towards the end of his life Einthoven suffered from various ailments. He died 29 September 1927 in Leiden and his mortal remains were buried in the graveyard of the Reformed Church in Oegstgeest.
Trivia
Einthoven was also very fond of sports and was a keen sportsman in his student days. Later he became the President of the Gymnastics and Fencing Union. He was also one of the founders of the Utrecht Student Rowing Club.
// Famous General Practitioners
Paul Tournier
Paul Tournier was a Swiss physician and author; he is regarded as the twentieth century's most famous Christian physician. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Bidhan Chandra Roy
Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy was an eminent Indian freedom fighter and the second Chief Minister of West Bengal. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Upendranath Brahmachari
Upendranath Brahmachari was a renowned Indian scientist and a prominent medical practitioner of his era. This biography of Upendranath Brahmachari provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Willem Einthoven's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine | |
Willem Einthoven biography timelines
- // 21st May 1860Willem Einthoven was born on May 21, 1860, in Semarang on the island of Java, Indonesia, then known as Dutch East Indies. His father, Jacob Einthoven, born and educated in Netherlands, was an army medical officer posted there. He later became parish doctor in Semarang.
- // 1878Willem graduated from the secondary school in 1878 and then entered the University of Utrecht as a medical student. Initially it was expected that he would follow his father’s foot step and become a doctor; but soon he began to show an outstanding talent in research work.
- // 1885He next studied under physiologist F.C. Donders and in 1885 published his second paper entitled ‘Stereoscopie door kleurverschil’ (Stereoscopy by means of colour variation). It served as his doctoral thesis.
- // 4th Jul 1885 To Jan 1886On July 4, 1885, Einthoven received his medical doctoral degree from the University of Utrecht. In the same year, he was appointed as the Professor of Physiology at the University of Leiden. However, he took up the position in January 1886, after he had qualified as a general practitioner.
- // 1886In 1886, Einthoven married his first cousin Frédérique Jeanne Louise de Vogel. She was the sister of Dr. W.Th. de Vogel, former Director of Public Health Service in the Dutch East Indies. The couple had four children; Augusta, Louise, Willem and Johanna.
- // 1887Einthoven is best remembered for his invention of string galvanometer, which was the first practical electrocardiograph suitable for medical use. Although one such machine had been recorded in 1887 it could not produce any quantifiable result.
- // 1889However much before that, in 1889, Einthoven had witnessed Augustus Desiré Waller registering the current of the heart as deduced from the body surface with the help of a capillary electrometer at the First International Congress of Physiologists. It interested young Einthoven a great deal.
- // 1892At Leiden, Einthoven continued with his research work. In 1892, he published his first important paper titled ‘Über die Wirkung der Bronchialmuskeln nach einer neuen Methode untersucht, und über Asthma nervosum’ (On the function of the bronchial muscles investigated by a new method, and on nervous asthma) from there.
- // 1898At the same time, he began working on optics and remained devoted to the topic throughout his life. In 1898, he published another paper titled ‘Eine einfache physiologische Erklärung für verschiedene geometrisch-optische Täuschungen’ (A simple physiological explanation for various geometric-optical illusions).
- // 1901In 1901, after intense research he invented a prototype of string galvanometer, which did not involve any kind of mathematical calculation. However, the instrument needed to be more sophisticated and precise if it were to be used for medical purpose.
- // 1902He then went on to refine the instrument and at the same time continued his work on optics. In 1902, he published his second important paper, titled Die Accommodation des menschlichen Auges" (The accommodation of the human eye) on the topic.
- // 1902In 1902, Einthoven became a Member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
- // 1903Finally in 1903, after a hard labor, Einthoven developed the first string galvanometer, later known as the Einthoven galvanometer. The device could measure the changes of electrical potential caused by contractions of the heart muscle and record them graphically.
- // 1908At the same time, he worked with W. A. Jolly to carry on research into retina current. In 1908, Einthoven published his third most important paper on optics titled ‘The form and magnitude of the electric response of the eye to stimulation by light at various intensities’.
- // 1912Among them, Willem was the Director of the Radio Laboratory in Bandung, Java. He was also a reputed electro-technical engineer. Around 1912, he along with his father developed the first vacuum model of the string galvanometer and used it for wireless communication. Johanna was a physician.
- // 1923Einthoven spent his later years working on acoustic and capacity studies. It led to development of string phonograph in 1923. He continued working till his death publishing number of important papers from the University of Leiden.
- // 1924Willem Einthoven was awarded with the 1924 Nobel Prize in Medicine ‘for his discovery of the mechanism of the electrocardiogram’.
- // 29th Sep 1927Towards the end of his life Einthoven suffered from various ailments. He died 29 September 1927 in Leiden and his mortal remains were buried in the graveyard of the Reformed Church in Oegstgeest.
// Famous Taurus Celebrities peoples
Jason Simpson
Jason Simpson is the son of former NFL running back, broadcaster and actor O. J. Simpson. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, life, and little known facts about him.
Sophie Reade
Sophie Victoria Reade is a British model and reality show star. Let’s take a look at her family and personal life, including her age, birthday, boyfriends, and some interesting facts.
ASMR Aspen
ASMR Aspen is an American YouTuber. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin was a famous Swedish economist. This biography profiles his childhood, family life & achievements.
Josh Temple
Check out all that you wanted to know about Josh Temple (Slogoman), the famous British YouTube Personality; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Aidan Prince
Aidan Prince is an American dancer, actor and vlogger. Let’s have a look at his family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, and fun facts.
Willem Einthoven's FAQ
What is Willem Einthoven birthday?
Willem Einthoven was born at 1860-05-21
When was Willem Einthoven died?
Willem Einthoven was died at 1927-09-29
Where was Willem Einthoven died?
Willem Einthoven was died in Leiden
Which age was Willem Einthoven died?
Willem Einthoven was died at age 67
Where is Willem Einthoven's birth place?
Willem Einthoven was born in Semarang
What is Willem Einthoven nationalities?
Willem Einthoven's nationalities is Dutch
What was Willem Einthoven universities?
Willem Einthoven studied at Utrecht University
What is Willem Einthoven's inventions/discoveries?
String Galvanometer, Electrocardiography was invented (or discovered) by Willem Einthoven
What is Willem Einthoven's sun sign?
Willem Einthoven is Taurus
How famous is Willem Einthoven?
Willem Einthoven is famouse as Inventor of the first practical ECG