Martin Lewis Perl - Scientists, Timeline and Childhood
Martin Lewis Perl's Personal Details
Martin Lewis Perl was an American physicist who discovered the subatomic particle, tau lepton and won the Nobel Prize
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | June 24, 1927 |
| Died on | September 30, 2014 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Columbia University, Scientists, Physicists |
| Spouses | Teri Hoch Perl |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | New York City, New York |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Fay Perl |
| Mother | Oscar Perl |
| Sun Sign | Cancer |
| Born in | New York City, New York |
| Famous as | Physicist |
| Died at Age | 87 |
// Famous Columbia University
Helen Morris
Helen Morris is a former book editor, TV producer and the wife of Academy Award winning director Martin Scorsese. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Simon Kuznets
Simon Kuznets was a noted Russian-American economist, statistician, demographer, and economic historian. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to his life.
Anna Paquin
Anna Paquin is a Kiwi film, theatre and television actress known for her roles in movies like ‘The Piano’, ‘Fly Away Home’, and ‘X-Men. This biography provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
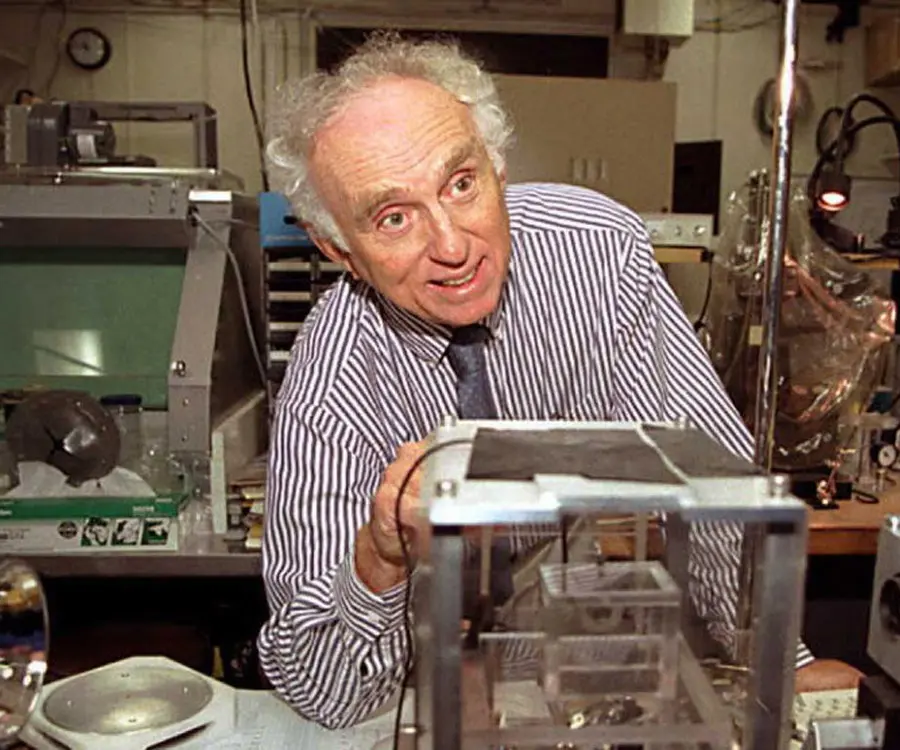
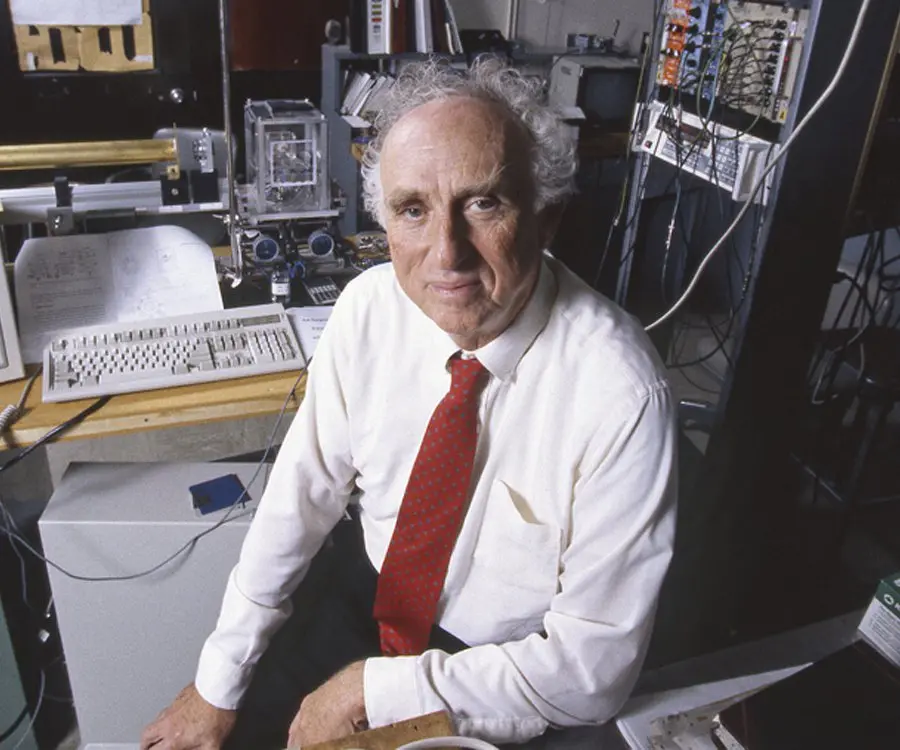
Martin Lewis Perl's photo
Who is Martin Lewis Perl?
Martin Lewis Perl was a noted American physicist who discovered the subatomic particle, tau lepton, thus helping better understand elementary physics. For his epochal work in particle physics, he was decorated with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995. Interestingly, today known as the prodigious child of physics, Perl wasn’t interested in pursuing research as his profession initially. Though being a bright student, he feared if he could make a living out of research in physics and opted for chemical engineering instead for a ‘brighter’ prospect. However, fate had something else in store for this born-genius who took to studying physics while working as a chemical engineer. Soon, he gained his PhD in the subject. Before taking up research work at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), Perl spent eight years at the University of Michigan. His best bit however came at SLAC where he discovered tau particle. It took several years of experiment to establish the existence of a new particle. His work which was earlier panned by the scientific society later gained acceptance and was eventually honoured with a Nobel Prize.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Martin Lewis Perl was born on June 24, 1927 in New York City, New York to Fay and Oscar Perl. His parents were Jewish who had immigrated to the USA from Polish-occupied Russia. His mother worked as a secretary and bookkeeper for a textile firm while his father worked as a stationery salesman before founding his own printing and advertising company.
Academically, Perl was a bright student. Upon completing his early education, he enrolled at James Madison High School in 1942. Despite being a good student and winning a physics prize, Perl did not aim to become a scientist as he wasn’t sure if he could make a living out of the profession. As such, he chose chemical engineering over physics research.
Following high school, he enrolled at the Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn for a course in chemical engineering. However, with the onset of World War II, he left his studies to take up a course in the United States Merchant Marine Academy. For a year, he was drafted into the army. Post war, he resumed his studies and graduated from the institute in 1948.
Career
Following his graduation, Perl took up work as a chemical engineer for the General Electric Company, producing electron vacuum tubes. His interest in the working of television tubes led him to enrol for a course in atomic physics and advanced calculus at Union College, Schenectady, New York.
Perl’s course in physics ignited his interest in the subject so much so that he decided to study the subject formally. He graduated as a physics student in 1950. Following this, Perl enrolled at the Columbia University for a PhD. Under the guidance of Isidor Isaac Rabi, he completed his thesis on measurements of the nuclear quadrupole moment of sodium, using the atomic beam resonance method. He received his PhD in 1955.
Post PhD, he worked at the University of Michigan for eight years. He studied the scattering of pions and later neutrons on protons using bubble chambers and spark chambers. Though he worked on the physics of strong interactions, he sought for a simpler interaction mechanism to study. He gave electron and muon interactions a steady consideration.
In 1963, he moved to Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), California. At Stanford, Perl was keen on satiating his curiosity in the understanding of muon. He wondered why muon interacted exactly like the electron despite being 206.8 times heavier and why it decayed through the route that it does.
His quest for the understanding of muon led him to a series of experiments. He wanted to know why there was a single muon and that was there a possibility that more muons’ existed?
Together with his group, he aimed at finding an even heavier electron than muon that would help explain the role of muon in the grand scheme of things. For this, he realized that such particles could be figured out only through the new collider, Stanford Positron Accelerating Ring. The method would lead to the decay of particles radioactively, leaving behind a distinctive trail of subatomic debris.
In 1973, Perl began the magnum opus of his career. The Spear machine became operational, colliding electrons and positrons in higher energy to produce tiny fireballs. Though the collision led to the production of a particle, the life of the unknown particle was just 2.9×10−13 second long, leading to its decay within a few millimetres of the collision.
By 1975, it was clear that there existed something that was heavier in mass than an electron. Perl excited by the new research, held a conference and made public his finding of a new particle.
Perl’s discovery of the new particle met with a lot of criticism early on. He was severely panned as there was no logical explanation of his finding. It took Perl and his group more than two years to collect data and establish the existence of ‘tau’, the elementary particle similar to electron. Together with electron and muon, it formed a triad.
‘Tau’, meaning ‘third’ in Greek was 3500 times as massive as electron. Despite its massive size, it lived for only third of the trillionth of a second before decaying into a spray of its lighter brethren, nuetrinos. Tau is the heaviest of the electron brothers. As per the rules laid down in the physical world, matter in the universe is divided into two sets of six particles each – six leptons comprising of three electron brothers and three nuetrinos and six quarks which make up for innards of particles protons and nuetrons.
Perl did not give up on his research career after his outstanding discovery of the tau lepton. He continued to investigate the nature of quarks. Post retirement as well, Perl continued his research, collaborating with scientists at SLAC on numerous projects including one investigating dark energy.
Apart from his research, Perl took up academic positions as well. From 1955 to 1963 he served as an instructor and later associate professor at the University of Michigan. In 1963, he joined the faculty of Stanford University, and became Professor Emeritus in 2004. He even joined University of Liverpool as a visiting professor.
Major Works
Perl’s most outstanding achievement came during the latter half of the 1970s. Along with his group of fellow physicists, he conducted several experiments between 1974 and 1977. Using the new machine Spear, he recorded the collision of electrons and positrons in high energy. Though the collision led to the production of a particle, the life of the unknown particle was just 2.9×10−13 second long, leading to its decay within a few millimetres of the collision. It was only after a couple more years and several more experiments that Perl made tau lepton known to the world. Tau lepton were heavier than electrons and considered the third brother of electron, other being muon.
Awards & Achievements
In 1995, Perl was felicitated with the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of tau lepton. The discovery established the fact that there was an additional family of particles alongside two previously known families. He shared the prize with physicist Frederick Reines, who discovered another subatomic particle, the neutrino, in the 1950s.
He served on the board of advisors of Scientists and Engineers for America, an organization focused on promoting sound science in American government.
In 2009, Perl received an honorary doctorate from the University of Belgrade.
Personal Life & Legacy
Martin Lewis Perl was married to Teri Hoch Perl. The couple was blessed with three sons and a daughter.
Perl breathed his last on September 30, 2014 at Stanford University Hospital due to heart attack. He was 87 years of age.
Trivia
Interestingly, he lived his childhood dream of having construction toys by amassing a large collection of them later in his life. He believed that it is these toys which could germ out the experimental creativity of people.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Martin Lewis Perl's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995 | |
Martin Lewis Perl biography timelines
- // 24th Jun 1927Martin Lewis Perl was born on June 24, 1927 in New York City, New York to Fay and Oscar Perl. His parents were Jewish who had immigrated to the USA from Polish-occupied Russia. His mother worked as a secretary and bookkeeper for a textile firm while his father worked as a stationery salesman before founding his own printing and advertising company.
- // 1942Academically, Perl was a bright student. Upon completing his early education, he enrolled at James Madison High School in 1942. Despite being a good student and winning a physics prize, Perl did not aim to become a scientist as he wasn’t sure if he could make a living out of the profession. As such, he chose chemical engineering over physics research.
- // 1948Following high school, he enrolled at the Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn for a course in chemical engineering. However, with the onset of World War II, he left his studies to take up a course in the United States Merchant Marine Academy. For a year, he was drafted into the army. Post war, he resumed his studies and graduated from the institute in 1948.
- // 1950 To 1955Perl’s course in physics ignited his interest in the subject so much so that he decided to study the subject formally. He graduated as a physics student in 1950. Following this, Perl enrolled at the Columbia University for a PhD. Under the guidance of Isidor Isaac Rabi, he completed his thesis on measurements of the nuclear quadrupole moment of sodium, using the atomic beam resonance method. He received his PhD in 1955.
- // 1963In 1963, he moved to Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), California. At Stanford, Perl was keen on satiating his curiosity in the understanding of muon. He wondered why muon interacted exactly like the electron despite being 206.8 times heavier and why it decayed through the route that it does.
- // 1973In 1973, Perl began the magnum opus of his career. The Spear machine became operational, colliding electrons and positrons in higher energy to produce tiny fireballs. Though the collision led to the production of a particle, the life of the unknown particle was just 2.9×10−13 second long, leading to its decay within a few millimetres of the collision.
- // 1974 To 1977Perl’s most outstanding achievement came during the latter half of the 1970s. Along with his group of fellow physicists, he conducted several experiments between 1974 and 1977. Using the new machine Spear, he recorded the collision of electrons and positrons in high energy. Though the collision led to the production of a particle, the life of the unknown particle was just 2.9×10−13 second long, leading to its decay within a few millimetres of the collision. It was only after a couple more years and several more experiments that Perl made tau lepton known to the world. Tau lepton were heavier than electrons and considered the third brother of electron, other being muon.
- // 1975By 1975, it was clear that there existed something that was heavier in mass than an electron. Perl excited by the new research, held a conference and made public his finding of a new particle.
- // 1995In 1995, Perl was felicitated with the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of tau lepton. The discovery established the fact that there was an additional family of particles alongside two previously known families. He shared the prize with physicist Frederick Reines, who discovered another subatomic particle, the neutrino, in the 1950s.
- // 2009In 2009, Perl received an honorary doctorate from the University of Belgrade.
- // 30th Sep 2014Perl breathed his last on September 30, 2014 at Stanford University Hospital due to heart attack. He was 87 years of age.
// Famous Cancer Celebrities peoples
Jacob Elordi
Jacob Elordi is an Australian actor. Let’s take a look at his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Riele Downs
Riele Downs is a Canadian-American actress & Musical.ly star. Let’s take a look at her family and personal life including age, birthday, net worth, boyfriends and fun facts.
Yammy Xox
Check out all that you wanted to know about Yammy Xox, the famous British YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Kaylee Quinn
Kaylee Quinn is an American dancer, model, and actress. Let’s have a look at her family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, relationships, and fun facts.
Sophia Montero
Sophia Montero is an American singer and YouTuber. Let’s have a look at her family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, relationships, and fun facts.
Domo Wilson
Check out all that you wanted to know about Domo Wilson, the famous American Vlogger & YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, fun trivia facts and more.
Martin Lewis Perl's FAQ
What is Martin Lewis Perl birthday?
Martin Lewis Perl was born at 1927-06-24
When was Martin Lewis Perl died?
Martin Lewis Perl was died at 2014-09-30
Where was Martin Lewis Perl died?
Martin Lewis Perl was died in Palo Alto, California
Which age was Martin Lewis Perl died?
Martin Lewis Perl was died at age 87
Where is Martin Lewis Perl's birth place?
Martin Lewis Perl was born in New York City, New York
What is Martin Lewis Perl nationalities?
Martin Lewis Perl's nationalities is American
Who is Martin Lewis Perl spouses?
Martin Lewis Perl's spouses is Teri Hoch Perl
What was Martin Lewis Perl universities?
Martin Lewis Perl studied at Columbia University, NYU-Poly and Columbia University
What was Martin Lewis Perl notable alumnis?
Martin Lewis Perl's notable alumnis is Columbia University
Who is Martin Lewis Perl's father?
Martin Lewis Perl's father is Fay Perl
Who is Martin Lewis Perl's mother?
Martin Lewis Perl's mother is Oscar Perl
What is Martin Lewis Perl's sun sign?
Martin Lewis Perl is Cancer
How famous is Martin Lewis Perl?
Martin Lewis Perl is famouse as Physicist