Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac - Chemists, Birthday and Childhood
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac's Personal Details
Joseph Louis Gay Lussac was a French chemist and physicist who made notable advances in applied chemistry
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | December 6, 1778 |
| Died on | May 9, 1850 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Inventors & Discoverers, Physicists, Chemists, Chemists, Physicists |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Saint-Léonard-de-Noblat |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Sagittarius |
| Born in | Saint-Léonard-de-Noblat |
| Famous as | Chemist and Physicist |
| Died at Age | 71 |
// Famous Chemists
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. This biography of Louis Pasteur provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
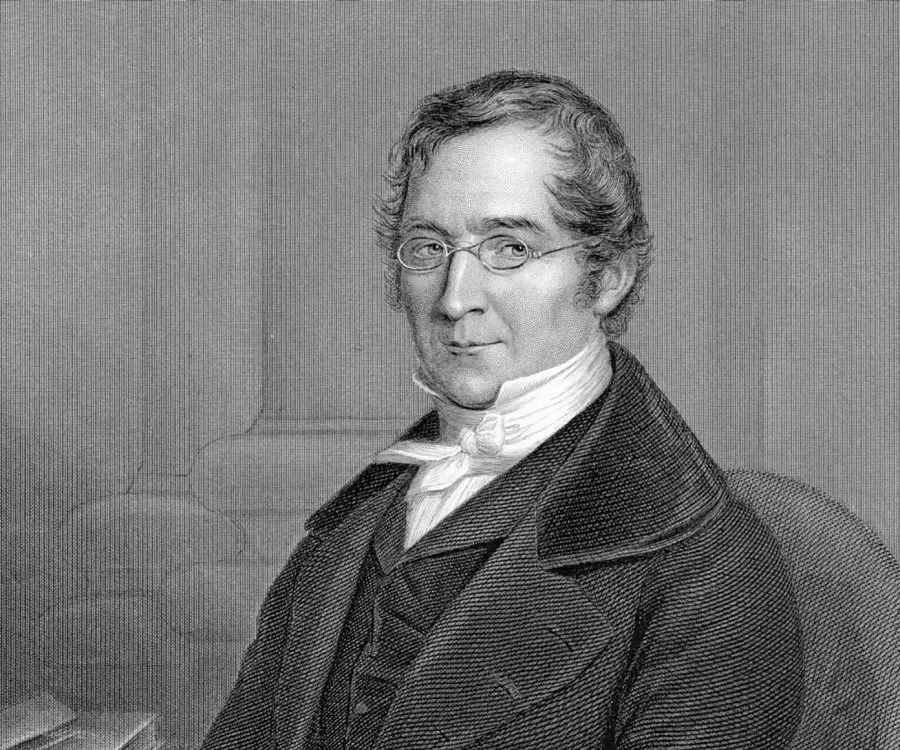
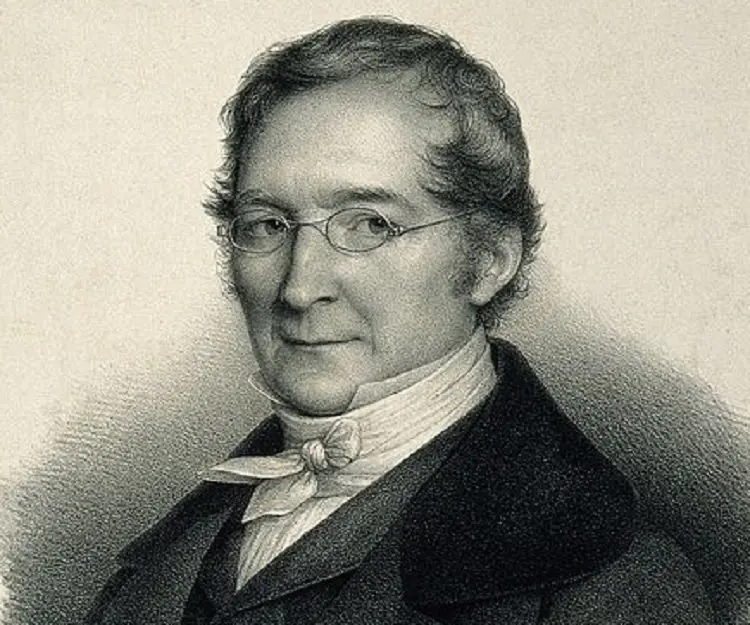
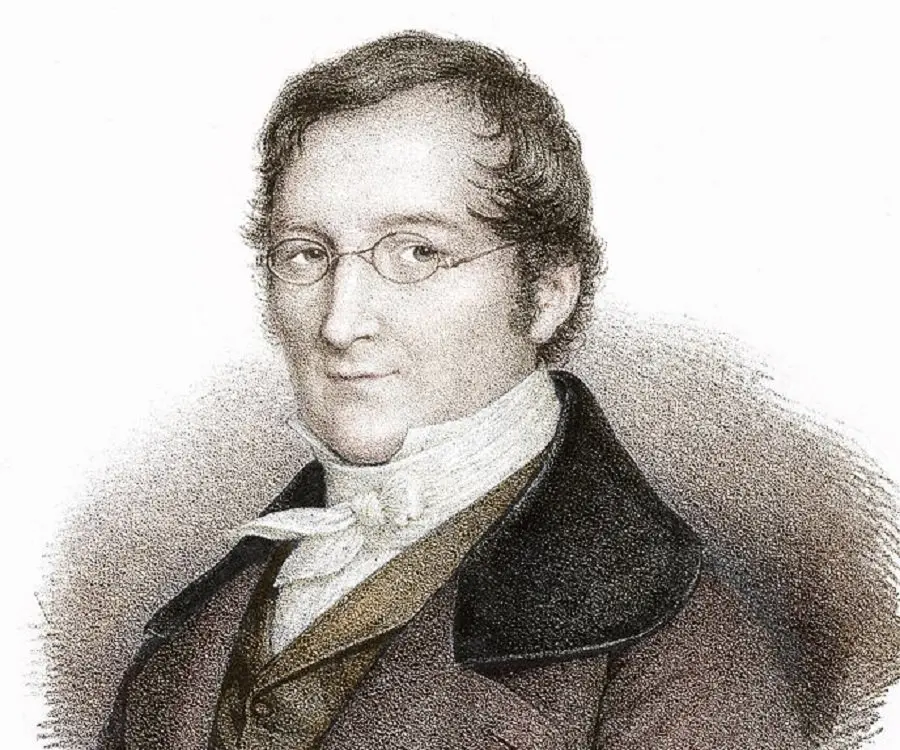
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac's photo
Who is Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac?
Joseph Louis Gay Lussac was a French chemist and physicist who made notable advances in applied chemistry. He was noted for his pioneering investigations into the behavior of gases and for his studies of the properties of cyanogen and iodine. Born as the son of a successful lawyer, he had a privileged childhood that was rudely disturbed during the French Revolution of 1789 following which his father lost much of his fortunes. The revolution also delayed his education as the Abbey of Bourdeix who had been giving Joseph private tuitions fled the country in the midst of the political turmoil. Initially his father wanted him to become a lawyer though the young boy had always been more interested in scientific pursuits. A bright student, he was successful in entering the École Polytechnique, a newly founded institute where students’ expenses were paid by the state. This enabled him to get a quality education in spite of his family’s modest financial status. Eventually he went on to become a reputed chemist and physicist and gained much fame for his work on the behavior of gases. Throughout his career, he collaborated with other noted scientists like Jean-Baptiste Biot, Alexander von Humboldt, and Louis Thenard to come up with significant scientific achievements.
// Famous Physicists
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Gabriel Lippmann
Gabriel Lippmann was a French physicist and inventor. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1908. This biography of Lippmann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Joseph Louis Gay Lussac was born on 6 December 1778 in Saint-Léonard-de-Noblat as the eldest son of Antoine Gay and Leonarde Bourigner. His father was a lawyer and prosecutor, who worked as a judge in Noblat Bridge. Joseph had four siblings.
His family was a financially sound one and he received a comfortable upbringing. Howeve,r the French Revolution changed the family’s fortunes drastically. His father was arrested as a suspect and imprisoned from 1793 to 1794. The family also lost much of its wealth.
Joseph’s education suffered initially due to the revolution but in 1797 he managed to clear the competitive entrance examination for admission into the newly opened Ecole Polytechnique where students’ expenses were paid by the state. Here he became the protégé of Claude Louis Berthollet and graduated in 1800.
Following his graduation, he entered the civil engineering school, the Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées. However, he soon dropped out to pursue his interest in chemistry.
Career
In 1801, Joseph Louis Gay Lussac became a research assistant to Claude Louis Berthollet who was much impressed with the young man’s abilities. Berthollet had recently set up a laboratory in his country house at Arcueil, just outside of Paris and he played a key role in the professional advancement of his protégé.
He collaborated with the eminent mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace to conduct experiments on capillarity in order to study short-range forces. He also carried out research on the thermal expansion of gases in 1801–02. Using dry gases and pure mercury in his experiments, he concluded that all gases expand equally over the temperature range 0–100 °C (32–212 °F).
He was appointed demonstrator to A. F. Fourcroy at the École Polytechnique in 1802, and in 1809 he was made the professor of chemistry. He also worked as a professor of physics at the Sorbonne from 1808 to 1832.
In 1805–06, he embarked on a European tour with the scientific explorer Alexander von Humboldt. On this expedition they discovered that the composition of the atmosphere does not change with decreasing pressure (increasing altitude). He also established that hydrogen and oxygen combine by volume in the ratio 2:1 to form water.
He discovered the law of the combining volumes of gases in 1808. He also investigated reactions between hydrogen chloride and ammonia, which combine in equal volumes to form ammonium chloride.
In 1816, he became the joint editor of the ‘Annales de chimie et de physique’, a position he shared with François Arago. This was an influential position and contributed significantly to his income.
He became a member of the government gunpowder commission in 1818 and was appointed as director of the assay department at the Paris Mint in 1829 where he came up with an accurate method for the assaying of silver. These positions too brought him a lot of wealth. Accepting these positions, however, also earned him considerable criticism from his colleagues who accused him of turning towards the path of financial gains rather than dedicating his life to pure science.
He was also an inventor and is credited with the development of portable barometer, steam injector pump, and air thermometer. He created an improved version of the burette that included a side arm in 1824 and coined the terms "pipette" and "burette".
Major Works
He is best remembered for formulating the Gay-Lussac's law which is used to refer to each of the two relationships which concern the properties of gases. The term is also applied to his law of combining volumes. The first law relates to volumes before and after a chemical reaction while the second concerns the pressure and temperature relationship for a sample of gas.
Awards & Achievements
He was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1821.
Joseph Louis Gay Lussac was made a peer by King Louis Philippe in 1839.
His name is one of the 72 names of French scientists, engineers, and mathematicians engraved in recognition of their contributions on the Eiffel Tower.
Personal Life & Legacy
Joseph Louis Gay Lussac married Geneviève-Marie-Joseph Rojot in 1809. Theirs was a happy marriage that lasted four decades and produced five children.
He suffered from ill health during his last days and died on 9 May 1850, in Paris, France.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac biography timelines
- // 6th Dec 1778Joseph Louis Gay Lussac was born on 6 December 1778 in Saint-Léonard-de-Noblat as the eldest son of Antoine Gay and Leonarde Bourigner. His father was a lawyer and prosecutor, who worked as a judge in Noblat Bridge. Joseph had four siblings.
- // 1793 To 1794His family was a financially sound one and he received a comfortable upbringing. Howeve,r the French Revolution changed the family’s fortunes drastically. His father was arrested as a suspect and imprisoned from 1793 to 1794. The family also lost much of its wealth.
- // 1797 To 1800Joseph’s education suffered initially due to the revolution but in 1797 he managed to clear the competitive entrance examination for admission into the newly opened Ecole Polytechnique where students’ expenses were paid by the state. Here he became the protégé of Claude Louis Berthollet and graduated in 1800.
- // 1801In 1801, Joseph Louis Gay Lussac became a research assistant to Claude Louis Berthollet who was much impressed with the young man’s abilities. Berthollet had recently set up a laboratory in his country house at Arcueil, just outside of Paris and he played a key role in the professional advancement of his protégé.
- // 1801He collaborated with the eminent mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace to conduct experiments on capillarity in order to study short-range forces. He also carried out research on the thermal expansion of gases in 1801–02. Using dry gases and pure mercury in his experiments, he concluded that all gases expand equally over the temperature range 0–100 °C (32–212 °F).
- // 1802 To 1832He was appointed demonstrator to A. F. Fourcroy at the École Polytechnique in 1802, and in 1809 he was made the professor of chemistry. He also worked as a professor of physics at the Sorbonne from 1808 to 1832.
- // 1805In 1805–06, he embarked on a European tour with the scientific explorer Alexander von Humboldt. On this expedition they discovered that the composition of the atmosphere does not change with decreasing pressure (increasing altitude). He also established that hydrogen and oxygen combine by volume in the ratio 2:1 to form water.
- // 1808He discovered the law of the combining volumes of gases in 1808. He also investigated reactions between hydrogen chloride and ammonia, which combine in equal volumes to form ammonium chloride.
- // 1809Joseph Louis Gay Lussac married Geneviève-Marie-Joseph Rojot in 1809. Theirs was a happy marriage that lasted four decades and produced five children.
- // 1816In 1816, he became the joint editor of the ‘Annales de chimie et de physique’, a position he shared with François Arago. This was an influential position and contributed significantly to his income.
- // 1818 To 1829He became a member of the government gunpowder commission in 1818 and was appointed as director of the assay department at the Paris Mint in 1829 where he came up with an accurate method for the assaying of silver. These positions too brought him a lot of wealth. Accepting these positions, however, also earned him considerable criticism from his colleagues who accused him of turning towards the path of financial gains rather than dedicating his life to pure science.
- // 1821He was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1821.
- // 1824He was also an inventor and is credited with the development of portable barometer, steam injector pump, and air thermometer. He created an improved version of the burette that included a side arm in 1824 and coined the terms "pipette" and "burette".
- // 1839Joseph Louis Gay Lussac was made a peer by King Louis Philippe in 1839.
- // 9th May 1850He suffered from ill health during his last days and died on 9 May 1850, in Paris, France.
// Famous Inventors & Discoverers
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Thomas Newcomen
Thomas Newcomen was a British inventor who developed the world’s first steam engine. Browse through this biography to learn in details about his life, career, works and timeline.
Erno Rubik
The famous inventor and educationist, Erno Rubik is known world-wide for his invention the ‘Rubik’s Cube’. To know more about the childhood, profile, timeline and career of this famous architect-inventor read on.
Ernst Ruska
Ernst Ruska was a German physicist who invented the electron microscope. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Howard Hughes
Howard Hughes was an American aviator, business tycoon, philanthropist and also a film maker. This biography explores his childhood, career, achievements and timeline.
Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick was a British inventor who was the pioneer of steam-powered road and rail transport. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac's FAQ
What is Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac birthday?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was born at 1778-12-06
When was Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac died?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was died at 1850-05-09
Where was Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac died?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was died in Paris
Which age was Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac died?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was died at age 71
Where is Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac's birth place?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac was born in Saint-Léonard-de-Noblat
What is Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac nationalities?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac's nationalities is French
What was Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac universities?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac studied at École Polytechnique
What is Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac's sun sign?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac is Sagittarius
How famous is Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac?
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac is famouse as Chemist and Physicist