Walther Bothe - Physicists, Career and Family
Walther Bothe's Personal Details
Walther Bothe was a German nuclear physicist who won the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | January 8, 1891 |
| Died on | February 8, 1957 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Scientists, Physicists |
| Spouses | Barbara Belowa |
| Known as | Walter Bothe |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Oranienburg |
| Religion | Lutheranism |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Capricorn |
| Born in | Oranienburg |
| Famous as | Physicist |
| Died at Age | 66 |
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
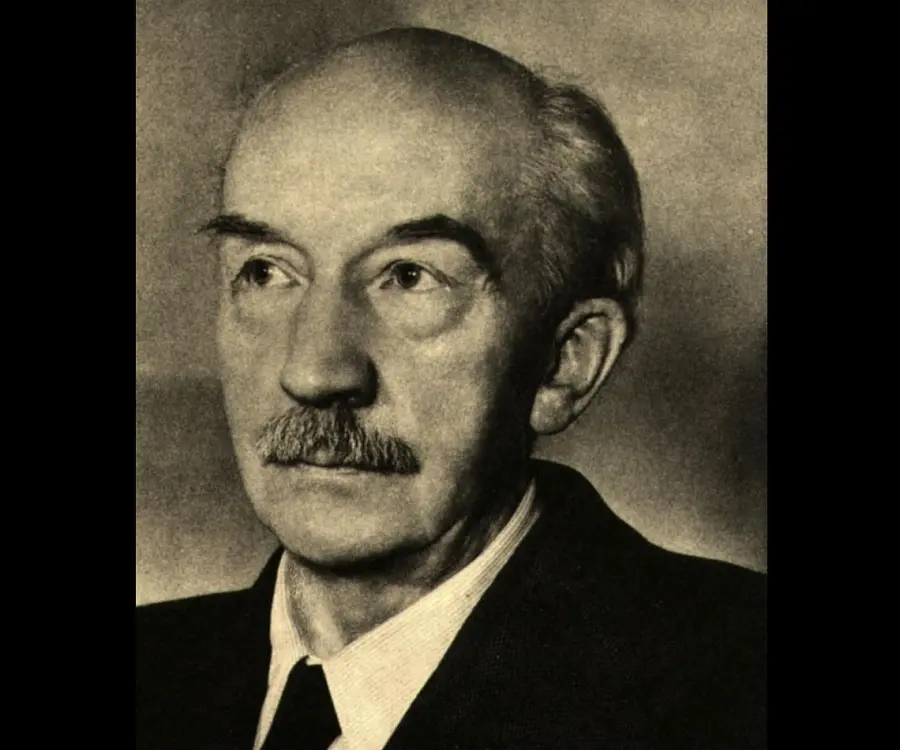
Walther Bothe's photo
Who is Walther Bothe?
Walther Bothe was a German nuclear physicist whose contributions play an important part in particle physics and various other spheres of science and technology. His research came at a time when nuclear physics was gaining popularity. Many of his works and their derivatives are used even to this day. Many ground-breaking discoveries and observations were able to see the light of day due to his work. His curious mind was so insatiable that even in captivity he made use of the time to study mathematics and read and write Russian. Throughout his life, he held many high-ranking positions and pushed the envelope in theoretical physics. Not only did he learn under many greats, he also taught a few. His efforts did not go in vain and he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Despite his illness and frail health, he continued to break new ground in physics. He supervised and gave his inputs to many others until the end of his life. His endless stream of work continued to be a foundation and an extensive source of knowledge in the world of physics.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
Walther Wilhelm Georg Bothe was born on January 8, 1891, in Oranienburg, near Berlin, Germany, to Charlotte Hartung and Fredrich Bothe
Growing up, he showed a great interest in Physics. Between 1908 and 1912 Bothe studied at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität (now known as the Humboldt University of Berlin).
He studied under the tutelage of the famous physicist, Max Planck and excelled in mathematics, physics, and chemistry. He became Planck’s teaching assistant in 1913. Just before the First World War broke out, he obtained his doctorate, in 1914, under Planck.
Career
In 1913, he was offered a job at the Physikalische-Technische Reichsanstalt (presently known as Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt). He served there as a ‘Professor Extraordinary’ until 1930.
In 1914, after obtaining his doctorate, he proceeded to join the German cavalry. He was captured by the Russians and imprisoned for over 5 years in Siberia. During his captivity, he chose to study mathematics and also learnt to read and write Russian. He was released in 1920 and he returned to Germany.
Walther Bothe was an active theoretical and experimental physicist. He worked on the scattering of alpha and beta rays and devised a theory involving scattering at small angles.
He and Hans Geiger, in 1924, performed an experiment involving the wavelike properties of radiation. Both of them formulated a new quantum theory of radiation. He published his coincidence method and applied it to the study of nuclear reactions, the “Compton Effect”, and the wave-particle duality of light.
In 1925, while still at Physikalische-Technische Reichsanstalt, he became a ‘Privatdozent’ (denotes an ability to teach independently at university level. Later on in 1929, he became an ‘ausserordentlicher Professor’ (extraordinarius professor) there 1929.
In 1929, he began another study focusing on cosmic rays. This subject would go on to become his lifelong muse. For this study, he collaborated with guest professors at the university, Werner Kolhörster and Bruno Rossi.
In 1930, he became an ‘ordentlicher Professor’ (ordinarius professor) and was appointed ‘Director of the Institute of Physics’ at the Justus Liebig-Universität Gießen (University of Giessen). In 1930, he discovered an unusual radiation emitted by beryllium when it is bombarded with alpha particles. This would later lead to the discovery of the neutron in 1932 by Sir James Chadwick.
Walther Bothe was appointed the Director of the ‘Physikalische und Radiologische Institut’ (Physical and Radiological Institute) at the University of Heidelberg, in 1932.
With the rise of Hitler, the concept of Deutsche Physik [German Physics] or Aryan Physics started gaining momentum. It was a political concept that was against theoretical, modern, atomic, and nuclear physics as well as against quantum mechanics. This led to a number of violent attacks on theoretical physicists. Under the influence of Philipp Lenard, he was able to move on to the Directorial position at Institut für Physik (Institute for Physics) at ‘Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut für medizinische Forschung’ (the Max-Planck-Institut für medizinische Forschung).
At Heidelberg, he set up a cyclotron from funds obtained from various research groups. During World War II, he was able to work on the diffusion theory of neutrons and related measurements.
His research paper, ‘Atlas of Typical Cloud Chamber Images’ was published in 1940. It contained images gathered from a cloud chamber built by Heinz Maier-Leibnitz. It depicts scattered particles and means to identify them.
He became an ‘ordentlicher Professor’ at the University of Heidelberg between 1946 and 1957. He was a member of the ‘Arbeitskreis Kernphysik’ (Nuclear Physics Working Group) of the ‘Deutschen Atomkommission’ [German Atomic Energy Commission) during 1956 and 1957.
Major Works
His most famous work is the ‘Coincidence Circuit’ that works on the coincidence principle. Walther Bothe used two Geiger counters and studied the coincidences between scattered X-rays and recoiling electrons. The observations indicated a small scale conservation of energy and momentum. He also used this principle to show that cosmic rays act like particles.
Awards & Achievements
For his coincidence method and the discoveries made therewith, Walther Bothe was co-awarded the “Nobel Prize in Physics” in 1954. The other recipient of the award was Max Born. The coincidence method and its circuits are widely used in many particle physics experiments and various other areas of science and technology.
In 1952, he was awarded Knight of the Order of Merit for Sciences and the Arts.
In 1953, he was honored with the Max-Planck-Medaille of the Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft..
Personal Life & Legacy
During his incarceration in Russia, Walther Bothe met Barbara Below. She was from Moscow and returned with him to Germany after their wedding in 1920. They sired two children.
Though he was a busy man, he took time off to paint. His inspirations were the mountains and he dabbled in oil and watercolor pieces. He discussed French impressionists with the same enthusiasm with which he discussed physics.
He was also a music lover, listening to pieces by Beethoven and Bach. He used to attend many concerts and learnt to play the piano.
At work, he was a highly difficult and strict teacher with a gift of concentration and speed. At home, however, he was a gracious and hospitable man with a lot of ease and happiness.
He died in Heidelberg, West Germany, on February 8, 1957, at the age of 66.
// Famous German peoples
Jordan Carver
Jordan Carver is a famous German model. Let’s take a close look at her personal life, including her age, career, net worth, achievements and some fun facts.
Jürgen Klopp
Jürgen Klopp is a German football manager, and a former professional football player. Check out this biography to know more about his childhood, family, personal life, etc.
Irma Grese
Irma Grese was a notorious German Nazi concentration camp guard during the Second World War. This biography profiles her childhood, life, horrifying acts, death and other facts.
Walther Bothe's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | 1954 - Nobel Prize in Physics | |
| 0 | 1953 - Max Planck Medal | |
Walther Bothe biography timelines
- // 8th Jan 1891Walther Wilhelm Georg Bothe was born on January 8, 1891, in Oranienburg, near Berlin, Germany, to Charlotte Hartung and Fredrich Bothe
- // 1908 To 1912Growing up, he showed a great interest in Physics. Between 1908 and 1912 Bothe studied at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität (now known as the Humboldt University of Berlin).
- // 1913 To 1914He studied under the tutelage of the famous physicist, Max Planck and excelled in mathematics, physics, and chemistry. He became Planck’s teaching assistant in 1913. Just before the First World War broke out, he obtained his doctorate, in 1914, under Planck.
- // 1913 To 1930In 1913, he was offered a job at the Physikalische-Technische Reichsanstalt (presently known as Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt). He served there as a ‘Professor Extraordinary’ until 1930.
- // 1914 To 1920In 1914, after obtaining his doctorate, he proceeded to join the German cavalry. He was captured by the Russians and imprisoned for over 5 years in Siberia. During his captivity, he chose to study mathematics and also learnt to read and write Russian. He was released in 1920 and he returned to Germany.
- // 1920During his incarceration in Russia, Walther Bothe met Barbara Below. She was from Moscow and returned with him to Germany after their wedding in 1920. They sired two children.
- // 1924He and Hans Geiger, in 1924, performed an experiment involving the wavelike properties of radiation. Both of them formulated a new quantum theory of radiation. He published his coincidence method and applied it to the study of nuclear reactions, the “Compton Effect”, and the wave-particle duality of light.
- // 1929In 1929, he began another study focusing on cosmic rays. This subject would go on to become his lifelong muse. For this study, he collaborated with guest professors at the university, Werner Kolhörster and Bruno Rossi.
- // 1932Walther Bothe was appointed the Director of the ‘Physikalische und Radiologische Institut’ (Physical and Radiological Institute) at the University of Heidelberg, in 1932.
- // 1940His research paper, ‘Atlas of Typical Cloud Chamber Images’ was published in 1940. It contained images gathered from a cloud chamber built by Heinz Maier-Leibnitz. It depicts scattered particles and means to identify them.
- // 1952In 1952, he was awarded Knight of the Order of Merit for Sciences and the Arts.
- // 1953In 1953, he was honored with the Max-Planck-Medaille of the Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft..
- // 1954For his coincidence method and the discoveries made therewith, Walther Bothe was co-awarded the “Nobel Prize in Physics” in 1954. The other recipient of the award was Max Born. The coincidence method and its circuits are widely used in many particle physics experiments and various other areas of science and technology.
- // 8th Feb 1957He died in Heidelberg, West Germany, on February 8, 1957, at the age of 66.
// Famous Capricorn Celebrities peoples
Weston Koury
All about American social media star Weston Koury, including his age, family life, girlfriends, birthday, and some fun facts.
Elin Nordegren
Elin Nordegren is the ex-wife of Tiger Woods. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her life.
ItsJustNick
ItsJustNick is a Canadian YouTube star & social media personality. Let’s take a look at his family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, girlfriends, and fun facts.
Rudan Custodio
Check out all that you wanted to know about Rudan Custodio, the famous American YouTube Personality; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Zahara Jolie-Pitt
Zahara Jolie-Pitt is the adopted daughter of former celebrity couple Angelina Jolie and Brad Pitt. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life and fun facts about her.
Adam Dahlberg
Check out all that you wanted to know about Adam Dahlberg, the famous YouTuber and gamer; his birthday, his family and personal life, his wife, fun trivia facts and more.
Walther Bothe's FAQ
What is Walther Bothe birthday?
Walther Bothe was born at 1891-01-08
When was Walther Bothe died?
Walther Bothe was died at 1957-02-08
Where was Walther Bothe died?
Walther Bothe was died in Heidelberg
Which age was Walther Bothe died?
Walther Bothe was died at age 66
Where is Walther Bothe's birth place?
Walther Bothe was born in Oranienburg
What is Walther Bothe nationalities?
Walther Bothe's nationalities is German
Who is Walther Bothe spouses?
Walther Bothe's spouses is Barbara Belowa
What was Walther Bothe universities?
Walther Bothe studied at Humboldt University of Berlin
What is Walther Bothe's religion?
Walther Bothe's religion is Lutheranism
What is Walther Bothe's sun sign?
Walther Bothe is Capricorn
How famous is Walther Bothe?
Walther Bothe is famouse as Physicist