Thomas Kuhn - Physicists, Life Achievements and Facts
Thomas Kuhn's Personal Details
Thomas Kuhn was a philosopher of science who changed the way the world perceived and envisioned science
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | July 18, 1922 |
| Died on | June 17, 1996 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Harvard University, Scientists, Physicists |
| Spouses | Jehane Kuhn |
| Known as | Thomas Samuel Kuhn |
| Childrens | Elizabeth Kuhn, Nathaniel Kuhn, Sarah Kuhn |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Cincinnati |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Samuel L. Kuhn |
| Sun Sign | Cancer |
| Born in | Cincinnati |
| Famous as | Physicist |
| Died at Age | 73 |
// Famous Harvard University
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin
Bertil Gotthard Ohlin was a famous Swedish economist. This biography profiles his childhood, family life & achievements.
Xi Mingze
Xi Mingze is the daughter of Chinese Leader Xi Jinping, Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Susan Sontag
Susan Sontag is an American critical essayist, cultural analyst, novelist, political activist, filmmaker and playwright of international repute. Read on to find out more about her childhood, career, profile and timeline.
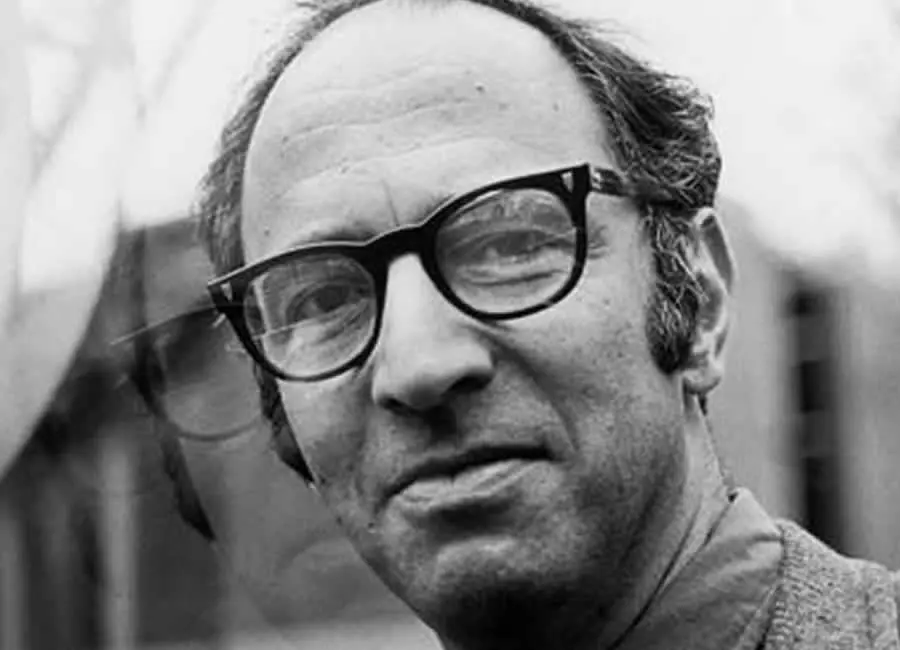
Thomas Kuhn's photo
Who is Thomas Kuhn?
One of the most influential ‘philosophers of science’ of the 20th century, Thomas Kuhn is regarded as the man who changed the way the world perceived and envisioned science. His book, ‘The Structure of Scientific Revolutions’ was a landmark publication that generated worldwide discussions and debates among scholarly communities. It is also one of the most cited academic books, often referred to by scientific guilds and student communities. He is credited with coining the term, ‘Paradigm Shift’, which today, has become an integral part of English and scientific terminology. His impact has been felt in all academic fields, including the field of science, education theory and research. His contribution to the philosophy of science has inspired various student bodies and has influenced more than one billion readers and researchers at large. His works have so far, laid the foundation for many aspiring researchers who plan to pursue a study of the philosophy of science in the future. He is credited for the accurate representation of science and for introducing a new method towards approaching this branch of study.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Thomas Kuhn was born to Minette Scroock Kuhn and Samuel L. Kuhn in Cincinnati, Ohio. He attended the Hessian Hills School in New York, a liberal school that encouraged students to think independently.
He discovered his passion for physics and mathematics at The Taft School in Watertown, from where he graduated, in 1940.
In 1943, he graduated from Harvard University with a B.S in Physics. He also obtained a M.S. and Ph.D. degree from the Harvard University in 1946 and 1949, respectively.
He was a ‘Harvard Junior Fellow’ for three years and this phase played a crucial role in shaping his future. It was here that he decided to switch from physics to history and philosophy of science.
Career
Thomas Kuhn began his career with the Radio Research Laboratory at Harvard and the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development in Europe, where he worked with the radar team.
After he graduated, he taught ‘History of Science’ at Harvard University, from 1948 to 1956, at the suggestion of the University President, James Conant.
In 1957, he refuted the claims of other prominent scientists and stated that the earth was at the centre of the Solar System, in his book, ‘The Copernican Revolution’.
In 1961, he was appointed as the Professor of ‘the History of Science’ at the University of California, where he was part of both, the philosophy department and the history department.
In 1962, his influential work, ‘The Structure of Scientific Revolutions’ was published, which was first published as part of the ‘Foundations of the Unity of Science’ series. In these works, he stated that competing paradigms are frequently incommensurable.
He proposed the notion of ‘paradigm shifts’ and indicated that scientific fields undergo periodic shifts and do not progress in a linear and continuous pattern.
In 1964, he became the ‘M. Taylor Pyne Professor’ of Philosophy and History of Science at Princeton University.
In 1977, ‘The Essential Tension’, a collection of his essays on philosophy and the history of science, was published.
From 1979 to 1991, he was the ‘Laurance S. Rockefeller Professor of Philosophy’, at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
His second historical monograph on the early history of quantum mechanics, ‘Black-Body Theory and the Quantum Discontinuity’ was published, in 1988.
At the time of his death in 1996, he was working on his second philosophical monograph that dealt with, ‘evolutionary conception of scientific change’ and ‘concept acquisition in developmental psychology’.
Major Works
‘The Copernican Revolution’, published in 1957, analyses the 16th century Scientific Revolution and the Ptolemaic understanding of the solar system. This went on to become a best-seller.
His 1962 book, ‘The Structure of Scientific Revolutions’, is regarded as one of the most influential and frequently cited academic books, in which he introduced the term, ‘ paradigm shift’. The Times Literary Supplement, London, labelled it as one of ‘The Hundred Most Influential Books Since the Second World War’. The book sold one million copies by the mid-1990s and was translated into sixteen languages.
Awards & Achievements
Thomas Kuhn was elected to the esteemed ‘Society of Fellows’ at Harvard University.
In 1954, he was conferred the prestigious title of ‘Guggenheim Fellow’.
In 1982, the History of Science Society awarded him the ‘George Sarton Medal’.
Personal Life & Legacy
Thomas Kuhn married Kathryn Muhs and the couple had three children. He later got married to Jehane Barton Burns.
He was diagnosed with lung cancer in 1994, which ultimately claimed his life.
In his honor ‘Thomas Kuhn Paradigm Shift Award’ is awarded by the American Chemical Society to people who offer original views contradictory to mainstream science.
Trivia
This physicist was accused of plagiarism, for his book, ‘The Structure of Scientific Revolutions’.
This famous physicist and scientific philosopher introduced the term, ‘normal science’ and defined it to be cumulative and also stated that its main goal was precision and focus on details.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Thomas Kuhn's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | 1982 - George Sarton Medal | |
Thomas Kuhn biography timelines
- // 18th Jul 1922Thomas Kuhn was born to Minette Scroock Kuhn and Samuel L. Kuhn in Cincinnati, Ohio. He attended the Hessian Hills School in New York, a liberal school that encouraged students to think independently.
- // 1940He discovered his passion for physics and mathematics at The Taft School in Watertown, from where he graduated, in 1940.
- // 1943In 1943, he graduated from Harvard University with a B.S in Physics. He also obtained a M.S. and Ph.D. degree from the Harvard University in 1946 and 1949, respectively.
- // 1948 To 1956After he graduated, he taught ‘History of Science’ at Harvard University, from 1948 to 1956, at the suggestion of the University President, James Conant.
- // 1957In 1957, he refuted the claims of other prominent scientists and stated that the earth was at the centre of the Solar System, in his book, ‘The Copernican Revolution’.
- // 1961In 1961, he was appointed as the Professor of ‘the History of Science’ at the University of California, where he was part of both, the philosophy department and the history department.
- // 1962In 1962, his influential work, ‘The Structure of Scientific Revolutions’ was published, which was first published as part of the ‘Foundations of the Unity of Science’ series. In these works, he stated that competing paradigms are frequently incommensurable.
- // 1964In 1964, he became the ‘M. Taylor Pyne Professor’ of Philosophy and History of Science at Princeton University.
- // 1966At the time of his death in 1996, he was working on his second philosophical monograph that dealt with, ‘evolutionary conception of scientific change’ and ‘concept acquisition in developmental psychology’.
- // 1977In 1977, ‘The Essential Tension’, a collection of his essays on philosophy and the history of science, was published.
- // 1979 To 1991From 1979 to 1991, he was the ‘Laurance S. Rockefeller Professor of Philosophy’, at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- // 1988His second historical monograph on the early history of quantum mechanics, ‘Black-Body Theory and the Quantum Discontinuity’ was published, in 1988.
- // 1994He was diagnosed with lung cancer in 1994, which ultimately claimed his life.
// Famous Cancer Celebrities peoples
Jacob Elordi
Jacob Elordi is an Australian actor. Let’s take a look at his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Riele Downs
Riele Downs is a Canadian-American actress & Musical.ly star. Let’s take a look at her family and personal life including age, birthday, net worth, boyfriends and fun facts.
Yammy Xox
Check out all that you wanted to know about Yammy Xox, the famous British YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Kaylee Quinn
Kaylee Quinn is an American dancer, model, and actress. Let’s have a look at her family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, relationships, and fun facts.
Sophia Montero
Sophia Montero is an American singer and YouTuber. Let’s have a look at her family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, relationships, and fun facts.
Domo Wilson
Check out all that you wanted to know about Domo Wilson, the famous American Vlogger & YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, fun trivia facts and more.
Thomas Kuhn's FAQ
What is Thomas Kuhn birthday?
Thomas Kuhn was born at 1922-07-18
When was Thomas Kuhn died?
Thomas Kuhn was died at 1996-06-17
Where was Thomas Kuhn died?
Thomas Kuhn was died in Cambridge
Which age was Thomas Kuhn died?
Thomas Kuhn was died at age 73
Where is Thomas Kuhn's birth place?
Thomas Kuhn was born in Cincinnati
What is Thomas Kuhn nationalities?
Thomas Kuhn's nationalities is American
Who is Thomas Kuhn spouses?
Thomas Kuhn's spouses is Jehane Kuhn
Who is Thomas Kuhn childrens?
Thomas Kuhn's childrens is Elizabeth Kuhn, Nathaniel Kuhn, Sarah Kuhn
What was Thomas Kuhn universities?
Thomas Kuhn studied at Harvard University, Harvard University
What was Thomas Kuhn notable alumnis?
Thomas Kuhn's notable alumnis is Harvard University
Who is Thomas Kuhn's father?
Thomas Kuhn's father is Samuel L. Kuhn
What is Thomas Kuhn's sun sign?
Thomas Kuhn is Cancer
How famous is Thomas Kuhn?
Thomas Kuhn is famouse as Physicist