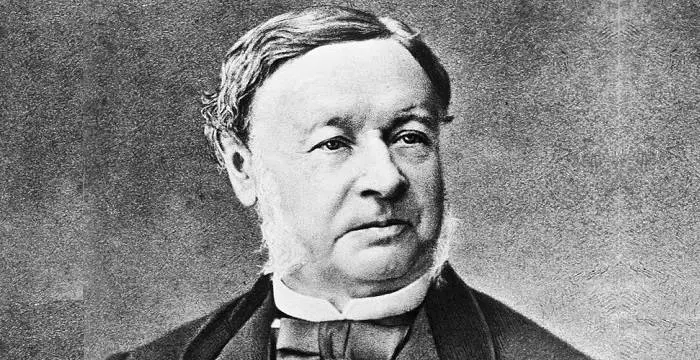Philip Allen Sharp - Scientists, Timeline and Childhood
Philip Allen Sharp's Personal Details
Philip Allen Sharp is an American geneticist and molecular biologist who co-discovered RNA splicing
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | June 6, 1944 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Scientists, Biologists, Geneticists, Molecular Biologists |
| Spouses | Ann Holcombe |
| Birth Place | Falmouth, Kentucky |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Joseph Sharp |
| Mother | Katherine Sharp |
| Sun Sign | Gemini |
| Born in | Falmouth, Kentucky |
| Famous as | Geneticist, Molecular Biologist |
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
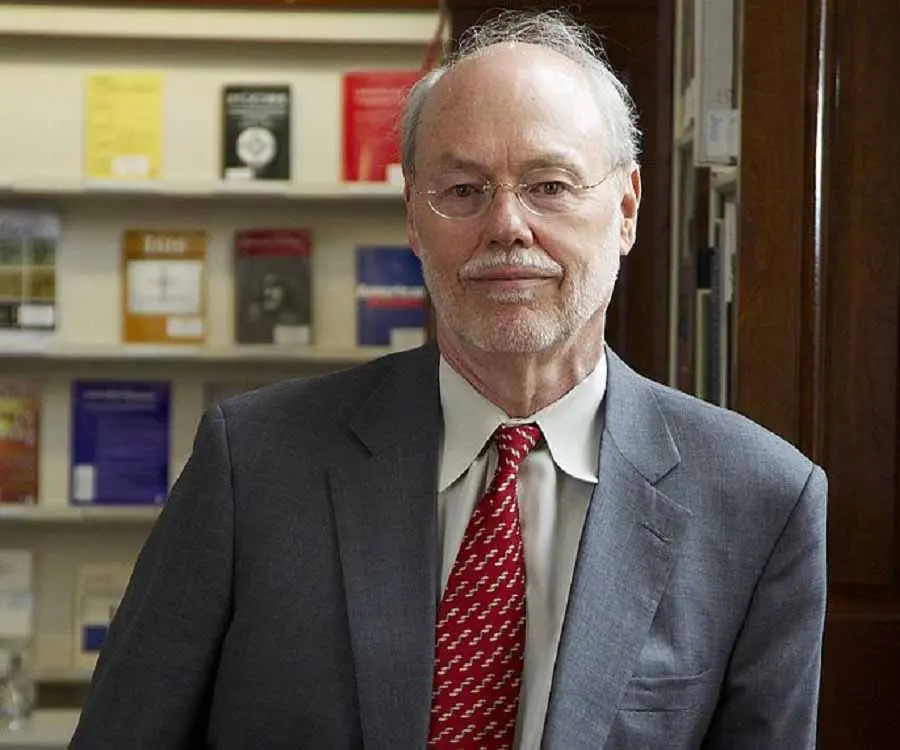
Philip Allen Sharp's photo
Who is Philip Allen Sharp?
Philip Allen Sharp is an American geneticist and molecular biologist won the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for co-discovering RNA splicing. He shared the prize with Richard J Roberts; the two scientists worked independently on the subject. The duo discovered that individual genes are often interrupted by long sections of DNA that do not encode protein structure. The discovery was crucial as it crushed the age-old belief that genes were continuous stretches of DNA that served as direct templates for mRNA in the assembly of proteins. Sharp’s scientific career began when he pursued a doctorate in chemistry from University of Illinois. Having gained his PhD, he started working at the California Institute of Technology before moving to Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. In 1971, he joined the Center for Cancer Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology where he conducted his prize-winning research. For his outstanding and noteworthy scientific career, he was bestowed with numerous awards and prizes.
// Famous Geneticists
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
George Wells Beadle
George Wells Beadle was an American geneticist who won the 1958 Nobel Prize in Medicine. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian scientist and monk credited with being the father of modern genetics for his pioneering work in the study of heredity. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Philip Allen Sharp was born on June 6, 1944, to Katherine and Joseph Sharp, in Falmouth, Kentucky.
He gained his early education from an array of public schools in Pendleton County. He started off by studying at McKinneysburg Elementary School. Later, he enrolled in Butler Elementary and High School, finishing off his higher education from Pendleton County High School.
On the insistence of his parents, he enrolled at the Union College, a liberal arts school in eastern Kentucky, majoring in chemistry and mathematics. Upon completing his graduation, he decided to study further and enrolled at the University of Illinois.
In 1969, he completed his PhD in chemistry from the University of Illinois. His thesis centred on the description of DNA as a polymer using statistical and physical theories.
Career
While studying for his PhD, Philip Allen Sharp chanced upon reading the 1966 volume of ‘The Genetic Code’. The work propelled his interest in molecular biology and genetics. Resultantly, he did his postdoctoral training at the California Institute of Technology in a research program in molecular biology. He studied plasmids, how they acquired genomic sequences from the bacterial chromosome.
Following his end of term at Caltech, he extended his postdoctoral period, studying the structure and pathway of expression of genes in human cells. He later moved to Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory where he furthered his postdoctoral studies under the guidance of Jim Watson. He worked there as a senior scientist.
At Cold Spring Laboratory, he collaborated with Joe Sambrook to map sequences in the simian virus 40 genome that were expressed as stable RNAs in both infected cells and oncogenic cells transformed by this virus using hybridization techniques. The result of the research was important as it assisted in the understanding of the biology of the papovavirus.
At Cold Spring Laboratory, he befriended Ulf Pettersson, who was an expert in the growth of human adenovirus. Together, the two discovered various unknown facts about adenovirus, beginning with the fact that only one specific fragment of the genome, the E1 region, was responsible for oncogenic transformation. They also found that restriction endonuclease length polymorphism could be utilized to generate genetic maps. They also found the mapping of specific genes on the viral genome; and generation of a viral map of sequences expressed as stable RNAs.
In 1974, biologist Salvador Luria offered Sharp a position at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He joined MIT's Center for Cancer Research, which is now known as the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research.
Sharp was accompanied by Jane Flint at the MIT, where the duo focussed on quantitating the levels of RNA from all parts of the genome in the nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments of the cell.
After much experimentation, Sharp and Flint concluded that nuclei of cells productively infected by adenovirus contained abundant sets of viral RNAs which were not transported to the cytoplasm. They believed that the long nuclear RNAs were processed to generate the cytoplasmic mRNAs. They in turn compared the relative structures of nuclear precursor RNA and cytoplasmic mRNA from the adenovirus genome.
In 1977, he and his team discovered that the messenger RNA of an adenovirus corresponded to four separate, discontinuous segments of DNA. They realised that the segments of DNA that coded for proteins (exons) were separated by long stretches of DNA (introns) that did not contain genetic information. Interestingly, Richard J Roberts also came up with a similar finding though independently.
The discovery made by Sharp and Roberts thwarted the age-old belief that genes were continuous stretches of DNA that served as direct templates for mRNA in the assembly of proteins. Instead, it was found that discontinuous gene structure is the most common one found in eukaryotes, among which are all higher organisms, including humans. The discovery earned them Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
In 1985, Sharp was appointed Director of MIT’s Center for Cancer Research, a position he served until 1991. From 1991, he was made head of the Biology Department until 1999.
Following his stint at MIT, in 2000, he took up directorship at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research, serving in the position until 2004.
Currently, he serves as a professor of Biology and member of the Koch Institute. Since 1999, he has been an Institute Professor.
In addition to his scientific research work, Sharp is the cofounder of Biogen, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, and Magen Biosciences. At Biogen, the scientists developed agents to treat hairy cell leukaemia and certain autoimmune disorders. Following his work on introns and splicing, Sharp began investigating the role of RNA in controlling genes. This led to his involvement as a cofounder for Alnylam Pharmaceuticals.
Major Works
Philip Allen Sharp’s most extraordinary work came in the latter half of the 1970s. In 1977, he demonstrated how RNA can be divided up into introns (elements not needed for protein formation) and exons (elements needed for protein formation), after which the exons can be joined together. This can occur in different ways, giving a gene the potential to form a number of different proteins.
Awards & Achievements
Together with Thomas R Cech, he won the 1988 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize from Columbia University. In the same year, he also won the Albert Lasker Basic Medican Research Award.
In 1993, Sharp received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of split genes. He shared the prize with Richard J Roberts.
In 1999, he won the Benjamin Franklin Medal for Distinguished Achievement in the Sciences of the American Philosophical Society.
In 2011, he was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS). Following year, he was elected the president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
In 2015, he received the Othmer Gold Medal.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married Ann Holcombe in 1964. The couple is blessed three daughters. Ann works as a preschool teacher in Newtown, Massachusetts.
A middle school in his hometown, Pendleton County, Kentucky has been named after this Nobel Laureate molecular biologist.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Philip Allen Sharp's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize (1993) | |
| 0 | National Medal of Science (2004) | |
| 0 | NAS Award in Molecular Biology (1980) | |
| 0 | Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize (1988) | |
| 0 | Dickson Prize (1991) | |
Philip Allen Sharp biography timelines
- // 6th Jun 1944Philip Allen Sharp was born on June 6, 1944, to Katherine and Joseph Sharp, in Falmouth, Kentucky.
- // 1964He married Ann Holcombe in 1964. The couple is blessed three daughters. Ann works as a preschool teacher in Newtown, Massachusetts.
- // 1966While studying for his PhD, Philip Allen Sharp chanced upon reading the 1966 volume of ‘The Genetic Code’. The work propelled his interest in molecular biology and genetics. Resultantly, he did his postdoctoral training at the California Institute of Technology in a research program in molecular biology. He studied plasmids, how they acquired genomic sequences from the bacterial chromosome.
- // 1969In 1969, he completed his PhD in chemistry from the University of Illinois. His thesis centred on the description of DNA as a polymer using statistical and physical theories.
- // 1974In 1974, biologist Salvador Luria offered Sharp a position at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He joined MIT's Center for Cancer Research, which is now known as the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research.
- // 1977In 1977, he and his team discovered that the messenger RNA of an adenovirus corresponded to four separate, discontinuous segments of DNA. They realised that the segments of DNA that coded for proteins (exons) were separated by long stretches of DNA (introns) that did not contain genetic information. Interestingly, Richard J Roberts also came up with a similar finding though independently.
- // 1985 To 1999In 1985, Sharp was appointed Director of MIT’s Center for Cancer Research, a position he served until 1991. From 1991, he was made head of the Biology Department until 1999.
- // 1988Together with Thomas R Cech, he won the 1988 Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize from Columbia University. In the same year, he also won the Albert Lasker Basic Medican Research Award.
- // 1993In 1993, Sharp received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of split genes. He shared the prize with Richard J Roberts.
- // 1999Currently, he serves as a professor of Biology and member of the Koch Institute. Since 1999, he has been an Institute Professor.
- // 1999In 1999, he won the Benjamin Franklin Medal for Distinguished Achievement in the Sciences of the American Philosophical Society.
- // 2000 To 2004Following his stint at MIT, in 2000, he took up directorship at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research, serving in the position until 2004.
- // 2011In 2011, he was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS). Following year, he was elected the president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
- // 2015In 2015, he received the Othmer Gold Medal.
// Famous Molecular Biologists
Susumu Tonegawa
Susumu Tonegawa is a Japanese molecular biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1987. This biography of Susumu Tonegawa provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
James Watson
James Watson is an American molecular biologist and geneticist who played a crucial role in the discovery of the molecular structure of D.N.A. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Francis Crick
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist, who received the Nobel Prize for Medicine. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert is an American biochemist and physicist who won a share of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980. This biography of Walter Gilbert provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Sidney Altman
Sidney Altman is a Canadian-American molecular biologist who was bestowed with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1989. This biography explores his childhood, life, research career, achievements and timeline.
Arthur Kornberg
Arthur Kornberg was an American biochemist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959. This biography of Arthur Kornberg provides detailed information about his childhood, life, career, research, achievements and timeline.
Philip Allen Sharp's FAQ
What is Philip Allen Sharp birthday?
Philip Allen Sharp was born at 1944-06-06
Where is Philip Allen Sharp's birth place?
Philip Allen Sharp was born in Falmouth, Kentucky
What is Philip Allen Sharp nationalities?
Philip Allen Sharp's nationalities is American
Who is Philip Allen Sharp spouses?
Philip Allen Sharp's spouses is Ann Holcombe
Who is Philip Allen Sharp's father?
Philip Allen Sharp's father is Joseph Sharp
Who is Philip Allen Sharp's mother?
Philip Allen Sharp's mother is Katherine Sharp
What is Philip Allen Sharp's sun sign?
Philip Allen Sharp is Gemini
How famous is Philip Allen Sharp?
Philip Allen Sharp is famouse as Geneticist, Molecular Biologist