Walter Kohn - Chemists, Timeline and Facts
Walter Kohn's Personal Details
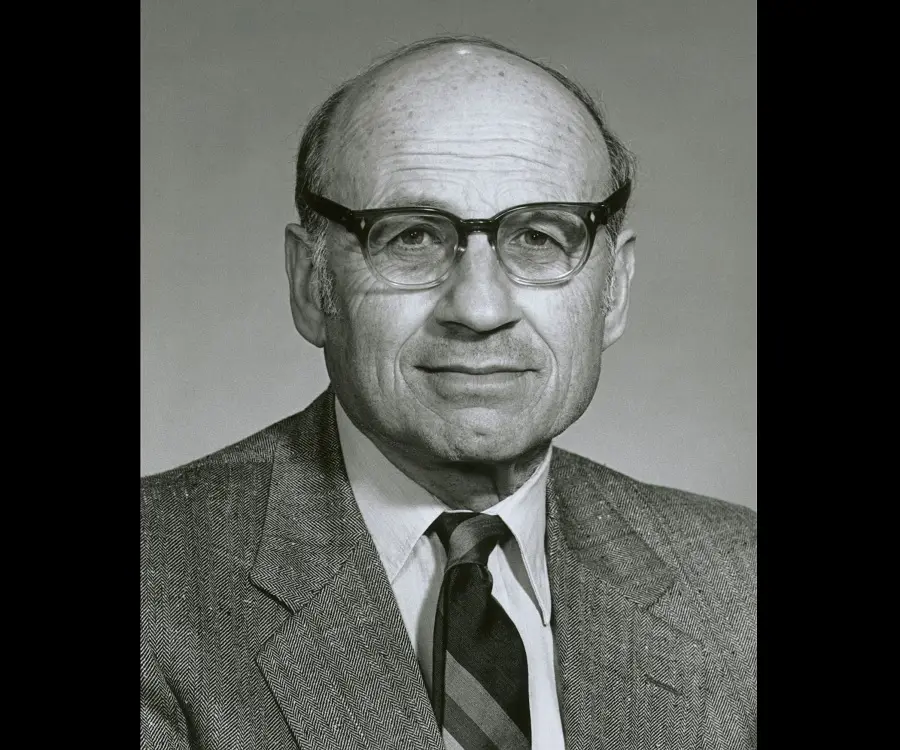
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | March 9, 1923 |
| Died on | April 19, 2016 |
| Nationality | Austrian |
| Famous | Harvard University, University Of Toronto, Scientists, Physicists, Chemists, Chemists, Physicists |
| Spouses | Lois Kohn (m. 1948), Mara Schiff (m. 1955) |
| Childrens | Ingrid Kohn, Marilyn Kohn, Martin Steven Kohn, Minna Kohn, Ros Dimenstein, Sharon Ruth Kohn, Thomas David Kohn |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Vienna, Austria |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Pisces |
| Born in | Vienna, Austria |
| Famous as | Physicist and Chemist |
| Died at Age | 93 |
// Famous Chemists
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. This biography of Louis Pasteur provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday was the most celebrated British scientist of the 19th century. Know more about his childhood and life with this biography.
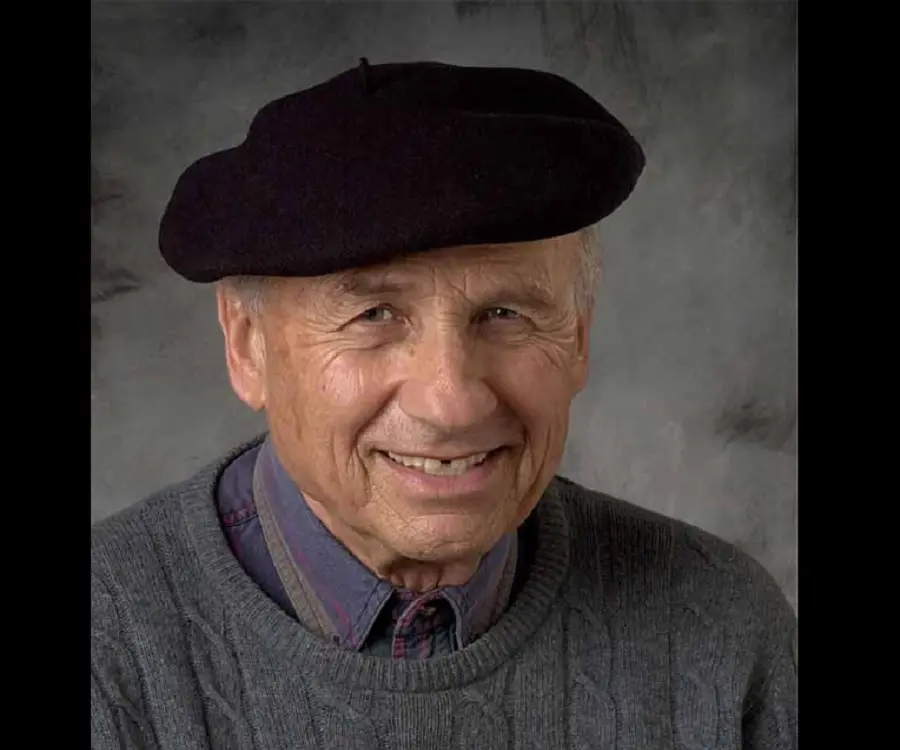
Walter Kohn's photo
Who is Walter Kohn?
Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical physicist and theoretical chemist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1998 for his development of the density -functional theory. He shared the prize with John Pople who independently carried out computational work in quantum mechanics. Kohn’s density-functional theory helped incorporate quantum mechanical effects in electronic density. Furthermore, it was due to his theory that the age-old belief of accounting every electron's movement was thwarted. Instead, he showed that one could look at the average density of electrons in the space. This gave the scientific world a better understanding and new insight for calculations involving chemical structures and reactions. It also simplified the computation needed to understand the electron bonding between atoms within molecules. In his lifetime, Kohn was felicitated with numerous awards and honours for his remarkable contribution to the sciience. He was a member of numerous prestigious scientific institutions and communities.
// Famous Physicists
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Gabriel Lippmann
Gabriel Lippmann was a French physicist and inventor. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1908. This biography of Lippmann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Karl Ferdinand Braun
Karl Ferdinand Braun was a German physicist and inventor who received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1909. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, inventions, career, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Walter Kohn was born on March 9, 1923 in Vienna, Austria, to Salomon and Gittel Kohn. His earliest memory of his childhood was that of being subjugated by the Austrian Nazi regime.
Kohn gained his early education from a public elementary school. He later enrolled at the Akademische Gymnasium where he developed an interest for Latin and Greek.
In 1938, when Hitler’s Germany annexed Austria, the Kohns’ were tarnished financially and socially. Their family business was confiscated and they were ripped off their freedom. Young Kohn was expelled from his school. Subsequently, he entered a Jewish school where he developed his interest in mathematics and science.
During World War II, Kohn was transported to England in the famous Kindertransport rescue operation, his parents being unable to leave Austria. He was first taken to England where he stayed with the Hauffs’ who had business relation with senior Kohn. However, since he had a German nationality, he was sent to Canada by the British. In Canada, Dr Bruno Mendel served as his guardian.
He finally settled at the camp in Trois-Rivieres, meant for German internees and refugees, in Canada. Kohn’s completed his high school studies from the educational facilities at the camp. Academically bright, he passed the McGill University junior Matriculation exam and exams in mathematics, physics and chemistry on the senior matriculation level.
Kohn successfully gained admission at the University of Toronto. Since he wasn’t allowed to enter the chemistry building, he opted for physics and mathematics instead. In 1945, he graduated with a BA in applied mathematics and a year later was awarded an MA in the subject.
Obtaining a Lehmann fellowship, Kohn entered the prestigious Harvard University. Under the guidance to Julian Schwinger, he worked on Green’s function variational method of three-body scattering problem as the subject for his thesis. In 1948, Kohn struck success by discovering an elementary formulation for variational principle of scattering. Same year, he was awarded a PhD degree in physics.
Career
After completing his doctoral studies, Kohn remained in Harvard, serving as a researcher and teacher. For two years, he shared an office with Sidney Borowitz and assisted Schwinger in his work on quantum electrodynamics and the emerging field theory of strong interactions between nucleons and mesons.
While at Harvard, he also fell under the influence of Van Vleck and the sub-genre, solid state physics. Kohn even temporarily chaired Vleck’s position as a solid state physics teacher during the latter’s absence. The job gave him the opportunity to broaden his knowledge in a new arena of physics which was relatively lesser known to him.
In 1950, he secured a fellowship at the National Research Council in Copenhagen. Simultaneously, he also got a job at the Carnegie Institute of Technology. Requesting a leave of absence, he fulfilled his fellowship in Copenhagen. In Copenhagen, he turned to solid state physics. He served as a substitute teacher of the subject and did research on the subject along with Res Jost.
In 1952, he moved to Carnegie Institute of Technology. At Carnegie, he did much of his seminal work on multiple-scattering band-structure work, now known as the KKR method. Other work done by him include the image of the metallic Fermi Surface in the phonon spectrum, exponential localization of Wannier functions and the nature of the insulating state.
In 1953, supported by Van Vleck, he attained a summer job at Bell Labs as an assistant to W. Shockley. His project was on radiation damage of Si and Ge by energetic electrons, critical for the use of the then recently-developed semiconductor devices for applications in outer space. The Bell Labs, which the premier center for research in the field of solid state physics, became the summer home of Kohn where he returned every year until 1966.
Kohn’s association with Bell Labs got him involved with semiconductor physics. His collaboration with Luttinger bore fruitful results as the two came up with several unknown concepts in semiconductor physics including development of an effective Hamiltonian in the presence of magnetic fields, development of the first non-heuristic derivation of the Boltzman transport equation for quantum mechanical particles and development of the Luttinger-Kohn model of semiconductor band structure.
In 1960, Kohn took up an academic position as the Physics Department chair at the then newly founded University of California, San Diego. He spent a sabbatical semester at the Ecole Normale Superieure in Paris in 1963 when he initiated his work in the development of density functional theory.
Kohn’s quest to know whether an alloy is completely or only partially characterized by its electronic density distribution led to his unearthing of the act that for a single particle, there is an explicit elementary relation between the potential and the density of the ground-state. He realized that two different potentials with associated different groundstates could give rise to the same density distribution.
He laid the foundation for a theory that stated it was not necessary to account for every electron's movement. Instead, one could look at the average density of electrons in the space. His finding presented new opportunities for calculations involving chemical structures and reactions.
Along with his associate Pierre Hohenberg, Kohn came up with the Hohenberg Kohn (HK) variational principle that gave the details of his findings. The duo published the report with various approximations. The Hohenberg-Kohn theorem was further developed in association with Lu Jeu Sham. Kohn and Sham came up with the Kohn-Sham equations, which has become the standard work horse of modern materials science and is even used in quantum theories of plasmas
Kohn’s stint at the University of California, San Diego lasted until 1979. Following this, he accepted the Founding Director's position at the new National Science Foundation’s Institute for Theoretical Physics in Santa Barbara. Therein, he continued to work with post-doctoral fellows on DFT.
In 1984, Kohn took up the position of a professor in the Physics Department at the University of California at Santa Barbara. He continued to work there until the end of his life.
Major Works
Kohn’s most significant contribution came with his development of the density-functional theory. All through his career, he used quantum mechanics to comprehend the electro bonding between atoms to form molecules. In 1964, he laid the foundation for a theory that stated it was not necessary to account for every electron's movement. Instead, one could look at the average density of electrons in the space. This gave the scientific world a better understanding and new insight for calculations involving chemical structures and reactions. It also simplified the computation needed to understand the electron bonding between atoms within molecules.
Awards & Achievements
For his contribution in the field of semiconductor physics, he was awarded the Oliver E. Buckley Prize and the Davison Germer Prize by the American Physical Society. He also received the Feenburg Medal.
In 1988, he received the National Medal of Science.
In 1998, Kohn was bestowed with the prestigious Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his development of the density-functional theory. He shared the prize with John Pople.
Austria honoured him with the Austria Decoration for Science and Art award and Grand Decoration of Honor in Silver with Star for Services to the Republic of Austria.
He received an honorary doctorate degree from the University of Oxford and Harvard University.
He was elected as the Foreign Member of the Royal Society. Furthermore, he became a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, National Academy of Sciences and the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science. He became an honorary member of the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
Personal Life & Legacy
Kohn was twice married in his lifetime. His first marriage was to Lois Adams and later on he married Mara Schiff.
He died of jaw cancer on April 19, 2016, at the age of 93.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie was a Physicist and Chemist, who was world renowned for her work on radioactivity. She also was the winner of two Nobel Prize. Read this biography to get info about her life and profile.
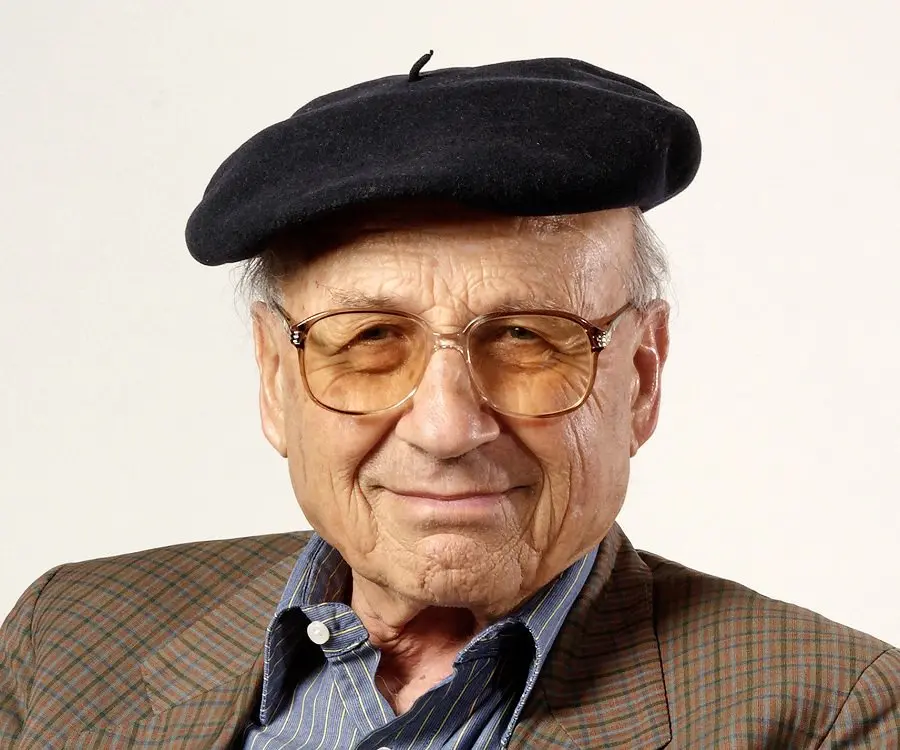
Walter Kohn's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 2008 | Decoration of Honour for Services to the Republic of Austria | |
| 1999 | Austrian Decoration for Science and Art | |
| 1961 | Oliver E. Buckley Condensed Matter Prize - Solid-state physics | |
| 1977 | Davisson–Germer Prize in Atomic or Surface Physics | |
| 1988 | National Medal of Science for Physical Science | |
| 0 | 1998 - Nobel Prize in Chemistry | |
| 0 | 1963 - Guggenheim Fellowship for Natural Sciences | |
| 0 | US & Canada | |
Walter Kohn biography timelines
- // 9th Mar 1923Walter Kohn was born on March 9, 1923 in Vienna, Austria, to Salomon and Gittel Kohn. His earliest memory of his childhood was that of being subjugated by the Austrian Nazi regime.
- // 1938In 1938, when Hitler’s Germany annexed Austria, the Kohns’ were tarnished financially and socially. Their family business was confiscated and they were ripped off their freedom. Young Kohn was expelled from his school. Subsequently, he entered a Jewish school where he developed his interest in mathematics and science.
- // 1945Kohn successfully gained admission at the University of Toronto. Since he wasn’t allowed to enter the chemistry building, he opted for physics and mathematics instead. In 1945, he graduated with a BA in applied mathematics and a year later was awarded an MA in the subject.
- // 1948Obtaining a Lehmann fellowship, Kohn entered the prestigious Harvard University. Under the guidance to Julian Schwinger, he worked on Green’s function variational method of three-body scattering problem as the subject for his thesis. In 1948, Kohn struck success by discovering an elementary formulation for variational principle of scattering. Same year, he was awarded a PhD degree in physics.
- // 1950In 1950, he secured a fellowship at the National Research Council in Copenhagen. Simultaneously, he also got a job at the Carnegie Institute of Technology. Requesting a leave of absence, he fulfilled his fellowship in Copenhagen. In Copenhagen, he turned to solid state physics. He served as a substitute teacher of the subject and did research on the subject along with Res Jost.
- // 1952In 1952, he moved to Carnegie Institute of Technology. At Carnegie, he did much of his seminal work on multiple-scattering band-structure work, now known as the KKR method. Other work done by him include the image of the metallic Fermi Surface in the phonon spectrum, exponential localization of Wannier functions and the nature of the insulating state.
- // 1953 To 1966In 1953, supported by Van Vleck, he attained a summer job at Bell Labs as an assistant to W. Shockley. His project was on radiation damage of Si and Ge by energetic electrons, critical for the use of the then recently-developed semiconductor devices for applications in outer space. The Bell Labs, which the premier center for research in the field of solid state physics, became the summer home of Kohn where he returned every year until 1966.
- // 1960 To 1963In 1960, Kohn took up an academic position as the Physics Department chair at the then newly founded University of California, San Diego. He spent a sabbatical semester at the Ecole Normale Superieure in Paris in 1963 when he initiated his work in the development of density functional theory.
- // 1964Kohn’s most significant contribution came with his development of the density-functional theory. All through his career, he used quantum mechanics to comprehend the electro bonding between atoms to form molecules. In 1964, he laid the foundation for a theory that stated it was not necessary to account for every electron's movement. Instead, one could look at the average density of electrons in the space. This gave the scientific world a better understanding and new insight for calculations involving chemical structures and reactions. It also simplified the computation needed to understand the electron bonding between atoms within molecules.
- // 1979Kohn’s stint at the University of California, San Diego lasted until 1979. Following this, he accepted the Founding Director's position at the new National Science Foundation’s Institute for Theoretical Physics in Santa Barbara. Therein, he continued to work with post-doctoral fellows on DFT.
- // 1984In 1984, Kohn took up the position of a professor in the Physics Department at the University of California at Santa Barbara. He continued to work there until the end of his life.
- // 1988In 1988, he received the National Medal of Science.
- // 1998In 1998, Kohn was bestowed with the prestigious Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his development of the density-functional theory. He shared the prize with John Pople.
- // 19th Apr 2016He died of jaw cancer on April 19, 2016, at the age of 93.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Robert Andrews Millikan
Robert Andrews Millikan was an eminent American experimental physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for his work on photoelectric effect. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton was an English scientist and mathematician, who discovered gravitation and Newtonian Mechanics. Read this biography to find more on his life.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie was a Physicist and Chemist, who was world renowned for her work on radioactivity. She also was the winner of two Nobel Prize. Read this biography to get info about her life and profile.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Walter Kohn's FAQ
What is Walter Kohn birthday?
Walter Kohn was born at 1923-03-09
When was Walter Kohn died?
Walter Kohn was died at 2016-04-19
Which age was Walter Kohn died?
Walter Kohn was died at age 93
Where is Walter Kohn's birth place?
Walter Kohn was born in Vienna, Austria
What is Walter Kohn nationalities?
Walter Kohn's nationalities is Austrian
Who is Walter Kohn spouses?
Walter Kohn's spouses is Lois Kohn (m. 1948), Mara Schiff (m. 1955)
Who is Walter Kohn childrens?
Walter Kohn's childrens is Ingrid Kohn, Marilyn Kohn, Martin Steven Kohn, Minna Kohn, Ros Dimenstein, Sharon Ruth Kohn, Thomas David Kohn
What was Walter Kohn universities?
Walter Kohn studied at Harvard University,University Of Toronto
What was Walter Kohn notable alumnis?
Walter Kohn's notable alumnis is Harvard University, University Of Toronto
What is Walter Kohn's sun sign?
Walter Kohn is Pisces
How famous is Walter Kohn?
Walter Kohn is famouse as Physicist and Chemist