Georges J. F. Kohler - Biologists, Timeline and Childhood
Georges J. F. Kohler's Personal Details
Georges J
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | April 17, 1946 |
| Died on | March 1, 1995 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Scientists, Biologists, Immunologists |
| Birth Place | Munich, Germany |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Aries |
| Born in | Munich, Germany |
| Famous as | Immunologist, Biologist |
| Died at Age | 48 |
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
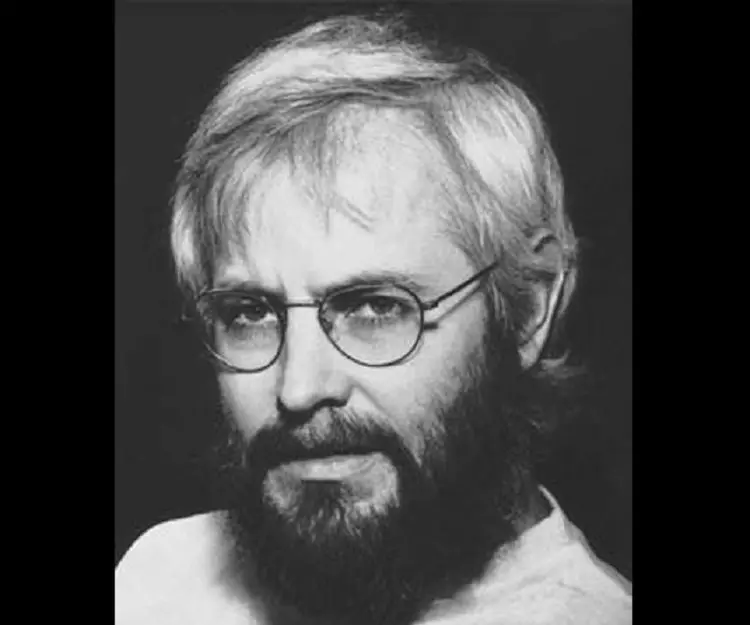
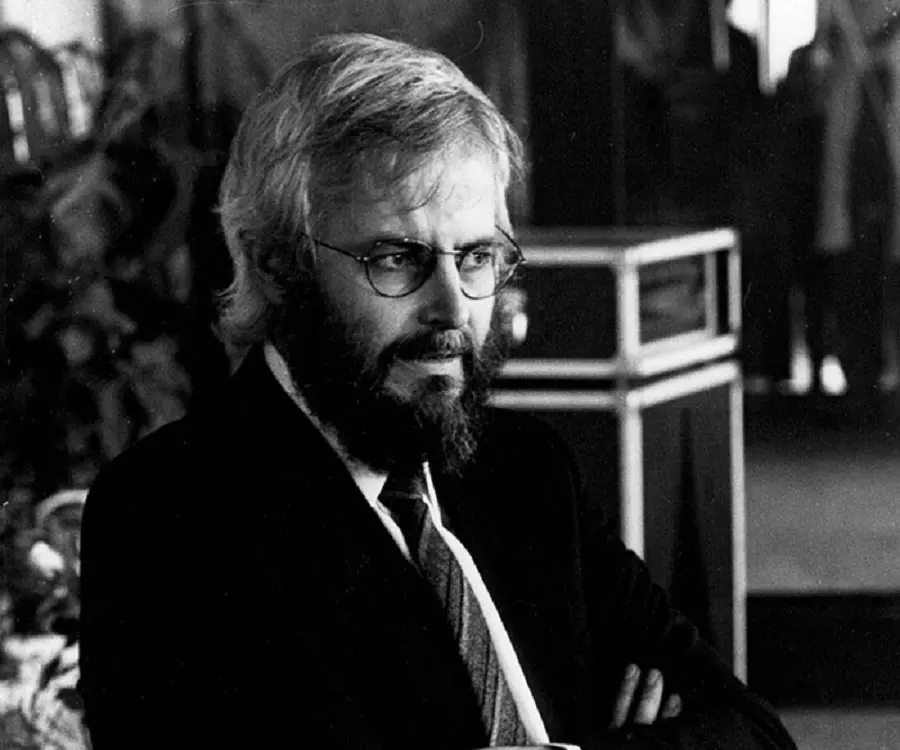
Georges J. F. Kohler's photo
Who is Georges J. F. Kohler?
Georges J. F. Kohler was a German immunologist and biologist who received Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1984 for his role in the development of monoclonal antibodies. He shared the prize with Cesar Milstein, a renowned immunologist and biochemist. Kohler tasted success early on in his career. He was merely 28 when he was selected for a postdoctoral fellowship at the Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England. Kohler grabbed the opportunity and travelled to Cambridge in 1974. Same year, Kohler successfully invented a method of forcing immune system cells to make pure antibodies against a chosen antigen, instead of the profusion of different agents that usually greet an invading virus or bacterium. The discovery of the principle for production of monoclonal antibodies was revolutionary in the scientific world as it helped in the diagnosis of diseases and in carrying therapeutic agents to particular body tissues. Interestingly, though Kohler was the driving force behind the discovery, as he played a prominent role in conceiving and executing the experiment, he was written off by the scientific world who credited Milstein for the same. It was only in 1984 that his role in developing hybridomas was fully recognized and he was jointly awarded the Nobel Prize along with Cesar Milstein.
// Famous Immunologists
Cesar Milstein
Cesar Milstein was an Argentinian biochemist who received the Nobel Prize for his discovery of monoclonal antibody. Explore this biography to get details about his life, career and scientific discoveries.
Susumu Tonegawa
Susumu Tonegawa is a Japanese molecular biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1987. This biography of Susumu Tonegawa provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Harold E. Varmus
Harold E. Varmus is an American scientist who won a share of the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. This biography of Harold E. Varmus provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Georges Jean Franz Köhler was born on April 17, 1946, in Munich, Germany.
Upon completing his preliminary education, he enrolled at the University of Freiburg from where he graduated in the year 1971. Immediately following his graduation, Kohler applied for a PhD degree in biology which he received in 1974.
Career
After completing his honorary doctorate degree, Kohler received a two year postdoctoral fellowship at Milstein's lab at the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England.
Starting from 1974, Kohler worked under Cesar Milstein for two years. In 1974, the duo made the revolutionary discovery of monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies started a new chapter in the history of immunology and immunogenetics, as they were pure, uniform and highly sensitive protein molecule used for diagnosing and combating various types of diseases.
Kohler realized that the body’s immune system secreted various types of antibodies, whose function was to attach themselves to antigens. However, the antibodies formed from the procedure were never pure and identical. He anticipated that if he could find a way to clone lymphocytes and later subdivide them indefinitely in culture medium, the result would be identical. He fused lymphocytes with the cells of a myeloma and later made them to reproduce indefinitely. The hybrid cells thus formed produced a single species of antibody. Thus, he successfully created a powerful general method for raising pure antibodies against any antigen of interest.
Kohler and Milstein published a paper on the discovery of monoclonal antibodies in 1975 thus proclaiming to the world the emergence of pure, uniform and highly sensitive protein molecules. The development of monoclonal antibodies revolutionized many diagnostic procedures and led to new therapeutic agents for fighting disease.
In 1976, Kohler moved to Switzerland where he continued his research in monoclonal antibodies at the Basel Institute for Immunology. In his nine years of tenure at the Basel Institute, he refined his method of producing monoclonal antibodies, though he was not interested in producing them commercially. He stepped further by identifying myelomas that allowed the production of antibody clones originating from only the spleen cell with which it was fused.
Throughout the decade of 1980s, Kohler continued investigating upon antibody diversity and began working on the development of transgenic mice as a tool to understand the mechanism that underlies self-tolerance.
In 1986, Köhler took up the position of a director at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology. He retained this position until his death in 1995. While at the Max Planck Institute, Kohler expanded his studies to explain the mechanisms of immunoglobulin expression, B cell development and the receptors with which they respond to the hormone interleukin. He found out that the receptors had a major role in the human response to parasitic infections. Furthermore, he also explored the effects of cytokines on immune responses through the development of various knockout mice.
Major Works
Georges J. F. Kohler is known for his discovery of the principle for production of monoclonal antibodies. Together with Cesar Milstein, he successfully invented a method of forcing immune system cells to make pure antibodies against a chosen antigen, instead of the profusion of different agents that usually greet an invading virus or bacterium. The development of monoclonal antibodies was revolutionary in the scientific world as they transformed many diagnostic procedures and led to the development of new therapeutic agents for fighting diseases.
Awards & Achievements
Georges J. F. Köhler, along with César Milstein and Niels K. Jerne, was jointly awarded with the 1984 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for theories concerning the specificity in development and control of the immune system and the discovery of the principle for production of monoclonal antibodies”.
Personal Life & Legacy
Georges J. F. Kohler’s married Claudia Kohler, a biologist, and the couple was blessed with three children.
Kohler died of heart failure on March 1, 1995, in Freiburg, Germany, at the age of 48.
Trivia
Though Kohler was the main driving force behind the hybridoma technique, he was overshadowed by Cesar Milstein for most of his career. It was only in 1984 that the significance of his role in discovering monoclonal antibodies was realized.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Georges J. F. Kohler's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | 1984 - Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine | |
| 0 | 1984 - Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research | |
| 0 | 1981 - Gairdner Foundation International Award | |
Georges J. F. Kohler biography timelines
- // 17th Apr 1946Georges Jean Franz Köhler was born on April 17, 1946, in Munich, Germany.
- // 1971 To 1974Upon completing his preliminary education, he enrolled at the University of Freiburg from where he graduated in the year 1971. Immediately following his graduation, Kohler applied for a PhD degree in biology which he received in 1974.
- // 1974Starting from 1974, Kohler worked under Cesar Milstein for two years. In 1974, the duo made the revolutionary discovery of monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies started a new chapter in the history of immunology and immunogenetics, as they were pure, uniform and highly sensitive protein molecule used for diagnosing and combating various types of diseases.
- // 1975Kohler and Milstein published a paper on the discovery of monoclonal antibodies in 1975 thus proclaiming to the world the emergence of pure, uniform and highly sensitive protein molecules. The development of monoclonal antibodies revolutionized many diagnostic procedures and led to new therapeutic agents for fighting disease.
- // 1976In 1976, Kohler moved to Switzerland where he continued his research in monoclonal antibodies at the Basel Institute for Immunology. In his nine years of tenure at the Basel Institute, he refined his method of producing monoclonal antibodies, though he was not interested in producing them commercially. He stepped further by identifying myelomas that allowed the production of antibody clones originating from only the spleen cell with which it was fused.
- // 1984Georges J. F. Köhler, along with César Milstein and Niels K. Jerne, was jointly awarded with the 1984 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for theories concerning the specificity in development and control of the immune system and the discovery of the principle for production of monoclonal antibodies”.
- // 1984Though Kohler was the main driving force behind the hybridoma technique, he was overshadowed by Cesar Milstein for most of his career. It was only in 1984 that the significance of his role in discovering monoclonal antibodies was realized.
- // 1986 To 1995In 1986, Köhler took up the position of a director at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology. He retained this position until his death in 1995. While at the Max Planck Institute, Kohler expanded his studies to explain the mechanisms of immunoglobulin expression, B cell development and the receptors with which they respond to the hormone interleukin. He found out that the receptors had a major role in the human response to parasitic infections. Furthermore, he also explored the effects of cytokines on immune responses through the development of various knockout mice.
- // 1st Mar 1995Kohler died of heart failure on March 1, 1995, in Freiburg, Germany, at the age of 48.
// Famous German peoples
Jordan Carver
Jordan Carver is a famous German model. Let’s take a close look at her personal life, including her age, career, net worth, achievements and some fun facts.
Jürgen Klopp
Jürgen Klopp is a German football manager, and a former professional football player. Check out this biography to know more about his childhood, family, personal life, etc.
Irma Grese
Irma Grese was a notorious German Nazi concentration camp guard during the Second World War. This biography profiles her childhood, life, horrifying acts, death and other facts.
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Jawed Karim
Jawed Karim is a German-American internet entrepreneur, technologist and co-founder of the video-sharing website, YouTube. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, personal life, achievements, age, etc.
Charles Bukowski
Charles Bukowski was a German-born American novelist, short story writer and poet. With this biography, learn in details about his childhood, life, works, career and timeline
Georges J. F. Kohler's FAQ
What is Georges J. F. Kohler birthday?
Georges J. F. Kohler was born at 1946-04-17
When was Georges J. F. Kohler died?
Georges J. F. Kohler was died at 1995-03-01
Which age was Georges J. F. Kohler died?
Georges J. F. Kohler was died at age 48
Where is Georges J. F. Kohler's birth place?
Georges J. F. Kohler was born in Munich, Germany
What is Georges J. F. Kohler nationalities?
Georges J. F. Kohler's nationalities is German
What is Georges J. F. Kohler's sun sign?
Georges J. F. Kohler is Aries
How famous is Georges J. F. Kohler?
Georges J. F. Kohler is famouse as Immunologist, Biologist