François Jacob - Scientists, Timeline and Facts
François Jacob's Personal Details
François Jacob was a French biologist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | June 17, 1920 |
| Died on | April 19, 2013 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Biologists |
| Spouses | Geneviève Barrier, Lise Bloch |
| Childrens | Henri, Laurent, Odile, Pierre |
| Birth Place | Nancy, France |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Thérèse (Franck) Jacob |
| Mother | Simon |
| Sun Sign | Gemini |
| Born in | Nancy, France |
| Famous as | Biologist |
| Died at Age | 92 |
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
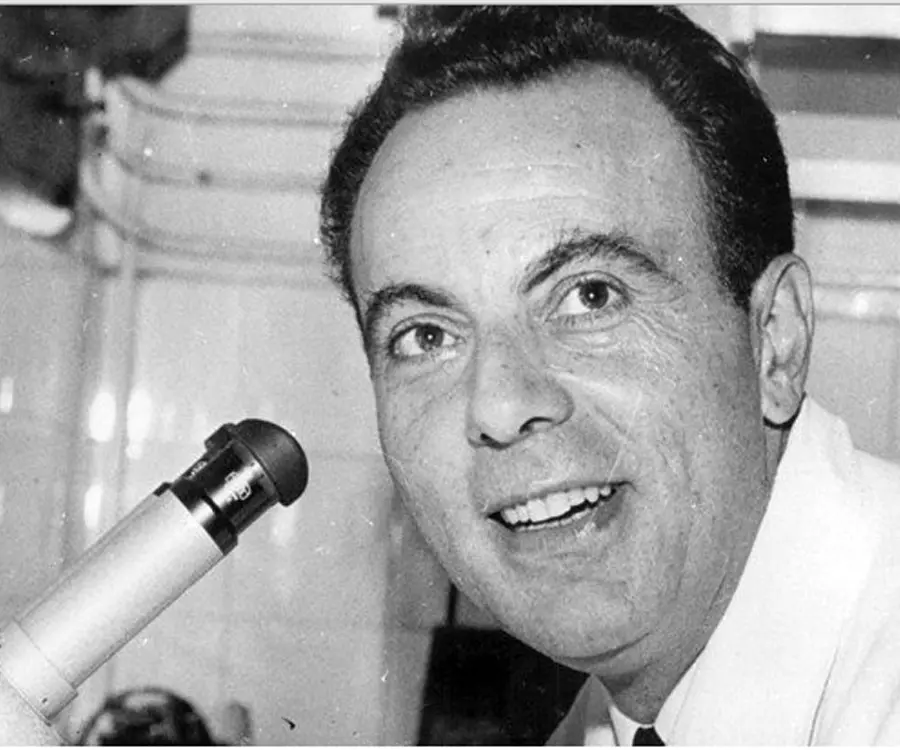
François Jacob's photo
Who is François Jacob?
François Jacob was a French biologist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965 along with another French biologist Jacques Monod and French microbiologist Andre Lwoff for their discoveries regarding genetic control of enzyme and synthesis of virus. Jacob made many significant contributions in the field of genetics by successfully collaborating with other noted scientists like Monod and Lwoff while serving the renowned ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France. His most remarkable finding was recognizing the regulator genes that regulate the activities of the structural genes. He is also known for the Jacob-Monod operon model that helps in elucidating the way genes are controlled. They elucidated on the effects of balance and imbalance between regulator genes and structural genes in a normal cell. They also examined messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), which convey genetic information from the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) – carrier of genetic instructions to the ribosome – the protein synthesizer of the cell. He showed that similar standards with regard to natural preference and evolution are followed by bacteria as done by other higher organisms. He was awarded ‘Grand Prix Charles-Leopold Mayer’ in 1962 by ‘Académie des Sciences’. In 1973 he was elected as a ‘Foreign Member of the Royal Society’ (‘ForMemRS’).
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
He was born on June 17, 1920, Nancy, France, to Thérèse (Franck) Jacob and his wife Simon as their only child. His father was a "conformist in religion", while his mother and other close family members were secular Jews.
When he was seven-year-old he joined the public secondary and higher education school ‘Lycée Carnot’ in Paris and studied there for ten years.
As a child he looked up to his maternal grandfather Albert Franck, a four-star general. Jacob became an atheist some time after his bar mitzvah.
After completing school education he enrolled at the Faculty of Paris with the objective of becoming a surgeon and studied medicine. However his studies were interrupted during the ‘Second World War’ in 1940 when the German Army invaded France.
While in his second year of studies he fled to England in a boat in June 1940 and joined the ‘Free French Forces’ in London. Jacob was relocated to Africa where he served as a medical officer and witnessed several actions in Libya, Tunisia, Tripolitania and Fezzan.
In 1944 while stationed with the French ‘2nd Armoured Division’ in Normandy he got wounded in a German air attack and had to return to Paris on August 1 that year. He remained hospitalized for 7 months.
He received the French Order ‘Cross of Liberation’ conferred to brave hearts of the ‘Liberation of France’ during the ‘Second world War’. He also received the highest French Order ‘Légion d'honneur’ and the French military decoration ‘Croix de guerre’.
Post war he continued with his medical studies in Paris and started examining tyrothricin and studying procedures of bacteriology. In 1947 he earned his M.D. after submitting his doctoral thesis on effectiveness of antibiotics in combating local infections. However due to his wartime injuries he was unable to pursue his career as a surgeon.
Career
He joined the renowned ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France in 1950 as a research assistant and began working under French microbiologist Dr. André Lwoff. The following year he received his science degree.
His work centred on the genetic mechanisms present in bacteriophages and bacteria as also with regard to the biochemical effects of mutations. He examined properties of lysogenic bacteria and showed their immunity.
In 1954 he earned his PhD. in science from the ‘University of Paris’ (Sorbonne) submitting his thesis on ‘Lysogenic bacteria and the provirus concept’. The same year he started collaborating with French microbial geneticist, Elie Wollman and examined the relation between the genetic substance of bacteria and prophage. The investigation resulted in defining the mechanics of unification of bacteria as also facilitated a research of the genetic device of the bacterial cell. The work led to a number of new concepts like the procedure of genetic transfer from male to female and the episome concept. A summary of this work was given by him in the book ‘Sexuality and the Genetics of Bacteria’, which was published in 1961.
In 1956 he was made the Laboratory Director at the ‘Pasteur Institute’ and after a few years in 1960 he became the Head of the Department of Cell Genetics, a position which was created sometime recently.
In 1961 Jacob along with Jacques Monod investigated on the mechanics that are responsible for genetic data transfer and the controlling pathways present in bacterial cell that regulate the activities and synthesis of macromolecules. The duo suggested a number of new concepts like those of allosteric proteins, regulator genes and messenger RNA.
Jacob and Monod became reputed for their work on E.coli Lac operon that encodes protein required for the transfer and breakdown of sugar lactose. The duo displayed a model that showed the way levels of some of the cell proteins are regulated. According to their model the formation of proteins is restricted when a repressor that is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein, put into code by a regulatory gene, binds to a segment of DNA i.e., its operator.
The findings of Jacob and Monod convey that the balance between regulator genes and structural genes in a normal cell allows it to adjust in varying conditions while an imbalance can result in production of new enzymes which can be either favourable or harmful for the cell.
In 1962 he became a foreign member of the ‘Danish Royal Academy of Arts and Sciences’.
Along with South African biologist Sydney Brenner, he came up with the ‘replicon’ hypothesis in 1963 to detail a few facets of bacterial cell division. From that time he dedicated himself to the genetic study of the mechanics of cell division.
In 1964 he was inducted as a Professor at the prestigious higher education and research establishment ‘Collège de France’. A chair of cell Genetics was created there for Jacob. That year he also became a foreign member of the ‘American Academy of Arts and Sciences’.
In 1969 he became a foreign member of the ‘American Philosophical Society’ and also the ‘National Academy of Sciences’ of the US.
From 1970 he investigated cultured cells of mammals, especially some of the facets of the genetic properties of cells. He published a book ‘La logique du vivant, une Histoire de l'Hérédité’ (‘The Logic of Life: A History of Heredity’) in 1970 that showed the steps and phases in the study of living beings starting from the sixteenth century thereby leading to the area of molecular biology.
He was conferred honorary degrees by many universities.
Awards & Achievements
In 1965 he received the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ together with Jacques Monod and Andre Lwoff.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married pianist Lise Bloch in 1947. They were blessed with three sons and one daughter. Their four children were Pierre (born in 1949); Odile and Laurent (born in 1952) and Henri (born in 1954). His wife Lise died in 1983.
In 1999 Jacob married for the second time to Geneviève Barrier.
On April 19, 2013, he died in Paris, France, at the age of 92 survived by his second wife Geneviève and four children from his first marriage.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
François Jacob's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Grand Prix Charles-Leopold Mayer (1962) | |
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1965) | |
| 0 | ForMemRS (1973) | |
François Jacob biography timelines
- // 17th Jun 1920He was born on June 17, 1920, Nancy, France, to Thérèse (Franck) Jacob and his wife Simon as their only child. His father was a "conformist in religion", while his mother and other close family members were secular Jews.
- // 1940After completing school education he enrolled at the Faculty of Paris with the objective of becoming a surgeon and studied medicine. However his studies were interrupted during the ‘Second World War’ in 1940 when the German Army invaded France.
- // Jun 1940While in his second year of studies he fled to England in a boat in June 1940 and joined the ‘Free French Forces’ in London. Jacob was relocated to Africa where he served as a medical officer and witnessed several actions in Libya, Tunisia, Tripolitania and Fezzan.
- // 1944In 1944 while stationed with the French ‘2nd Armoured Division’ in Normandy he got wounded in a German air attack and had to return to Paris on August 1 that year. He remained hospitalized for 7 months.
- // 1947Post war he continued with his medical studies in Paris and started examining tyrothricin and studying procedures of bacteriology. In 1947 he earned his M.D. after submitting his doctoral thesis on effectiveness of antibiotics in combating local infections. However due to his wartime injuries he was unable to pursue his career as a surgeon.
- // 1950He joined the renowned ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France in 1950 as a research assistant and began working under French microbiologist Dr. André Lwoff. The following year he received his science degree.
- // 1954 To 1961In 1954 he earned his PhD. in science from the ‘University of Paris’ (Sorbonne) submitting his thesis on ‘Lysogenic bacteria and the provirus concept’. The same year he started collaborating with French microbial geneticist, Elie Wollman and examined the relation between the genetic substance of bacteria and prophage. The investigation resulted in defining the mechanics of unification of bacteria as also facilitated a research of the genetic device of the bacterial cell. The work led to a number of new concepts like the procedure of genetic transfer from male to female and the episome concept. A summary of this work was given by him in the book ‘Sexuality and the Genetics of Bacteria’, which was published in 1961.
- // 1956 To 1960In 1956 he was made the Laboratory Director at the ‘Pasteur Institute’ and after a few years in 1960 he became the Head of the Department of Cell Genetics, a position which was created sometime recently.
- // 1961In 1961 Jacob along with Jacques Monod investigated on the mechanics that are responsible for genetic data transfer and the controlling pathways present in bacterial cell that regulate the activities and synthesis of macromolecules. The duo suggested a number of new concepts like those of allosteric proteins, regulator genes and messenger RNA.
- // 1962In 1962 he became a foreign member of the ‘Danish Royal Academy of Arts and Sciences’.
- // 1963Along with South African biologist Sydney Brenner, he came up with the ‘replicon’ hypothesis in 1963 to detail a few facets of bacterial cell division. From that time he dedicated himself to the genetic study of the mechanics of cell division.
- // 1964In 1964 he was inducted as a Professor at the prestigious higher education and research establishment ‘Collège de France’. A chair of cell Genetics was created there for Jacob. That year he also became a foreign member of the ‘American Academy of Arts and Sciences’.
- // 1965In 1965 he received the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ together with Jacques Monod and Andre Lwoff.
- // 1969In 1969 he became a foreign member of the ‘American Philosophical Society’ and also the ‘National Academy of Sciences’ of the US.
- // 1970From 1970 he investigated cultured cells of mammals, especially some of the facets of the genetic properties of cells. He published a book ‘La logique du vivant, une Histoire de l'Hérédité’ (‘The Logic of Life: A History of Heredity’) in 1970 that showed the steps and phases in the study of living beings starting from the sixteenth century thereby leading to the area of molecular biology.
- // 1999In 1999 Jacob married for the second time to Geneviève Barrier.
- // 19th Apr 2013On April 19, 2013, he died in Paris, France, at the age of 92 survived by his second wife Geneviève and four children from his first marriage.
// Famous Gemini Celebrities peoples
Wentworth Miller
Wentworth Miller is an American actor and screenwriter who achieved recognition for his role in the TV series ‘Prison Break’.
Joyce Meyer
Joyce Meyer is a Christian author and speaker. This biography provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Zoe LaVerne
Zoe LaVerne is an American musical.ly star. Check out this biography to know more about her family, personal life, including her age, birthday, etc.
WolfieRaps
Check out all that you wanted to know about WolfieRaps, the famous YouTube Personality; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Adam Saleh
Check out all that you wanted to know about Adam Saleh, the famous YouTube Personality; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Isaak Presley
All about American actor and singer Isaak Presley including his age, birthday, family life, girlfriends, net worth, and some fun facts.
François Jacob's FAQ
What is François Jacob birthday?
François Jacob was born at 1920-06-17
When was François Jacob died?
François Jacob was died at 2013-04-19
Where was François Jacob died?
François Jacob was died in Paris, France
Which age was François Jacob died?
François Jacob was died at age 92
Where is François Jacob's birth place?
François Jacob was born in Nancy, France
What is François Jacob nationalities?
François Jacob's nationalities is French
Who is François Jacob spouses?
François Jacob's spouses is Geneviève Barrier, Lise Bloch
Who is François Jacob childrens?
François Jacob's childrens is Henri, Laurent, Odile, Pierre
Who is François Jacob's father?
François Jacob's father is Thérèse (Franck) Jacob
Who is François Jacob's mother?
François Jacob's mother is Simon
What is François Jacob's sun sign?
François Jacob is Gemini
How famous is François Jacob?
François Jacob is famouse as Biologist