Victor Grignard - Scientists, Facts and Personal Life
Victor Grignard's Personal Details
François Auguste Victor Grignard was a French chemist who developed the synthetic reaction, the ‘Grignard reaction’
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | May 6, 1871 |
| Died on | December 13, 1935 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Chemists, Organic Chemists |
| Spouses | Augustine Marie Boulant |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Cherbourg-Octeville, France |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Taurus |
| Born in | Cherbourg-Octeville, France |
| Famous as | Chemist |
| Died at Age | 64 |
// Famous Organic Chemists
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist who is best known for his discovery of the periodic law. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Aleksandr Borodin
Aleksandr Borodin was a prodigal Russian music composer and scientist. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
Hermann Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer was a Nobel Prize winning chemist from Germany who is known for inventing the ‘Fischer Projection’ method. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
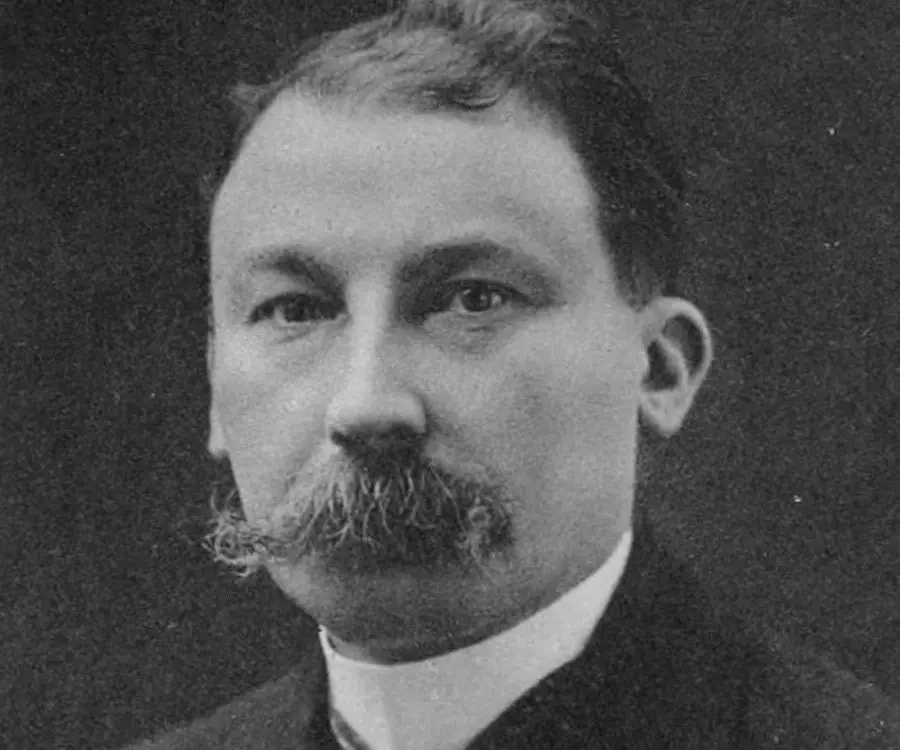
Victor Grignard's photo
Who is Victor Grignard?
François Auguste Victor Grignard was a French chemist who developed the synthetic reaction that came to be known as the ‘Grignard reaction’. The discovery, which was part of his doctoral thesis relating to organomagnesium compounds, opened a wide spectrum of organic synthesis. It earned him the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1912 that he shared with another French organic chemist Paul Sabatier. He served as a teacher of chemistry at the ‘University of Lyon’. He also remained a Professor of ‘Organic Chemistry’ and Professor of ‘General Chemistry’ at the ‘University of Nancy’ and at the ‘University of Lyon’ respectively. He served as Director of ‘École de Chimie Industrielle de Lyons’ for over a decade. During the ‘First World War’, he examined the chemical warfare agents, especially the production of phosgene and also detected dichloroethyl sulfide that is mustard gas for its application as chemical weaponry. His other studies include ozonization of unsaturated compounds and condensation of ketones and aldehydes. He received several awards including ‘Cahours Prize’ in 1901 and 1902; ‘Berthelot Medal’ in 1902; ‘Prix Jecker Prize’ in 1905 and ‘Lavoisier Medal’ in 1912. He was honoured with the order of ‘French Legion of Honor’ as Chevalier in 1912 and as Officer in 1920 and as Commander in 1933. He received honorary doctorates from universities of Louvain and Brussels. He was foreign member of ‘Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences’ and Honorary Fellow of ‘Chemical Society’ of London.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Childhood & Early Life
He was born on May 6, 1871, in Cherbourg, France in the family of a marine carpenter, Théophile Henri Grignard.
From 1883 to 1887 he studied in local schools.
After earning a scholarship, he joined the ‘École Normale Spécial’ school in Cluny in 1889. The objective of the school was to prepare modern secondary school teachers. However, after a couple of years the school was closed following conflict between proponents of classic and modern methods of secondary education. The students were transferred to other schools to complete their scholarship education. This is how Grignard joined the ‘University of Lyons’ in its ‘Faculté des Sciences’ department.
He could not succeed in the licentiate examination in mathematics. Then from 1892 till the end of 1893 he went to fulfil his military service and thereafter came back to Lyons.
In 1894 he earned his ‘Licencié ès Sciences Mathématiques’ degree.
Career
He joined the ‘Faculté des Sciences’ at the ‘University of Lyon’, in a junior position in December 1894, where he worked with French scientist Louis Bouveault, who convinced him to take up chemistry.
After some time he was promoted to préparateur, and from that time he became associated with French organic chemist Philippe Barbier, who is considered as father of organometallic chemistry.
He became ‘chef des travaux pratiques’ in 1898 and the same year penned down his first paper along with Philippe Barbier.
His first research works were related to examination of branched unsaturated hydrocarbons and also on ethyl -isopropylacetobutyrate and the stereoisomeric diisopropylbutenedicarboxylic acids.
Upon advice of Philippe Barbier, he researched on organomagnesium compounds, while his invention of the composition of magnesium alkyl halides was conveyed first to the Académie des Sciences on May 11, 1900, by French chemist Henri Moissan.
Soon he developed the use of such reagents, which later played significant role in organic synthesis. There were at least six thousand papers that were published in 1935, at the time of his death, which convey applications of the ‘Grignard reaction’.
He applied the agents to develop and examine the exotic alcohols, keto-esters, nitriles, ketones and terpene compounds and came out with a procedure for the synthesis of fulvenes.
His other research works include the catalytic hydrogenation and dehydrogenation procedures, breaking up of hydrocarbons in presence of aluminium chloride and composition of unsaturated compounds with the aid of quantitative ozonization.
In 1901, he earned his PhD in Chemistry from the ‘University of Lyon’ after submitting his remarkable thesis ‘Sur les Combinaisons organomagnésiennes mixtes’ on organic magnesium compounds.
In 1905 he was inducted as Maître de Conférences at the ‘University of Besançon’.
The following year he joined ‘University of Lyon’ and held similar position until 1908 when he became a Professor of Chemistry in the university.
In 1909 he left ‘University of Lyon’ to join ‘University of Nancy’ as a Professor of organic chemistry.
At the outset of the ‘World War I’, Grignard was delegated to examine the cracking of Benzols at Nancy. He also worked on issues relating to chemical warfare in Paris.
In 1912 two volumes of his book, ‘Le Catalyse en Chimie Organique’ (Catalysis in Organic Chemistry) was published.
Around 1917 to 1918, he went to the United States and participated as chemical representative on the ‘Tardieu Committee’. He visited the ‘Mellon Institute’ where he delivered a lecture as well.
Post ‘World War I’, he returned to Nancy and thereafter joined the ‘University of Lyon’ in 1919 succeeding Philippe Barbier as Professor of General Chemistry. He served the post till 1935.
After the war, he began compiling his ‘Traité de Chimie Organique’ (Treatise on organic chemistry), two volumes of which were published in 1935, while the multi-volume treatise was completed by his collaborators after his death.
He remained Director of ‘École de Chimie Industrielle de Lyons’ from 1921 to 1935.
He was inducted as Dean of the Faculty of Sciences at the ‘University of Lyon’ in 1929.
Major Works
His most remarkable work was discovering a new process of developing carbon-carbon bonds applying magnesium to couple ketones and alkyl halides, which was famously known as the ‘ Grignard reaction’.
Awards & Achievements
He received the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1912 along with French organic chemist Paul Sabatier.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1910, he married Augustine Marie Boulant and the couple together had a son and a daughter.
His son, Roger Grignard, born in 1911, was also a chemist.
On December 13, 1935, he died in Lyon, France.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Victor Grignard's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize for Chemistry (1912) | |
Victor Grignard biography timelines
- // 6th May 1871He was born on May 6, 1871, in Cherbourg, France in the family of a marine carpenter, Théophile Henri Grignard.
- // 1883 To 1887From 1883 to 1887 he studied in local schools.
- // 1889After earning a scholarship, he joined the ‘École Normale Spécial’ school in Cluny in 1889. The objective of the school was to prepare modern secondary school teachers. However, after a couple of years the school was closed following conflict between proponents of classic and modern methods of secondary education. The students were transferred to other schools to complete their scholarship education. This is how Grignard joined the ‘University of Lyons’ in its ‘Faculté des Sciences’ department.
- // 1892 To 1893He could not succeed in the licentiate examination in mathematics. Then from 1892 till the end of 1893 he went to fulfil his military service and thereafter came back to Lyons.
- // 1894In 1894 he earned his ‘Licencié ès Sciences Mathématiques’ degree.
- // Dec 1894He joined the ‘Faculté des Sciences’ at the ‘University of Lyon’, in a junior position in December 1894, where he worked with French scientist Louis Bouveault, who convinced him to take up chemistry.
- // 1898He became ‘chef des travaux pratiques’ in 1898 and the same year penned down his first paper along with Philippe Barbier.
- // 11th May 1900Upon advice of Philippe Barbier, he researched on organomagnesium compounds, while his invention of the composition of magnesium alkyl halides was conveyed first to the Académie des Sciences on May 11, 1900, by French chemist Henri Moissan.
- // 1901In 1901, he earned his PhD in Chemistry from the ‘University of Lyon’ after submitting his remarkable thesis ‘Sur les Combinaisons organomagnésiennes mixtes’ on organic magnesium compounds.
- // 1905In 1905 he was inducted as Maître de Conférences at the ‘University of Besançon’.
- // 1908The following year he joined ‘University of Lyon’ and held similar position until 1908 when he became a Professor of Chemistry in the university.
- // 1909In 1909 he left ‘University of Lyon’ to join ‘University of Nancy’ as a Professor of organic chemistry.
- // 1910In 1910, he married Augustine Marie Boulant and the couple together had a son and a daughter.
- // 1911His son, Roger Grignard, born in 1911, was also a chemist.
- // 1912In 1912 two volumes of his book, ‘Le Catalyse en Chimie Organique’ (Catalysis in Organic Chemistry) was published.
- // 1912He received the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1912 along with French organic chemist Paul Sabatier.
- // 1917 To 1918Around 1917 to 1918, he went to the United States and participated as chemical representative on the ‘Tardieu Committee’. He visited the ‘Mellon Institute’ where he delivered a lecture as well.
- // 1919 To 1935Post ‘World War I’, he returned to Nancy and thereafter joined the ‘University of Lyon’ in 1919 succeeding Philippe Barbier as Professor of General Chemistry. He served the post till 1935.
- // 1921 To 1935He remained Director of ‘École de Chimie Industrielle de Lyons’ from 1921 to 1935.
- // 1929He was inducted as Dean of the Faculty of Sciences at the ‘University of Lyon’ in 1929.
- // 1935Soon he developed the use of such reagents, which later played significant role in organic synthesis. There were at least six thousand papers that were published in 1935, at the time of his death, which convey applications of the ‘Grignard reaction’.
- // 1935After the war, he began compiling his ‘Traité de Chimie Organique’ (Treatise on organic chemistry), two volumes of which were published in 1935, while the multi-volume treatise was completed by his collaborators after his death.
- // 13th Dec 1935On December 13, 1935, he died in Lyon, France.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Alex Lange
Alex Lange is a French-South African model, who is quite popular on Instagram. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Tina Kunakey
Tina Kunakey Di Vita is a model and wife of the French actor Vincent Cassel. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jeanne Calment
Jeanne Calment was a French supercentenarian who had the longest confirmed lifespan in human history. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, death, etc.
Victor Grignard's FAQ
What is Victor Grignard birthday?
Victor Grignard was born at 1871-05-06
When was Victor Grignard died?
Victor Grignard was died at 1935-12-13
Where was Victor Grignard died?
Victor Grignard was died in Lyon, France
Which age was Victor Grignard died?
Victor Grignard was died at age 64
Where is Victor Grignard's birth place?
Victor Grignard was born in Cherbourg-Octeville, France
What is Victor Grignard nationalities?
Victor Grignard's nationalities is French
Who is Victor Grignard spouses?
Victor Grignard's spouses is Augustine Marie Boulant
What was Victor Grignard universities?
Victor Grignard studied at University of Lyon
What is Victor Grignard's sun sign?
Victor Grignard is Taurus
How famous is Victor Grignard?
Victor Grignard is famouse as Chemist