Louis Pasteur - Chemists, Birthday and Childhood
Louis Pasteur's Personal Details
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | December 27, 1822 |
| Died on | September 28, 1895 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Microbiologists, Chemists, Biochemists, Bacteriologists, Chemists, Microbiologists |
| Spouses | Marie Pasteur (m. 1849) |
| Childrens | Camile Pasteur, Cécile Pasteur, Jean Baptiste Pasteur, Jeanne Pasteur, Marie Louise Pasteur |
| Universities |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Dole, Jura, Franche-Comté, France |
| Religion | Roman Catholic |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Jean-Joseph Pasteur |
| Mother | Jeanne-Etiennette Roqui |
| Sun Sign | Capricorn |
| Born in | Dole, Jura, Franche-Comté, France |
| Famous as | Chemist and Microbiologist |
| Died at Age | 72 |
// Famous Chemists
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday was the most celebrated British scientist of the 19th century. Know more about his childhood and life with this biography.
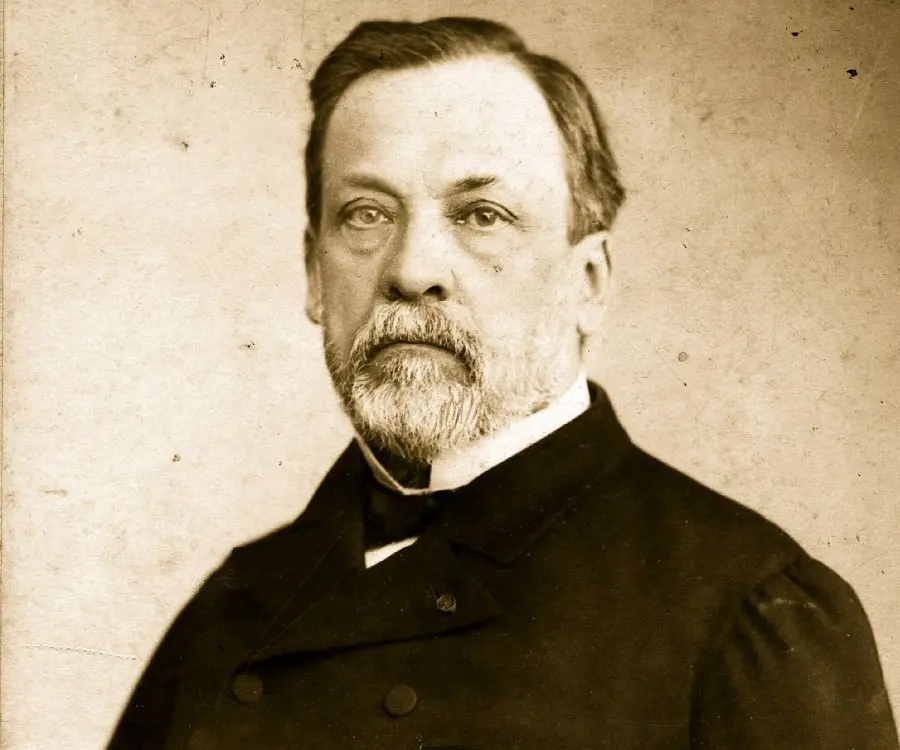
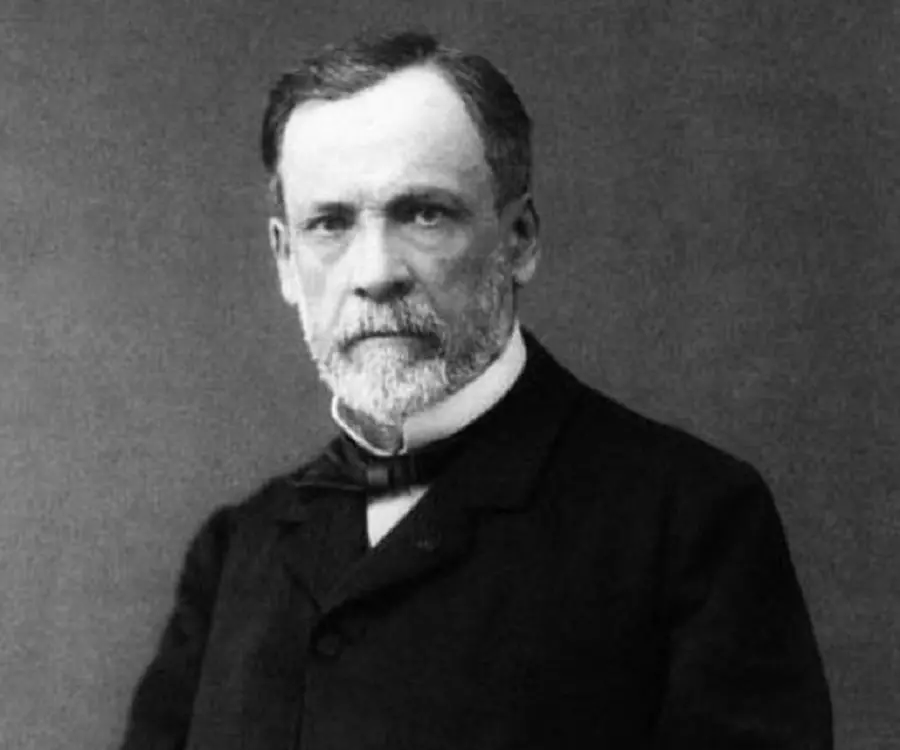
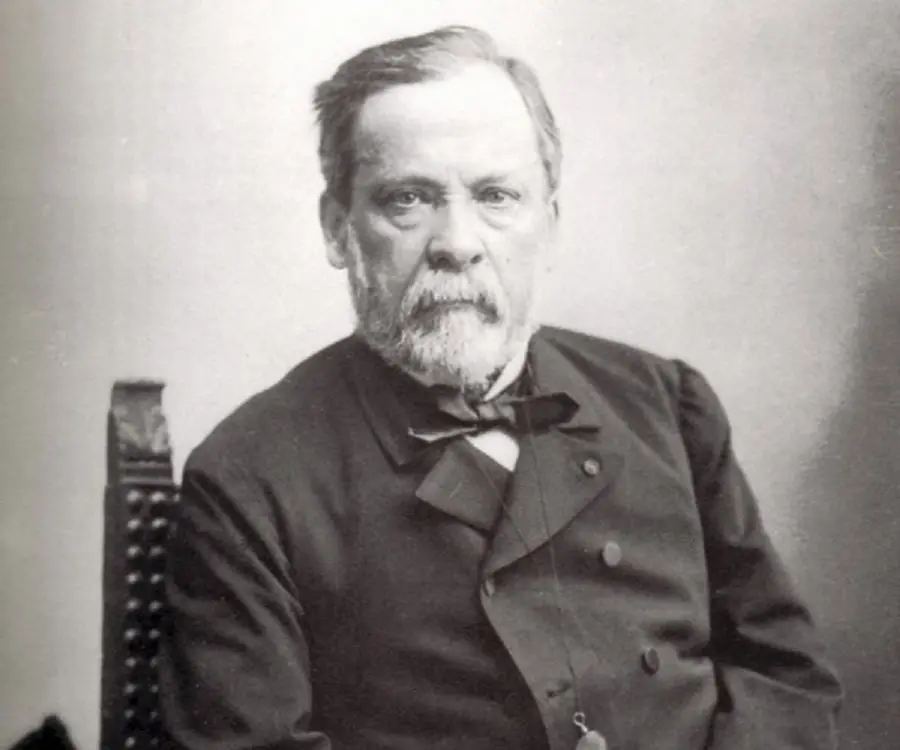
Louis Pasteur's photo
Who is Louis Pasteur?
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. He is also credited with the invention of the technique of treating milk and wine to stop bacterial contamination, a process named “pasteurization” after him. One of the pioneers in the field of microbiology, Pasteur, along with Ferdinand Cohn and Robert Koch, is regarded as one of the three main founders of bacteriology. Born as the son of a tanner who had served in the Napoleonic Wars, Louis grew up listening to his father’s patriotic tales which instilled in him a deep love for his country. As a young boy he loved to draw and paint, but his parents wanted him to focus on his studies. He was an average student who even failed in his first attempt to clear the entrance test for École Normale Supérieur though he eventually went on complete his doctorate. In his career as a chemist he disproved many of the long-held erroneous “scientific” beliefs such as the concept of spontaneous generation. He received international acclaim for developing the first vaccination against rabies and for his seminal work in the field of germ theory. Although much renowned for his groundbreaking scientific works, Pasteur’s life has also been the subject of several controversies.
// Famous Microbiologists
Jules Bordet
Jules Bordet was a Belgian microbiologist and immunologist who won the 1919 Nobel Prize in Medicine "for his discoveries relating to immunity". Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Werner Arber
Werner Arber is a Swiss microbiologist and a geneticist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1978. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, career, research, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Louis Pasteur was born on December 27, 1822, in Dole, Jura, France, as the third child of Jean-Joseph Pasteur and Jeanne-Etiennette Roqui. His father was a tanner who had served as a sergeant major during the Napoleonic Wars.
He was a creative young boy who loved to draw and paint. He was an average student in school and displayed little interest in academics.
After completing his primary education he joined the Collège Royal de Besançon in 1839 and he earned his Bachelor of Arts degree (1840) and Bachelor of Science degree (1842).
He entered the École Normale Supérieure (a teachers’ college in Paris) in 1843 and received his Master of Science degree in 1845 and then acquired an advanced degree in physical sciences. He later earned his doctorate in sciences in 1847.
Career
In 1848, he was appointed professor of physics at the Dijon Lycée. However, he quit the job to become professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg the same year.
He became the dean of the new faculty of sciences at Lille University in 1854 where he began his studies on fermentation. Through his experiments, he demonstrated that fermentation is caused by the growth of micro-organisms, and that the growth of bacteria is due to biogenesis and not due to spontaneous generation as was normally believed at that time.
In 1857, he was selected to be the director of scientific studies at the École Normale Supérieure where he served till 1867. There he introduced several reforms, which were often very rigid. This helped to increase the institution’s prestige, but also instigated two major student revolts.
He became a professor of geology, physics, and chemistry at the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts in 1862 and held this position until his resignation in 1867.
His research in fermentation showed that the growth of micro-organisms was responsible for spoiling beverages, such as beer, wine and milk. He went on to invent a process in which the beverages were heated to a temperature between 60 and 100 °C which killed most bacteria already present within them. He patented the method, which became known as pasteurization in 1865.
His first important work in the field of vaccination came in 1879 while studying a disease called chicken cholera. He accidentally exposed some chickens to the attenuated form of a culture of the disease causing virus, and observed that they became resistant to the actual virus. This formed the foundation for his further studies in the field.
In the 19th century rabies was a much dreaded disease, and Pasteur and his colleagues began working on a vaccine. They experimented on infected rabbits and developed a vaccine that they tested on 50 dogs. But the vaccine was yet to be tested on a human being. Pasteur, in spite of not being a licensed medical practitioner took a chance and administered the vaccine to a young boy who was bitten by a rabid dog in 1885. The boy did not develop any symptom of the disease even after three months and Pasteur was hailed a hero.
In 1887, he established the Pasteur Institute and served as its director for the rest of his life. A year after its inauguration, the institute started the first course of microbiology ever taught in the world, then titled ‘Cours de Microbie Technique’ (Course of microbe research techniques).
Major Works
Louis Pasteur is best remembered for developing the process of what came to be known as “Pasteurization”, in which beverages like beer, wine, or milk are heated up to a certain temperature in order to reduce the number of viable pathogens so they are unlikely to cause disease. The process is today widely used in the food industry.
He also achieved considerable fame for developing the first vaccine for rabies. Pasteur and his colleagues were working on a rabies vaccine that had been tested on 50 dogs but was yet to be tested on a human. Pasteur first administered the vaccine to a nine-year old boy who had been bitten by a rabid dog in 1885. The boy did not develop rabies and lived to become an adult.
Awards & Achievements
The Royal Society of London presented him the Rumford Medal for his discovery of the nature of racemic acid and its relations to polarized light in 1856.
The French Academy of Sciences awarded him the Montyon Prize in 1859 for experimental physiology, the Jecker Prize in 1861, and the Alhumbert Prize in 1862.
He was awarded the Copley medal in 1874 for his work on fermentation.
In 1883 he became a foreign member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
He won the Leeuwenhoek medal, microbiology's highest Dutch honor in Arts and Sciences, in 1895.
Personal Life & Legacy
While working as a professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg, he fell in love with Marie Laurent, daughter of the university's rector, and married her in 1849. The couple had five children, but only two of them survived to adulthood. The other three died of diseases and these personal tragedies strengthened Pasteur’s resolve to find cures for infectious diseases.
He suffered a series of strokes beginning in 1868. He was severely impaired following a stroke in 1894 stroke and never recovered fully. He died on September 28, 1895 and was given a state funeral.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Louis Pasteur's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | 1874 - Copley Medal | |
| 0 | - Rumford Medal | |
| 0 | - Leeuwenhoek Medal | |
Louis Pasteur biography timelines
- // 27th Dec 1822Louis Pasteur was born on December 27, 1822, in Dole, Jura, France, as the third child of Jean-Joseph Pasteur and Jeanne-Etiennette Roqui. His father was a tanner who had served as a sergeant major during the Napoleonic Wars.
- // 1839 To 1842After completing his primary education he joined the Collège Royal de Besançon in 1839 and he earned his Bachelor of Arts degree (1840) and Bachelor of Science degree (1842).
- // 1848In 1848, he was appointed professor of physics at the Dijon Lycée. However, he quit the job to become professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg the same year.
- // 1849While working as a professor of chemistry at the University of Strasbourg, he fell in love with Marie Laurent, daughter of the university's rector, and married her in 1849. The couple had five children, but only two of them survived to adulthood. The other three died of diseases and these personal tragedies strengthened Pasteur’s resolve to find cures for infectious diseases.
- // 1854He became the dean of the new faculty of sciences at Lille University in 1854 where he began his studies on fermentation. Through his experiments, he demonstrated that fermentation is caused by the growth of micro-organisms, and that the growth of bacteria is due to biogenesis and not due to spontaneous generation as was normally believed at that time.
- // 1856The Royal Society of London presented him the Rumford Medal for his discovery of the nature of racemic acid and its relations to polarized light in 1856.
- // 1857 To 1867In 1857, he was selected to be the director of scientific studies at the École Normale Supérieure where he served till 1867. There he introduced several reforms, which were often very rigid. This helped to increase the institution’s prestige, but also instigated two major student revolts.
- // 1862 To 1867He became a professor of geology, physics, and chemistry at the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts in 1862 and held this position until his resignation in 1867.
- // 1865His research in fermentation showed that the growth of micro-organisms was responsible for spoiling beverages, such as beer, wine and milk. He went on to invent a process in which the beverages were heated to a temperature between 60 and 100 °C which killed most bacteria already present within them. He patented the method, which became known as pasteurization in 1865.
- // 1874He was awarded the Copley medal in 1874 for his work on fermentation.
- // 1879His first important work in the field of vaccination came in 1879 while studying a disease called chicken cholera. He accidentally exposed some chickens to the attenuated form of a culture of the disease causing virus, and observed that they became resistant to the actual virus. This formed the foundation for his further studies in the field.
- // 1883In 1883 he became a foreign member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.
- // 1885In the 19th century rabies was a much dreaded disease, and Pasteur and his colleagues began working on a vaccine. They experimented on infected rabbits and developed a vaccine that they tested on 50 dogs. But the vaccine was yet to be tested on a human being. Pasteur, in spite of not being a licensed medical practitioner took a chance and administered the vaccine to a young boy who was bitten by a rabid dog in 1885. The boy did not develop any symptom of the disease even after three months and Pasteur was hailed a hero.
- // 1885He also achieved considerable fame for developing the first vaccine for rabies. Pasteur and his colleagues were working on a rabies vaccine that had been tested on 50 dogs but was yet to be tested on a human. Pasteur first administered the vaccine to a nine-year old boy who had been bitten by a rabid dog in 1885. The boy did not develop rabies and lived to become an adult.
- // 1887In 1887, he established the Pasteur Institute and served as its director for the rest of his life. A year after its inauguration, the institute started the first course of microbiology ever taught in the world, then titled ‘Cours de Microbie Technique’ (Course of microbe research techniques).
- // 1895He won the Leeuwenhoek medal, microbiology's highest Dutch honor in Arts and Sciences, in 1895.
- // 28th Dec 1895He suffered a series of strokes beginning in 1868. He was severely impaired following a stroke in 1894 stroke and never recovered fully. He died on September 28, 1895 and was given a state funeral.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie was a Physicist and Chemist, who was world renowned for her work on radioactivity. She also was the winner of two Nobel Prize. Read this biography to get info about her life and profile.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn was a Nobel Prize winning German scientist who discovered the phenomenon of nuclear fission and the element protactinium. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Louis Pasteur's FAQ
What is Louis Pasteur birthday?
Louis Pasteur was born at 1822-12-27
When was Louis Pasteur died?
Louis Pasteur was died at 1895-09-28
Where was Louis Pasteur died?
Louis Pasteur was died in Marnes-la-Coquette, Hauts-de-Seine, France
Which age was Louis Pasteur died?
Louis Pasteur was died at age 72
Where is Louis Pasteur's birth place?
Louis Pasteur was born in Dole, Jura, Franche-Comté, France
What is Louis Pasteur nationalities?
Louis Pasteur's nationalities is French
Who is Louis Pasteur spouses?
Louis Pasteur's spouses is Marie Pasteur (m. 1849)
Who is Louis Pasteur childrens?
Louis Pasteur's childrens is Camile Pasteur, Cécile Pasteur, Jean Baptiste Pasteur, Jeanne Pasteur, Marie Louise Pasteur
What was Louis Pasteur universities?
Louis Pasteur studied at École Normale Supérieure
What is Louis Pasteur's inventions/discoveries?
Anaerobiosis was invented (or discovered) by Louis Pasteur
What is Louis Pasteur's religion?
Louis Pasteur's religion is Roman Catholic
Who is Louis Pasteur's father?
Louis Pasteur's father is Jean-Joseph Pasteur
Who is Louis Pasteur's mother?
Louis Pasteur's mother is Jeanne-Etiennette Roqui
What is Louis Pasteur's sun sign?
Louis Pasteur is Capricorn
How famous is Louis Pasteur?
Louis Pasteur is famouse as Chemist and Microbiologist













