Richard J. Roberts - Biochemists, Family and Life
Richard J. Roberts's Personal Details
Richard J
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | September 6, 1943 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Atheists, University Of Sheffield, Scientists, Molecular Biologists, Biochemists |
| Spouses | Jean |
| Known as | Sir Richard John Roberts |
| Childrens | Alison, Amanda, Andrew, Christopher |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Derby, England, |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | John Roberts |
| Mother | Edna Allsop |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Derby, England, |
| Famous as | Biochemist, Molecular Biologist |
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
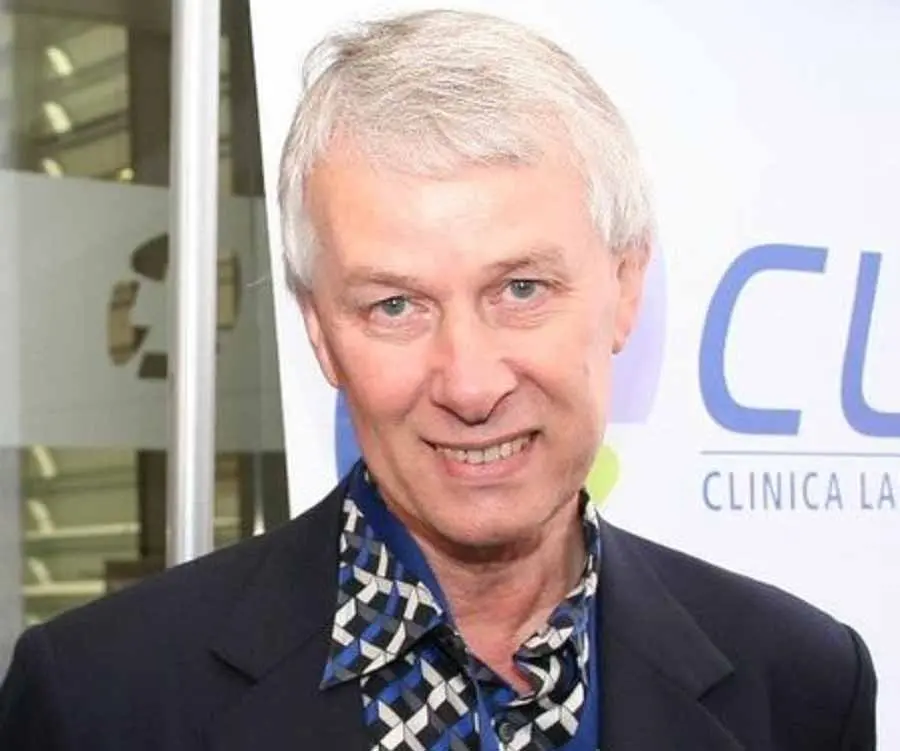
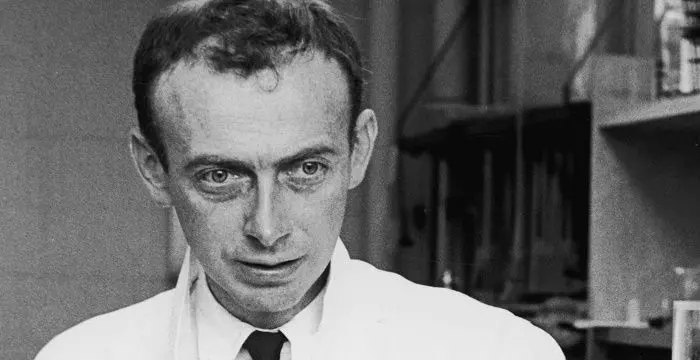
Richard J. Roberts's photo
Who is Richard J. Roberts?
Richard John Roberts is an English biochemist and molecular biologist who was felicitated with Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of the mechanism of gene-splicing. He shared the prize with Philip Sharp who independently carried out similar work in the field. Roberts’ fantasy with chemistry started as early as in high school. He was so interested by the subject that he chose to make it his career. Following his graduate studies and doctoral thesis, Roberts made his way to Harvard and eventually the Cold Harbor Laboratory. It was at the laboratory that Roberts first found success in restriction enzymes. By 1972, he discovered or characterized almost three quarter of the world’s first restriction enzymes. Later in 1977, Roberts demonstrated how RNA can be divided up into introns and exons, after which the exons can be joined together. The discovery was crucial as until then the scientific world believed that genes comprised of unbroken sketches of DNA. The discovery had important implication for the study of genetic diseases. Furthermore, it allowed different parts of the gene to be brought together in new combinations.
// Famous Molecular Biologists
Susumu Tonegawa
Susumu Tonegawa is a Japanese molecular biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1987. This biography of Susumu Tonegawa provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
James Watson
James Watson is an American molecular biologist and geneticist who played a crucial role in the discovery of the molecular structure of D.N.A. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Francis Crick
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist, who received the Nobel Prize for Medicine. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Richard John Roberts was born on September 6, 1943 in Derby, England, to Edna Allsop and John Roberts. His father was an auto mechanic by profession while his mother was a homemaker.
When young Robert was just four, the family shifted to Bath. There, he attended the Christ Church infant school and later St Stephen’s Boys’ School. It was at Stephen’s that Roberts developed a passion for logic and mathematics. He was encouraged by his headmaster, Mr Broakes who would spend hours producing problems and later helping Roberts solve them.
Completing his elementary studies, he attended City of Bath Boys’ School. Early on, Robert aimed at becoming a detective but when he was handed a chemistry play set, he changed his mind. His chemistry play set was transformed into a large in-house chemistry laboratory that comprised of real apparatus and chemicals. He soon found his real calling in chemistry.
Following his preliminary education, he enrolled at the University of Sheffield. He graduated from the same with a Bachelor of Science degree in Chemistry in 1965. Four years later, he attained his PhD in the subject, his thesis being in phytochemical studies of neoflavonoids and isoflavonoids.
Career
While doing his Ph.D, Richard J. Roberts came across a book by John Kendrew that turned his focus to molecular biology. The book detailed the early history of crystallography and molecular biology focussing on MRC Laboratory in Cambridge.
For postdoctoral studies, Roberts looked for a laboratory that would provide him the pathway into molecular biology. At Harvard, Jack Strominger offered him an opportunity. He engaged himself in the research work from 1969 to 1972.
In September 1972, he moved to Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory where he worked under James Dewey Watson, co-discoverer of the structure of DNA. Same year, he attended a seminar by Dan Nathans who described an enzyme Endonuclease R that could cleave DNA into specific pieces. Roberts realized that Nathans' restriction enzyme gave an immediate way to isolate small DNA molecules.
At Cold Harbor Laboratory, he made preparations of Endonuclease R and the few other restriction enzymes known then. By 1973, he had found superlative success in restriction enzyme. Almost three quarter of the world’s first restriction enzymes were discovered or characterized under his guidance. He had complied an enzyme collection that proved to be a valuable resource for scientists around the world.
In 1974, Roberts was joined by Richard Gelinas to characterize the initiation and termination signals for an Adenovirus-2mRNA. The main purpose was to sequence the 5'-end of an mRNA, map its location on a restriction fragment, and then sequence the upstream region. Just before beginning the project, mRNA caps were discovered. The duo developed an assessment of the capped oligonucleotides.
While working on the initiation and termination signals of Adenovirus-2mRNA, Roberts and Gelinas found that all late mRNAs seemed to begin with the same capped oligonucleotide, which was not encoded on the DNA next to the main body of the mRNA. Though they had biochemical evidence for the same, they did not have real proof.
In March 1977, Roberts came up with the experiment that displayed the proposed split structure for Adenovirus-2mRNAs was accurate. Soon, the duo was joined by Louise Chow and Tom Broker. The four scientists aimed at visualizing the split structure by hybridizing an intact mRNA to its two different coding regions. Eventually, they came up with appropriate DNA fragments that were visible as split genes in the electron microscope.
Before the discovery made by Roberts, scientists believed that genes consisted of unbroken stretches of DNA, all of which encoded protein structure. However, with his discovery, it was found that the discontinuous gene structure is the most common structure found in higher organisms (eukaryotes). In addition to having important implications for the study of genetic diseases, this structure is believed to drive evolution by allowing information from different parts of the gene to be brought together in new combinations.
In 1992, Roberts moved to New England Biolabs. Don Cromb, founder and president of the establishment, had started the establishment mainly to produce restriction enzymes for commercial sale. Roberts started off as a chief consultant at the establishment and was no soon promoted as a joint Research Director.
Major Works
Richard J. Roberts’ most distinguished work came in 1970s when he successfully discovered split genes. The discovery was crucial and important in the scientific world as until then, scientists believed that the genes consisted of unbroken stretches of DNA, of which encoded protein structure. It was Roberts who established the discontinuous gene structure. Through his experiments, he proved that the segments of DNA that code for proteins are interrupted by lengthy stretches of DNA that do not contain genetic information. He demonstrated how RNA can be divided up into introns and exons, after which the exons can be joined together. This can occur in different ways, giving a gene the potential to form a number of different proteins.
Awards & Achievements
In 1993, Richard J. Roberts and Phillip A. Sharp were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries of split genes". Sharp worked independently on the subject
He was conferred with an Honorary Doctor of Science Degree by the University of Bath in 1994.
In 1995, he was elected Fellow of the Royal Society. .
Personal Life & Legacy
Roberts married Jean and has four children, namely Alison, Andrew, Christopher and Amanda.
In 2005, the chemistry department at his alma mater, University of Sheffield, was later named after him.
// Famous University Of Sheffield
David Blunkett
David Blunkett is a British Labour Party politician who became the first blind person to hold a ministerial position in Great Britain. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jessica Ennis-Hill
Jessica Ennis-Hill is a retired English track and field athlete. This biography profiles her childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, records, etc.
Richard J. Roberts's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1993) | |
| 0 | FRS (1995) | |
| 0 | Knight Bachelor (2008) | |
Richard J. Roberts biography timelines
- // 6th Sep 1943Richard John Roberts was born on September 6, 1943 in Derby, England, to Edna Allsop and John Roberts. His father was an auto mechanic by profession while his mother was a homemaker.
- // 1965Following his preliminary education, he enrolled at the University of Sheffield. He graduated from the same with a Bachelor of Science degree in Chemistry in 1965. Four years later, he attained his PhD in the subject, his thesis being in phytochemical studies of neoflavonoids and isoflavonoids.
- // 1969 To 1972For postdoctoral studies, Roberts looked for a laboratory that would provide him the pathway into molecular biology. At Harvard, Jack Strominger offered him an opportunity. He engaged himself in the research work from 1969 to 1972.
- // Sep 1972In September 1972, he moved to Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory where he worked under James Dewey Watson, co-discoverer of the structure of DNA. Same year, he attended a seminar by Dan Nathans who described an enzyme Endonuclease R that could cleave DNA into specific pieces. Roberts realized that Nathans' restriction enzyme gave an immediate way to isolate small DNA molecules.
- // 1973At Cold Harbor Laboratory, he made preparations of Endonuclease R and the few other restriction enzymes known then. By 1973, he had found superlative success in restriction enzyme. Almost three quarter of the world’s first restriction enzymes were discovered or characterized under his guidance. He had complied an enzyme collection that proved to be a valuable resource for scientists around the world.
- // 1974In 1974, Roberts was joined by Richard Gelinas to characterize the initiation and termination signals for an Adenovirus-2mRNA. The main purpose was to sequence the 5'-end of an mRNA, map its location on a restriction fragment, and then sequence the upstream region. Just before beginning the project, mRNA caps were discovered. The duo developed an assessment of the capped oligonucleotides.
- // Mar 1977In March 1977, Roberts came up with the experiment that displayed the proposed split structure for Adenovirus-2mRNAs was accurate. Soon, the duo was joined by Louise Chow and Tom Broker. The four scientists aimed at visualizing the split structure by hybridizing an intact mRNA to its two different coding regions. Eventually, they came up with appropriate DNA fragments that were visible as split genes in the electron microscope.
- // 1992In 1992, Roberts moved to New England Biolabs. Don Cromb, founder and president of the establishment, had started the establishment mainly to produce restriction enzymes for commercial sale. Roberts started off as a chief consultant at the establishment and was no soon promoted as a joint Research Director.
- // 1993In 1993, Richard J. Roberts and Phillip A. Sharp were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries of split genes". Sharp worked independently on the subject
- // 1994He was conferred with an Honorary Doctor of Science Degree by the University of Bath in 1994.
- // 1995In 1995, he was elected Fellow of the Royal Society. .
- // 2005In 2005, the chemistry department at his alma mater, University of Sheffield, was later named after him.
// Famous Biochemists
Robert Huber
Robert Huber is a German biochemist and Nobel Laureate. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Charles Best
Charles Best was a great scientist and a renowned physiologist who is remembered for being the co-discoverer of insulin. Read this biography to learn about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov was an American professor of biochemistry and a renowned author of science fiction and popular science books. Read this biography to know more about his life.
Gerty Cori
Gerty Theresa Cori was a Nobel Prize winning biochemist who discovered the catalytic conversion of glycogen. To know more about her childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Severo Ochoa
Severo Ochoa was a Spanish physician and biochemist who won the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. This biography of Louis Pasteur provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Richard J. Roberts's FAQ
What is Richard J. Roberts birthday?
Richard J. Roberts was born at 1943-09-06
Where is Richard J. Roberts's birth place?
Richard J. Roberts was born in Derby, England,
What is Richard J. Roberts nationalities?
Richard J. Roberts's nationalities is British
Who is Richard J. Roberts spouses?
Richard J. Roberts's spouses is Jean
Who is Richard J. Roberts childrens?
Richard J. Roberts's childrens is Alison, Amanda, Andrew, Christopher
What was Richard J. Roberts universities?
Richard J. Roberts studied at University Of Sheffield
What was Richard J. Roberts notable alumnis?
Richard J. Roberts's notable alumnis is University Of Sheffield
Who is Richard J. Roberts's father?
Richard J. Roberts's father is John Roberts
Who is Richard J. Roberts's mother?
Richard J. Roberts's mother is Edna Allsop
What is Richard J. Roberts's sun sign?
Richard J. Roberts is Virgo
How famous is Richard J. Roberts?
Richard J. Roberts is famouse as Biochemist, Molecular Biologist