Rodney R. Porter - Biochemists, Family and Life
Rodney R. Porter's Personal Details
Rodney Robert Porter was a Nobel Prize winning English biochemist who won the 1972 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | October 8, 1917 |
| Died on | September 6, 1985 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Scientists, Immunologists, Biochemists |
| Cause of death |
|
| Birth Place | Newton-le-Willows, United Kingdom |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Libra |
| Born in | Newton-le-Willows, United Kingdom |
| Famous as | Biochemist |
| Died at Age | 67 |
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
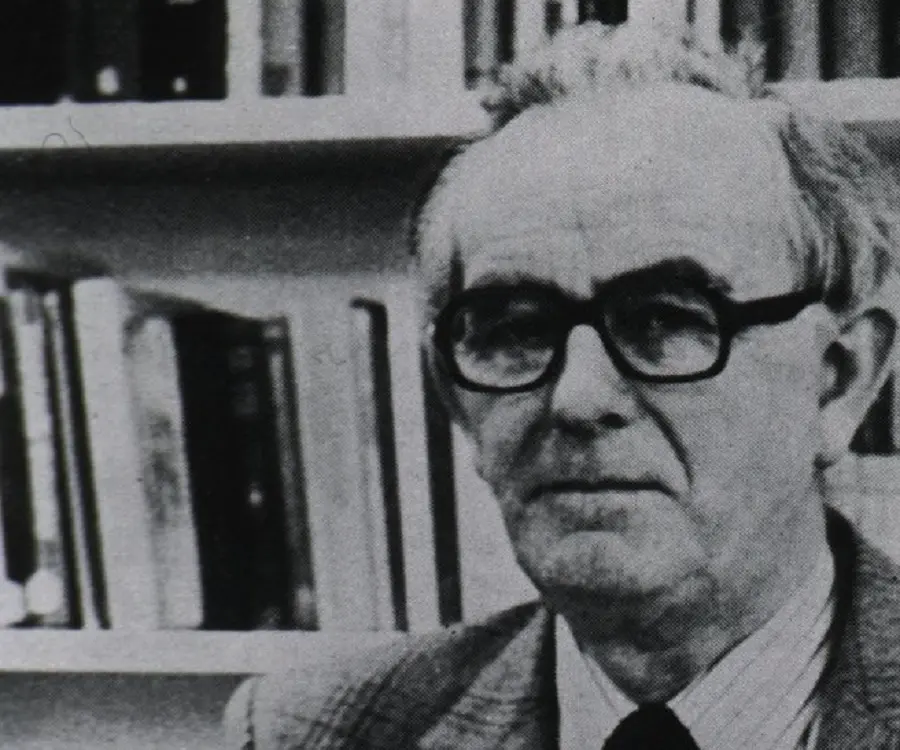
Rodney R. Porter's photo
Who is Rodney R. Porter?
Rodney Robert Porter was a Nobel Prize winning English biochemist who, along with Gerald M. Edelman, won the 1972 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. The duo won the award for their discoveries concerning the chemical structure of antibodies. Porter was fascinated with science from an early age. He later graduated from the University of Liverpool with biochemistry and then served in the British Army during the Second World War. Soon after being discharged from the army, he enrolled at the University of Cambridge, to earn his doctorate. His dissertation was on methods of seeking the active sites of the antibodies, a subject on which he had worked almost throughout his life. He established that an antibody, also known as immunoglobulin, was shaped like a Y and was made up of four chains of amino acids. He also established that they consisted of three domains, two of which had the capacity to bind the antigen, while the third segment linked the two heavy chains together. Later, he created a model of the antibody. However, Gerald Edelman, working separately on the same topic, preceded him in this. Interestingly, they were never competitors, but drew upon each other’s work. Together they founded the field of molecular immunology, which had a far reaching influence on medical science.
// Famous Immunologists
Georges J. F. Kohler
Georges J. F. Kohler was a German immunologist who received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1984. Check this biography to get details about his life, profile and timeline.
Cesar Milstein
Cesar Milstein was an Argentinian biochemist who received the Nobel Prize for his discovery of monoclonal antibody. Explore this biography to get details about his life, career and scientific discoveries.
Susumu Tonegawa
Susumu Tonegawa is a Japanese molecular biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1987. This biography of Susumu Tonegawa provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
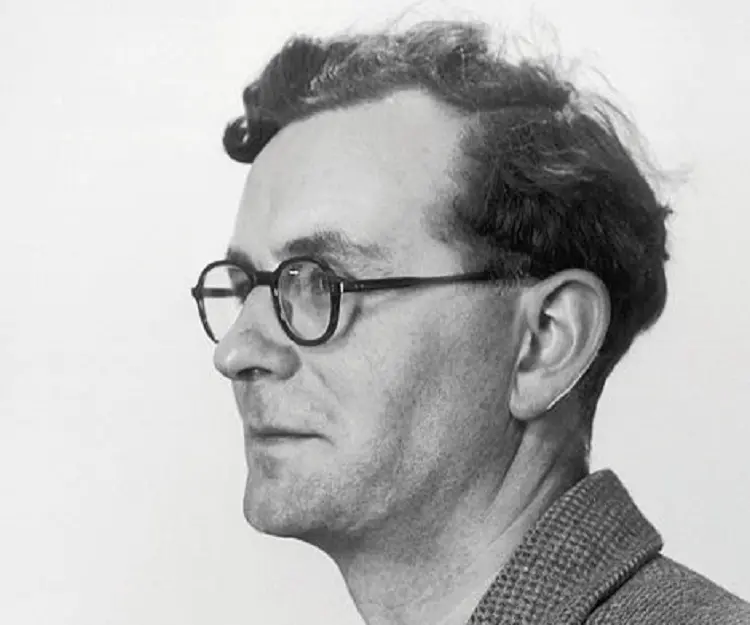
Rodney Robert Porter was born on 8 October 1917, in Newton-le-Willows, a market town located midway between Liverpool and Manchester. His father, Joseph L. Porter, was a railway clerk. His mother’s name was Isobel Reese Porter. He was the only child of his parents.
From an early age, Rodney Porter was fascinated by science and was especially interested in chemistry. He had his secondary education at Ashton-in-Makerfield Grammar School, located in Ashton-in-Makerfiel, Greater Manchester, passing out from there in 1935.
Subsequently, he entered the University of Liverpool, earning his B.S degree in biochemistry in 1939. As the Second World War set in, he joined the British Army serving in the Royal Artillery, the Royal Engineers, and the Royal Army Service Corps respectively and took part in the North African, Sicilian, and Italian campaigns.
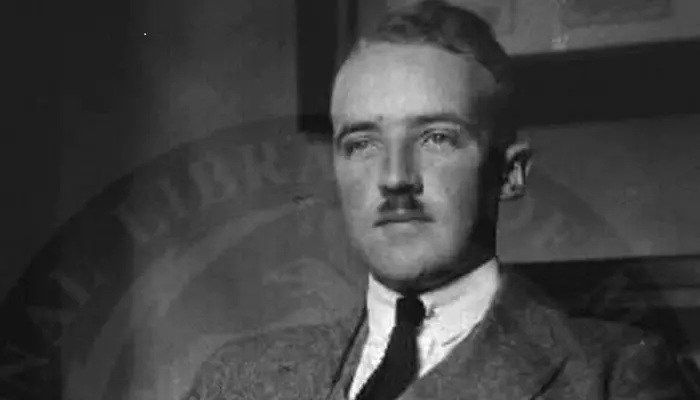
After being discharged in 1946, Porter enrolled at University of Cambridge as a graduate student. Inspired by Karl Landsteiner’s, ‘The Specificity of Serological Reactions’ (1936), he decided to study antibodies.
Working under Frederick Sanger, the two-time Nobel Prize winner, Porter wrote his dissertation on methods of seeking antibodies' active sites; finally receiving his PhD degree in 1948. His doctorate thesis was titled ‘The free amino groups of proteins’.
Career
After receiving his PhD in 1948, Porter spent one more year at the University of Cambridge as a postdoctoral fellow.
In 1949, he joined the National Institute for Medical Research at Mill Hill as scientific staff and remained there till 1960. Here, Porter continued his research on antibodies, which he had started as a doctoral.
Until then, it was only known that these antibodies, also referred as immunoglobulin, were groups of proteins that played an important role in defending our body against infections and diseases and that they are found in our blood. Otherwise, scientists had very little knowledge about their nature and mechanism of action.
Porter began by studying the molecular structure of antibodies. Subsequently, he decided to split these antibodies in order to identify those parts, which were responsible for specific reactivity. He was especially interested on chromatographic methods of fractionation.
Sometime in 1958-1959, Porter and his team treated the antibodies with a protein-splitting enzyme called papain under controlled condition. The treatment divided the antibody into three functionally different segments. He then began to study each part.
In 1960, Porter left National Institute for Medical Research to join St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London University, as Pfizer Professor of Immunology. Here, he continued his work on the separated segments of the antibody.
Subsequently, he found that out of the three segments in an antibody, two were quite identical, while the third one was functionally different. He also found that these identical sections had the capacity to bind the antigen, while the third section possessed other biological characteristics, but lacked the binding capacity.
In 1962, he put forward the peptide chain structure of antibodies. He established that these antibodies were composed of four chains of amino acids; two of which were identical light chains while the other two were identical heavy chains. He then proceeded to create a model of the antibody.
In 1967, Porter once more made a move and joined the University of Oxford as Whitley Professor of Biochemistry. He also chaired the Department of Biochemistry and was created a Fellow of Trinity College, Oxford. Here too, he continued working on antibodies.
Finally in 1969, Porter was able to create a complete model of an antibody, comprising of 1300 amino acids. However, American scientist, Gerald Edelman, working separately on the same subject, preceded him marginally in creating this model. Yet, Porter’s contribution to the study of immunoglobulin was held in high esteem and earned him the Nobel Prize.
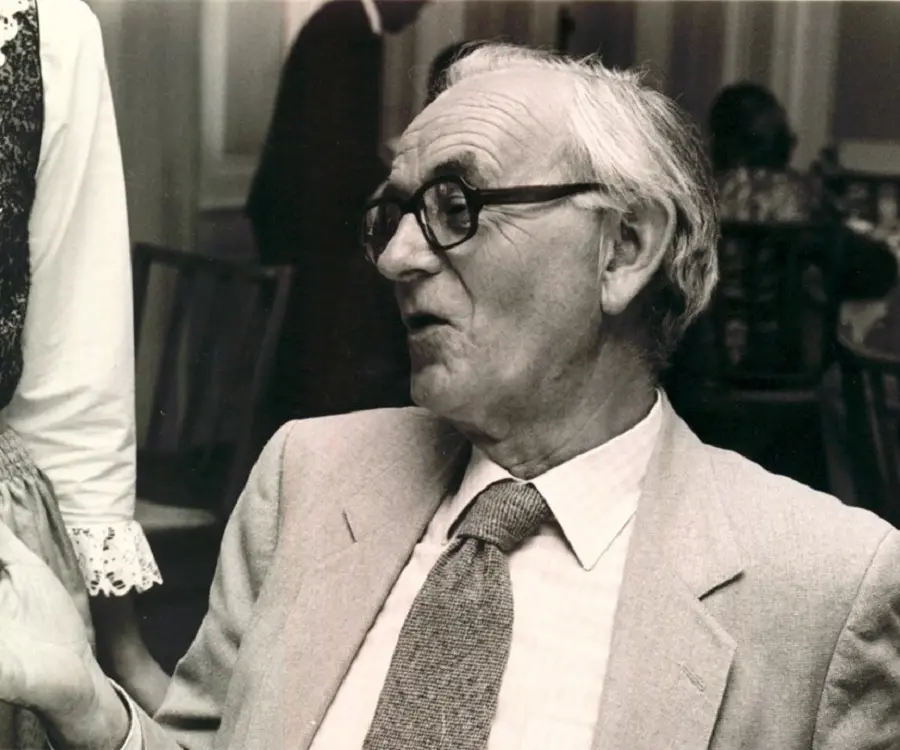
Porter next collaborated with other scientists such as Kenneth BM Reid, Robert Sim and Duncan Campbell to know more about the Complement Proteins associated with defense against infection. He kept on working at the University of Oxford till his death in 1985.
Major Works
Porter was first to recognize that antibodies had a Y-shaped structure. He was also the first to use enzyme papain to break it off at the point of branching and split it up into three segments. However, his main credit lay in identifying the antibody-binding (Fab) and the antibody tail (Fc) regions of the immunoglobulin
Although he was preceded by Gerald Edelman in creating an exact replica of an antibody, his contribution was no less significant. In fact, while working on the problem, the two scientists often drew upon each other’s work. It can be safely said that although they worked separately they together deduced the structure of the antibody.
Awards & Achievements
In 1966, Porter received the Gairdner Foundation International Award for outstanding contribution to medical science.
In 1972, Rodney R. Porter and Gerald Edelman were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the chemical structure of antibodies".
In 1973, he received the Royal Medal "in recognition of his penetrating investigations on the structure of immunoglobulins."
In 1983, he received Copley Medal "in recognition of his elucidation of the structure of immunoglobulins and of the reactions involved in activating the complement system of proteins".
He was named Order of the Companions of Honour by Queen Elizabeth II on 15 June, 1985,.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1948, Rodney R. Porter married Julia Frances New Porter. The couple had five children; two sons, Nigel and Tim Porter, and three daughters, Susan, Ruth and Helen Porter.
On 6 September 1985, Porter died in a road accident near Winchester, Hampshire. He was only 67 years old then and was survived by his wife and five children.
// Famous Biochemists
Robert Huber
Robert Huber is a German biochemist and Nobel Laureate. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Charles Best
Charles Best was a great scientist and a renowned physiologist who is remembered for being the co-discoverer of insulin. Read this biography to learn about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov was an American professor of biochemistry and a renowned author of science fiction and popular science books. Read this biography to know more about his life.
Rodney R. Porter's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | 1972 - Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine | |
| 0 | 1983 - Copley Medal | |
| 0 | 1966 - Gairdner Foundation International Award | |
Rodney R. Porter biography timelines
- // 1300 To 1969Finally in 1969, Porter was able to create a complete model of an antibody, comprising of 1300 amino acids. However, American scientist, Gerald Edelman, working separately on the same subject, preceded him marginally in creating this model. Yet, Porter’s contribution to the study of immunoglobulin was held in high esteem and earned him the Nobel Prize.
- // 8th Oct 1917Rodney Robert Porter was born on 8 October 1917, in Newton-le-Willows, a market town located midway between Liverpool and Manchester. His father, Joseph L. Porter, was a railway clerk. His mother’s name was Isobel Reese Porter. He was the only child of his parents.
- // 1935From an early age, Rodney Porter was fascinated by science and was especially interested in chemistry. He had his secondary education at Ashton-in-Makerfield Grammar School, located in Ashton-in-Makerfiel, Greater Manchester, passing out from there in 1935.
- // 1936 To 1946After being discharged in 1946, Porter enrolled at University of Cambridge as a graduate student. Inspired by Karl Landsteiner’s, ‘The Specificity of Serological Reactions’ (1936), he decided to study antibodies.
- // 1939Subsequently, he entered the University of Liverpool, earning his B.S degree in biochemistry in 1939. As the Second World War set in, he joined the British Army serving in the Royal Artillery, the Royal Engineers, and the Royal Army Service Corps respectively and took part in the North African, Sicilian, and Italian campaigns.
- // 1948Working under Frederick Sanger, the two-time Nobel Prize winner, Porter wrote his dissertation on methods of seeking antibodies' active sites; finally receiving his PhD degree in 1948. His doctorate thesis was titled ‘The free amino groups of proteins’.
- // 1948After receiving his PhD in 1948, Porter spent one more year at the University of Cambridge as a postdoctoral fellow.
- // 1948In 1948, Rodney R. Porter married Julia Frances New Porter. The couple had five children; two sons, Nigel and Tim Porter, and three daughters, Susan, Ruth and Helen Porter.
- // 1949 To 1960In 1949, he joined the National Institute for Medical Research at Mill Hill as scientific staff and remained there till 1960. Here, Porter continued his research on antibodies, which he had started as a doctoral.
- // 1958 To 1959Sometime in 1958-1959, Porter and his team treated the antibodies with a protein-splitting enzyme called papain under controlled condition. The treatment divided the antibody into three functionally different segments. He then began to study each part.
- // 1960In 1960, Porter left National Institute for Medical Research to join St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London University, as Pfizer Professor of Immunology. Here, he continued his work on the separated segments of the antibody.
- // 1962In 1962, he put forward the peptide chain structure of antibodies. He established that these antibodies were composed of four chains of amino acids; two of which were identical light chains while the other two were identical heavy chains. He then proceeded to create a model of the antibody.
- // 1966In 1966, Porter received the Gairdner Foundation International Award for outstanding contribution to medical science.
- // 1967In 1967, Porter once more made a move and joined the University of Oxford as Whitley Professor of Biochemistry. He also chaired the Department of Biochemistry and was created a Fellow of Trinity College, Oxford. Here too, he continued working on antibodies.
- // 1972In 1972, Rodney R. Porter and Gerald Edelman were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the chemical structure of antibodies".
- // 1973In 1973, he received the Royal Medal "in recognition of his penetrating investigations on the structure of immunoglobulins."
- // 1983In 1983, he received Copley Medal "in recognition of his elucidation of the structure of immunoglobulins and of the reactions involved in activating the complement system of proteins".
- // 1985Porter next collaborated with other scientists such as Kenneth BM Reid, Robert Sim and Duncan Campbell to know more about the Complement Proteins associated with defense against infection. He kept on working at the University of Oxford till his death in 1985.
- // 15th Jun 1985He was named Order of the Companions of Honour by Queen Elizabeth II on 15 June, 1985,.
- // 6th Sep 1985On 6 September 1985, Porter died in a road accident near Winchester, Hampshire. He was only 67 years old then and was survived by his wife and five children.
// Famous British peoples
Wentworth Miller
Wentworth Miller is an American actor and screenwriter who achieved recognition for his role in the TV series ‘Prison Break’.
Sophie Reade
Sophie Victoria Reade is a British model and reality show star. Let’s take a look at her family and personal life, including her age, birthday, boyfriends, and some interesting facts.
Josh Temple
Check out all that you wanted to know about Josh Temple (Slogoman), the famous British YouTube Personality; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Yammy Xox
Check out all that you wanted to know about Yammy Xox, the famous British YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Grian
Grian is an English YouTube gamer and social media influencer. Check out this biography to know about his birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Benjamin Atkinson
Benjamin Atkinson is the son of the world-renowned British actor and comedian, Rowan Atkinson. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, personal life, including his age, birthday, etc.
Rodney R. Porter's FAQ
What is Rodney R. Porter birthday?
Rodney R. Porter was born at 1917-10-08
When was Rodney R. Porter died?
Rodney R. Porter was died at 1985-09-06
Which age was Rodney R. Porter died?
Rodney R. Porter was died at age 67
Where is Rodney R. Porter's birth place?
Rodney R. Porter was born in Newton-le-Willows, United Kingdom
What is Rodney R. Porter nationalities?
Rodney R. Porter's nationalities is British
What is Rodney R. Porter's cause of dead?
Rodney R. Porter dead because of Accident
What is Rodney R. Porter's sun sign?
Rodney R. Porter is Libra
How famous is Rodney R. Porter?
Rodney R. Porter is famouse as Biochemist