William Beveridge - Social Reformers, Timeline and Family
William Beveridge's Personal Details
William Beveridge was a British social reformer and economist who came into prominence for his 1942 Beveridge Report
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | March 5, 1879 |
| Died on | March 16, 1963 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Humanitarian, Intellectuals & Academics, Economists, Social Reformers |
| Universities |
|
| Founder / Co-Founder |
|
| Birth Place | Rangpur City |
| Political Ideology | Political party - Liberal Party |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Henry Beveridge |
| Sun Sign | Pisces |
| Born in | Rangpur City |
| Famous as | Economist |
| Died at Age | 84 |
// Famous Social Reformers
Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar was an Indian polymath and a social reformer. This biography of Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Granville Sharp
Granville Sharp was a social reformer and a leading British abolitionist. This biography of Granville Sharp provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Baba Amte
Baba Amte was an Indian social activist best remembered for his work for rehabilitation of leprosy patients. This biography of Baba Amte provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
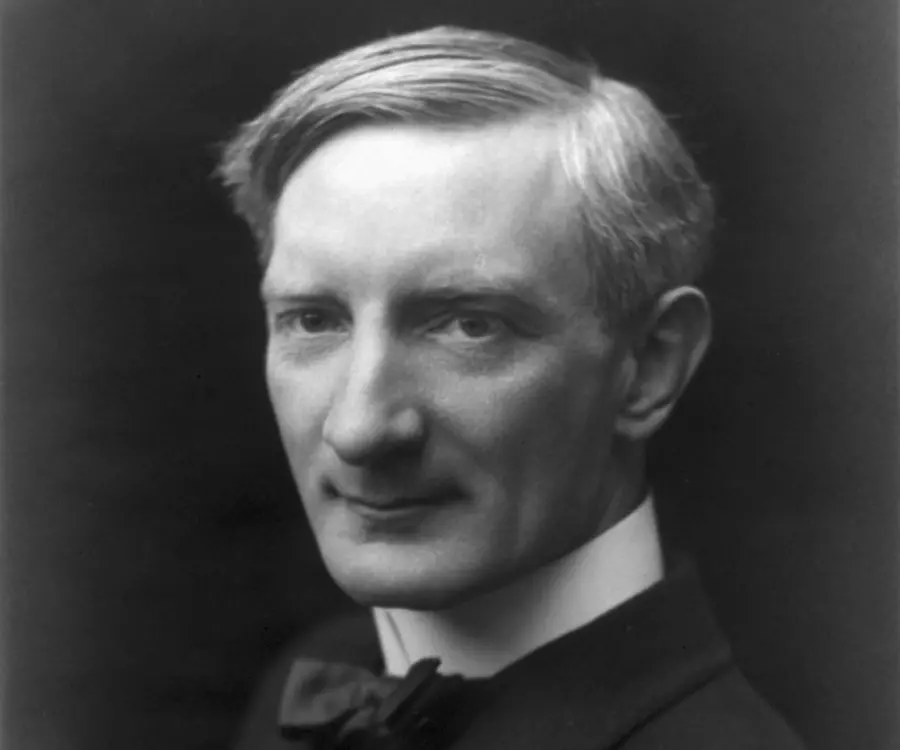
William Beveridge's photo
Who is William Beveridge?
William Beveridge was a British social reformer and economist who constantly fought against the evil of unemployment for the development of a welfare state. He came to prominence for his ‘Social Insurance and Allied Services’ report of 1942, popularly known as the Beveridge Report, which was implemented in the Labour government of 1945. Through the report, he aimed at shaping Britain’s post-war welfare state policies and institutions. He appealed to the government to fight against the five ‘Giant Evils’ of the society including Want, Disease, Ignorance, Squalor and Idleness. Early in his life, Beveridge worked against combating issues of unemployment and poverty. For the same, he took up a seat on the Board of Trade under Winston Churchill. He organized the implementation of national system of labour exchange and national insurance. He also served as the Director of the London School of Economics and Political Science and was elected as Master of University College, Oxford
// Famous Humanitarian
Joyce Meyer
Joyce Meyer is a Christian author and speaker. This biography provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Swami Vivekananda
Swami Vivekananda was the chief disciple of Sri Ramakrishna, and was responsible for awakening India spiritually. Check this biography to know in detail about his life, profile and timeline.
Nicole Kidman
Nicole Kidman is one of the most talented actors that the Hollywood film industry can boast of. Browse through this biography to get detailed information regarding her life, childhood, profile & timeline
Childhood & Early Life
William Henry Beveridge was born on March 5, 1879 in Rangpur, then a part of India to Henry Beveridge and Annette Akroyd. His father was employed as an officer in Indian Civil Service.
Young Beveridge attained his preliminary education at Charterhouse, in Godalming, Surrey. For higher education, he enrolled at Balliol College at the University of Oxford, studying mathematics and classics. Graduating in first class, he went on to study law.
Career
Completing studies, Beveridge commenced his career as a lawyer. He soon became interested in social service and started penning articles on the same for the Morning Post newspaper.
His lifelong interest in the causes of unemployment first began in 1903, after his appointment as a sub-warden at Toynbee Hall, a settlement house in London. During this time, he closely associated with Sidney Webb and Beatrice Webb, working on their theory of social reform
Beveridge actively took part in the social reform movement which targeted at changing the social scenario, by promoting free school meals, old age pension and so on. He also campaigned for a central labour exchange system that would put an end to unemployment and with that poverty.
In 1908, he was introduced to Winston Churchill by Beatrice Webb during a dinner party hosted by the latter. Impressed by Beveridge’s reformist ways, Churchill invited him to join the Board of Trade. As an advisor, Beveridge successfully implemented a national system of labour exchange and national insurance, thus fighting unemployment and poverty.
During the First World War, Beveridge was in charge of mobilising and controlling manpower. Post war, he was knighted and was made permanent secretary of Ministry of Food.
In 1919, he gave up on civil service to take up the chair of the London School of Economics and Political Science. He served the post until 1937. During the same time, he served as the director of LSE,.
In 1933, he established the Academic Assistance Council. Through this initiative, he recruited former academicians who had been removed from their posts on account of race, religion or political stand. In 1937, he was appointed as the master of the University College, Oxford.
in 1936, he was offered to take charge of the Welfare department of the Ministry of Labour by Ernest Bevin. Though he declined the offer, Beveridge expressed his interest in organizing manpower. As such, temporarily, he served as a civil servant.
In 1941, a committee of officials was formed by Ernest Brown, Minister of Health, to survey the existing social insurance and make recommendations. Beveridge was made chairman of commitee. He reluctantly accepted the appointment as he thought it to be a distraction from his work on manpower.
Complying with the new responsibility as chairman of the social insurance and allied services committee, Beveridge presented a report in 1942 stating that a weekly national insurance should be contributed by the working class, which in turn would be forwarded to people who are sick, unemployed, retired or widowed. This way, a minimum standard of living would be established
Beveridge argued in his 1942 report that the government should find ways to fight the five ‘Giant Evils’ – Want, Disease, Ignorance, Squalor and Idleness. He also proposed establishment of a National Health Service.
In 1944, Beveridge came up with his work, ‘Full Employment in a Free Society’ through which he brought to limelight ways in which full employment could be attained. Alternative measures included Keynesian-style fiscal regulation, direct control of manpower, and state control of the means of production.
On the political front, he became a member of the Liberal Party. In 1944, he was elected to the House of Commons in a by-election. He served as the MP for the constituency of Berwick-upon-Tweed. However, his parliamentary stint did not last long as he was defeated in 1945 general elections.
Following the defeat of the Churchill’s party in the 1945 general election, Clement Attlee came to power as the new prime minister. Immediately, he introduced the welfare state that was outlined in the 1942 Beveridge Report, which led to establishment of National Health Service which covered taxpayer funded medical treatment. Furthermore, a national system of benefits was also introduced to provide 'social security' to people from ‘cradle to grave’.
In 1946, he became leader of the Liberals in the House of Lords. For a decade, from 1952 to 1962, he served as the President of the charity Attend.
In his lifetime, he was a member of the Eugenics Society that promoted the study of methods to improve human race by controlling reproduction. He credited the promotion of children’s allowance in his 1942 Report to Eugenics Society.
Major Works
William Beveridge’s most notable contribution came with his 1942 report, Social Insurance and Allied Services. Through this work, he aimed at re-establishing Britain’s welfare state post World War II by providing social security to citizens from ‘cradle to grave’. He encouraged establishment of National Health Insurance which would provide free medical treatment.
In his lifetime, Beveridge penned numerous works including, ‘Unemployment: A Problem of Industry’, ‘Planning Under Socialism’, ‘Full Employment in a Free Society’, ‘Pillars of Security’, ‘Power and Influence’ and ‘A Defence of Free Learning’.
Awards & Achievements
In 1946, he made Baron Beveridge, of Tuggal in the County of Northumberland.
Personal Life & Legacy
William Beveridge entered into the wedlock with Jessy Janet, daughter of William Phillip.
He breathed his last on March 16, 1963 at the age of 84. He was buried in Thockrington churchyard on the Northumbrian moors. Upon his death, his baronecy became extinct.
// Famous Economists
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin was a famous Swedish economist. This biography profiles his childhood, family life & achievements.
Emily Greene Balch
Emily Greene Balch was an American economist, sociologist and pacifist who won the 1946 Nobel Peace Prize. This biography of Emily Greene Balch provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Paul Samuelson
Nobel laureate Paul Anthony Samuelson is referred to as the ‘Father of Modern Economics’. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and interesting facts about him.
William Beveridge biography timelines
- // 5th Mar 1879William Henry Beveridge was born on March 5, 1879 in Rangpur, then a part of India to Henry Beveridge and Annette Akroyd. His father was employed as an officer in Indian Civil Service.
- // 1903His lifelong interest in the causes of unemployment first began in 1903, after his appointment as a sub-warden at Toynbee Hall, a settlement house in London. During this time, he closely associated with Sidney Webb and Beatrice Webb, working on their theory of social reform
- // 1908In 1908, he was introduced to Winston Churchill by Beatrice Webb during a dinner party hosted by the latter. Impressed by Beveridge’s reformist ways, Churchill invited him to join the Board of Trade. As an advisor, Beveridge successfully implemented a national system of labour exchange and national insurance, thus fighting unemployment and poverty.
- // 1919 To 1937In 1919, he gave up on civil service to take up the chair of the London School of Economics and Political Science. He served the post until 1937. During the same time, he served as the director of LSE,.
- // 1933 To 1937In 1933, he established the Academic Assistance Council. Through this initiative, he recruited former academicians who had been removed from their posts on account of race, religion or political stand. In 1937, he was appointed as the master of the University College, Oxford.
- // 1936in 1936, he was offered to take charge of the Welfare department of the Ministry of Labour by Ernest Bevin. Though he declined the offer, Beveridge expressed his interest in organizing manpower. As such, temporarily, he served as a civil servant.
- // 1941In 1941, a committee of officials was formed by Ernest Brown, Minister of Health, to survey the existing social insurance and make recommendations. Beveridge was made chairman of commitee. He reluctantly accepted the appointment as he thought it to be a distraction from his work on manpower.
- // 1942Complying with the new responsibility as chairman of the social insurance and allied services committee, Beveridge presented a report in 1942 stating that a weekly national insurance should be contributed by the working class, which in turn would be forwarded to people who are sick, unemployed, retired or widowed. This way, a minimum standard of living would be established
- // 1942Beveridge argued in his 1942 report that the government should find ways to fight the five ‘Giant Evils’ – Want, Disease, Ignorance, Squalor and Idleness. He also proposed establishment of a National Health Service.
- // 1942 To 1945Following the defeat of the Churchill’s party in the 1945 general election, Clement Attlee came to power as the new prime minister. Immediately, he introduced the welfare state that was outlined in the 1942 Beveridge Report, which led to establishment of National Health Service which covered taxpayer funded medical treatment. Furthermore, a national system of benefits was also introduced to provide 'social security' to people from ‘cradle to grave’.
- // 1942In his lifetime, he was a member of the Eugenics Society that promoted the study of methods to improve human race by controlling reproduction. He credited the promotion of children’s allowance in his 1942 Report to Eugenics Society.
- // 1942William Beveridge’s most notable contribution came with his 1942 report, Social Insurance and Allied Services. Through this work, he aimed at re-establishing Britain’s welfare state post World War II by providing social security to citizens from ‘cradle to grave’. He encouraged establishment of National Health Insurance which would provide free medical treatment.
- // 1944In 1944, Beveridge came up with his work, ‘Full Employment in a Free Society’ through which he brought to limelight ways in which full employment could be attained. Alternative measures included Keynesian-style fiscal regulation, direct control of manpower, and state control of the means of production.
- // 1944 To 1945On the political front, he became a member of the Liberal Party. In 1944, he was elected to the House of Commons in a by-election. He served as the MP for the constituency of Berwick-upon-Tweed. However, his parliamentary stint did not last long as he was defeated in 1945 general elections.
- // 1946In 1946, he became leader of the Liberals in the House of Lords. For a decade, from 1952 to 1962, he served as the President of the charity Attend.
- // 1946In 1946, he made Baron Beveridge, of Tuggal in the County of Northumberland.
- // 16th Mar 1963He breathed his last on March 16, 1963 at the age of 84. He was buried in Thockrington churchyard on the Northumbrian moors. Upon his death, his baronecy became extinct.
// Famous Intellectuals & Academics
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin was a famous Swedish economist. This biography profiles his childhood, family life & achievements.
Emily Greene Balch
Emily Greene Balch was an American economist, sociologist and pacifist who won the 1946 Nobel Peace Prize. This biography of Emily Greene Balch provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Martin Buber
One of the greatest philosophers to have ever walked on earth, Martin Buber contributions to philosophy is a long-standing one. Explore all about his profile, childhood, life and timeline here.
Paul Samuelson
Nobel laureate Paul Anthony Samuelson is referred to as the ‘Father of Modern Economics’. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and interesting facts about him.
Lao Tzu (Laozi)
Lao Tzu was a legendary Chinese philosopher who wrote the important “Daodejing”. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Simon Kuznets
Simon Kuznets was a noted Russian-American economist, statistician, demographer, and economic historian. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to his life.
William Beveridge's FAQ
What is William Beveridge birthday?
William Beveridge was born at 1879-03-05
When was William Beveridge died?
William Beveridge was died at 1963-03-16
Where was William Beveridge died?
William Beveridge was died in Oxford
Which age was William Beveridge died?
William Beveridge was died at age 84
Where is William Beveridge's birth place?
William Beveridge was born in Rangpur City
What is William Beveridge nationalities?
William Beveridge's nationalities is British
What was William Beveridge universities?
William Beveridge studied at Balliol College, Charterhouse School
Which company or organization was founded by William Beveridge?
William Beveridge was the founder/co-founder of Council for Assisting Refugee Academics
What is William Beveridge's political ideology?
William Beveridge's political ideology is Political party - Liberal Party
Who is William Beveridge's father?
William Beveridge's father is Henry Beveridge
What is William Beveridge's sun sign?
William Beveridge is Pisces
How famous is William Beveridge?
William Beveridge is famouse as Economist














