Arthur Kornberg - Molecular Biologists, Timeline and Childhood
Arthur Kornberg's Personal Details
Arthur Kornberg was an American biochemist
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | March 3, 1918 |
| Died on | October 26, 2007 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Scientists, Molecular Biologists, Biochemists |
| Spouses | Carolyn Frey Dixon (1998–2007; his death), Charlene Walsh Levering (1988–1995; her death), Sylvy Ruth Levy (1943–1986; her death; 3 children) |
| Birth Place | New York City, United States |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Joseph |
| Mother | Lena (née Katz) Kornberg |
| Sun Sign | Pisces |
| Born in | New York City, United States |
| Famous as | Biochemist |
| Died at Age | 89 |
// Famous Molecular Biologists
Susumu Tonegawa
Susumu Tonegawa is a Japanese molecular biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1987. This biography of Susumu Tonegawa provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
James Watson
James Watson is an American molecular biologist and geneticist who played a crucial role in the discovery of the molecular structure of D.N.A. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Francis Crick
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist, who received the Nobel Prize for Medicine. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
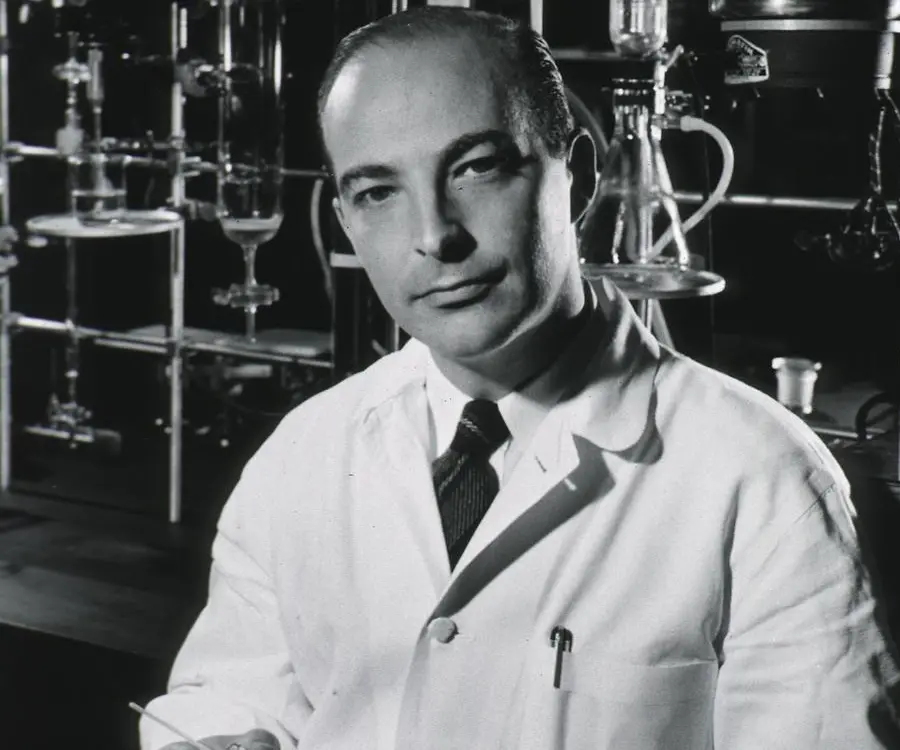
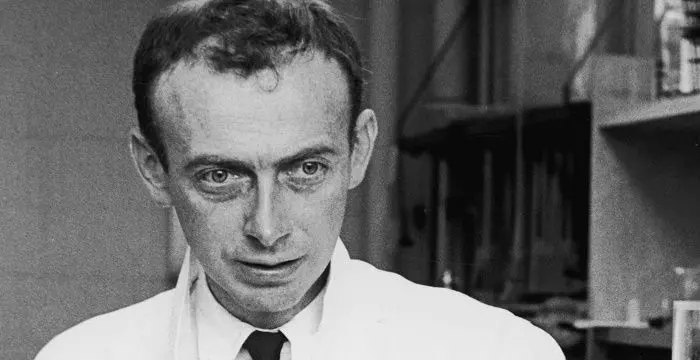
Arthur Kornberg's photo
Who is Arthur Kornberg?
Arthur Kornberg was an American biochemist, born in New York City in early twentieth century. His parents, who came to the USA at the turn of the century from Austrian Galicia, were not-so-well-off traders. Kornberg began his education at a public school and funded his college education with the help of scholarships. His initial aim was to become a doctor, but while studying for his medical degree, he began to take interest in research and started a survey to see if jaundice was common among medical students. The paper, which was published a year after he earned his MD, caught the attention of the Director of National Institutes of Health. On his invitation, Kornberg joined NIH and served there for eleven years; in-between he took breaks to update his knowledge on enzymes. Later he began his teaching career as a professor at Washington University, but continued with his research. Here he was able to isolate DNA polymerizing enzyme, which earned him Nobel Prize three years later. Later he shifted to the University of Stanford and remained there for rest of his life. He was also socially very aware and lent his name to relevant movements.
// Famous Biochemists
Robert Huber
Robert Huber is a German biochemist and Nobel Laureate. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Charles Best
Charles Best was a great scientist and a renowned physiologist who is remembered for being the co-discoverer of insulin. Read this biography to learn about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov was an American professor of biochemistry and a renowned author of science fiction and popular science books. Read this biography to know more about his life.
Childhood & Early Life
Arthur Kornberg was born on March 3, 1918 in Brooklyn, New York City. His parents, Joseph and Lena (née Katz) Kornberg, were Jewish emigrants from Austrian Galicia, now part of Poland.
Arthur's father, Joseph Kornberg, did not have any formal education, but could speak at least six languages. In New York, he operated a sweet shop, but later as his health failed, he opened a hardware store. When Arthur turned nine, he began to lend a helping hand at the store.
An exceptionally bright student from the start, Arthur studied at Abraham Lincoln High School at Brooklyn, graduating from there in 1933. Upon receiving a scholarship he next enrolled in premedical course at City College, New York with biology and chemistry as his major.
He received his B. Sc. degree in 1937. He then joined University of Rochester Medical Center for his medical degree and received his MD in 1941. Here he began to develop interest in medical research.
Kornberg suffered from a hereditary genetic condition called Gilbert syndrome and his blood contained a slightly higher level of bilirubin. It made him susceptible to jaundice. While studying at the medical school, he began to take survey of his fellow students, trying to establish how common the syndrome was.
Career
Upon receiving his medical degree in 1941, Kornberg entered Strong Memorial Hospital in Rochester for his internship, and completed the same in 1942. Subsequently, he joined the United States Coast Guard as a Lieutenant, serving as a ship's doctor, as part of his military service.
In 1942, he published the result of his above mentioned survey. Titled, ‘The Occurrence of Jaundice in an Otherwise Normal Medical Student’, it caught the attention of Rolla Dyer, the Director of National Institute of Health, who invited him to join his research team at the Nutritional Laboratory.
Kornberg took up this opportunity and joined National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland. Here he was assigned to the Nutrition Section of its Physiology Division. His job was to look for new vitamins by feeding rats with specialized diet. He did not find that motivating.
Instead, he developed interest in enzymes. In 1946, he got himself transferred to Dr Severo Ochoa's laboratory at New York University to learn more about enzyme purification techniques. Concurrently, he took summer courses at Columbia University to update his knowledge about organic and physical chemistry.
Next in 1947, Kornberg shifted to Washington University School of Medicine at St. Louis. Here he worked for few months with Carl Ferdinand Cori before returning to NIH at Bethesda.
At NIH, he was assigned to organize the Enzymes and Metabolism Section of the Physiology Division, which he did successfully. Subsequently, he became its Medical Director and served in this capacity until 1953.
During this period, Kornberg mainly concentrated on understanding how Adenosine triphosphate, a nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme, was produced from Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. This work laid the foundation for his later research on DNA.
In 1953, he moved to Washington University in St. Louis as Professor and Head of the Department of Microbiology and remained there until 1959. Here he continued to work on those enzymes, which were deemed necessary for the creation of DNA.
Finally in 1956, he was able to isolate DNA polymerizing enzyme, which later came to be known as DNA polymerase I. Incidentally, it was the first known polymerase. The discovery won him Nobel Prize three years later.
In 1959, Kornberg moved to the University of Stanford as Professor and Executive Head of the Department of Biochemistry and remained there for rest of his working life. Here, he took initiative in establishing a Department of Genetics, mainly to accommodate another Nobel Laurent Joshua Lederberg.
At Stanford, Kornberg continued his research on DNA biosynthesis. In this project he worked in close collaboration with Mehran Goulian. After years of grueling research, they finally announced their success on December 14, 1967.
Along with his work on DNA synthesis, Kornberg also tried to find out how spores store DNA and generate new cells. Although he earned limited success, he eventually abandoned this project.
Kornberg officially retired from his post in 1988. However, he had never ceased working and maintained an active research Laboratory at the University of Stanford until his death.
From 1991 onwards, Kornberg began to focus on the metabolism of inorganic polyphosphate, at that time, regarded as ‘molecular fossil’. Eventually, he found a variety of significant functions for it. For example, he found that it responds to stresses and stringencies; causes motility and virulence in some of the major pathogens.
In addition to his research work, Kornberg pursued teaching career with equal enthusiasm. Many of his students later went on to become internationally famous scientists and earned established awards.
He also p ublished several papers. His books include‘Enzymatic Synthesis of DNA (1961); DNA Synthesis, (1974); ‘DNA Replication’, (1980); ‘For the Love of Enzymes: The Odyssey of a Biochemist’ (1989); DNA Replication (2nd Edition) with Tania A. Baker (1992) and ‘The Golden Helix: Inside Biotech Ventures’ (2002).
Major Works
Kornberg is best remembered for his work on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase. In 1956, he identified DNA Polymerase I (or Pol I) in the intestinal bacterium E coli and recognized it as an essential enzyme for replication, repair and rearrangements of DNA.
He also showed how a single strand of DNA formed new strands of nucleotides and proved that DNA had a double helix structure, as theorized by earlier scientists. This discovery helped to start a biotechnology revolution, which had far reaching consequences.
Synthesis of artificial DNA, which was at the same time biologically active, was another of Kornberg’s major projects. The work not only helped in future studies of genetics, but also helped to provide cures to hereditary diseases and control viral infections.
Award & Achievements
In 1959, Kornberg received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for his “discovery of the mechanisms in the biological synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid". He shared the prize with Dr Severo Ochoa, who had been working on the same topic at the New York University College of Medicine.
Prior to that, Kornberg had received Paul-Lewis Award in Enzyme Chemistry from American Chemical Society in 1951.
In 1968, he received the Scientific Achievement Award of the American Medical Association, the Lucy Wortham James Award of the Society of Medical Oncology and the Borden Award in the Medical Sciences of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
In addition, he had received National Medal of Science in 1979, Cosmos Club Award and Gairdner Foundation Award in 1995.
He was also elected a Fellow of Royal Society. In addition, he was also a member of the National Academy of Sciences and American Philosophical Society. He received innumerable honorary degrees from many established institutions.
Personal Life & Legacy
On November 21, 1943, Kornberg married Sylvy Ruth Levy. She was also a noted biochemist and worked closely with him in the discovery of DNA Polymerase I. Unfortunately, she did not get any recognition for her contribution. She died in 1986, survived by Kornberg and their three sons.
Their eldest son, Roger David Kornberg is a Professor of Structural Biology at the University of Stanford and a Nobel Laureate. In 2006, he received the Nobel Prize for discovering how genetic information from DNA is copied to RNA.
Their second son, Thomas B. Kornberg, is a professor at the University of California, San Francisco and noted for his discovery of DNA polymerase II and III (1970). Their youngest son, Kenneth Andrew Kornberg, is an architect specializing in the design of biomedical and biotechnology laboratories.
Two years after the death of his first wife, Kornberg tied the knot for the second time and in 1988, married Charlene Walsh Levering, who also predeceased him in 1995. In December 1998, he married Carolyn Frey Dixon. They remained married till his death in 2007.
Kornberg died on 26 October, 2007 in Stanford of respiratory failure. He was survived by his third wife Carolyn and three sons.
Many of his children (his students and postdoctoral fellows) and grandchildren (their students) turned out to be intellectuals. Together, they are referred as ‘The Kornberg’s School of Biochemistry’.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Arthur Kornberg's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 1951 | ||
| 0 | National Medal of Science 1979 | |
| 0 | Gairdner Foundation Award 1995 | |
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959 | |
| 0 | Fellow of the Royal Society | |
| 0 | Paul-Lewis Award in Enzyme Chemistry | |
Arthur Kornberg biography timelines
- // 3rd Mar 1918Arthur Kornberg was born on March 3, 1918 in Brooklyn, New York City. His parents, Joseph and Lena (née Katz) Kornberg, were Jewish emigrants from Austrian Galicia, now part of Poland.
- // 1933An exceptionally bright student from the start, Arthur studied at Abraham Lincoln High School at Brooklyn, graduating from there in 1933. Upon receiving a scholarship he next enrolled in premedical course at City College, New York with biology and chemistry as his major.
- // 1937 To 1941He received his B. Sc. degree in 1937. He then joined University of Rochester Medical Center for his medical degree and received his MD in 1941. Here he began to develop interest in medical research.
- // 1941 To 1942Upon receiving his medical degree in 1941, Kornberg entered Strong Memorial Hospital in Rochester for his internship, and completed the same in 1942. Subsequently, he joined the United States Coast Guard as a Lieutenant, serving as a ship's doctor, as part of his military service.
- // 1942In 1942, he published the result of his above mentioned survey. Titled, ‘The Occurrence of Jaundice in an Otherwise Normal Medical Student’, it caught the attention of Rolla Dyer, the Director of National Institute of Health, who invited him to join his research team at the Nutritional Laboratory.
- // 21st Nov 1943 To 1986On November 21, 1943, Kornberg married Sylvy Ruth Levy. She was also a noted biochemist and worked closely with him in the discovery of DNA Polymerase I. Unfortunately, she did not get any recognition for her contribution. She died in 1986, survived by Kornberg and their three sons.
- // 1946Instead, he developed interest in enzymes. In 1946, he got himself transferred to Dr Severo Ochoa's laboratory at New York University to learn more about enzyme purification techniques. Concurrently, he took summer courses at Columbia University to update his knowledge about organic and physical chemistry.
- // 1947Next in 1947, Kornberg shifted to Washington University School of Medicine at St. Louis. Here he worked for few months with Carl Ferdinand Cori before returning to NIH at Bethesda.
- // 1951Prior to that, Kornberg had received Paul-Lewis Award in Enzyme Chemistry from American Chemical Society in 1951.
- // 1953At NIH, he was assigned to organize the Enzymes and Metabolism Section of the Physiology Division, which he did successfully. Subsequently, he became its Medical Director and served in this capacity until 1953.
- // 1953 To 1959In 1953, he moved to Washington University in St. Louis as Professor and Head of the Department of Microbiology and remained there until 1959. Here he continued to work on those enzymes, which were deemed necessary for the creation of DNA.
- // 1956Finally in 1956, he was able to isolate DNA polymerizing enzyme, which later came to be known as DNA polymerase I. Incidentally, it was the first known polymerase. The discovery won him Nobel Prize three years later.
- // 1956Kornberg is best remembered for his work on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase. In 1956, he identified DNA Polymerase I (or Pol I) in the intestinal bacterium E coli and recognized it as an essential enzyme for replication, repair and rearrangements of DNA.
- // 1959In 1959, Kornberg moved to the University of Stanford as Professor and Executive Head of the Department of Biochemistry and remained there for rest of his working life. Here, he took initiative in establishing a Department of Genetics, mainly to accommodate another Nobel Laurent Joshua Lederberg.
- // 1959In 1959, Kornberg received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for his “discovery of the mechanisms in the biological synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid". He shared the prize with Dr Severo Ochoa, who had been working on the same topic at the New York University College of Medicine.
- // 14th Dec 1967At Stanford, Kornberg continued his research on DNA biosynthesis. In this project he worked in close collaboration with Mehran Goulian. After years of grueling research, they finally announced their success on December 14, 1967.
- // 1968In 1968, he received the Scientific Achievement Award of the American Medical Association, the Lucy Wortham James Award of the Society of Medical Oncology and the Borden Award in the Medical Sciences of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
- // 1970Their second son, Thomas B. Kornberg, is a professor at the University of California, San Francisco and noted for his discovery of DNA polymerase II and III (1970). Their youngest son, Kenneth Andrew Kornberg, is an architect specializing in the design of biomedical and biotechnology laboratories.
- // 1979 To 1995In addition, he had received National Medal of Science in 1979, Cosmos Club Award and Gairdner Foundation Award in 1995.
- // 1988Kornberg officially retired from his post in 1988. However, he had never ceased working and maintained an active research Laboratory at the University of Stanford until his death.
- // 1991From 1991 onwards, Kornberg began to focus on the metabolism of inorganic polyphosphate, at that time, regarded as ‘molecular fossil’. Eventually, he found a variety of significant functions for it. For example, he found that it responds to stresses and stringencies; causes motility and virulence in some of the major pathogens.
- // 2006Their eldest son, Roger David Kornberg is a Professor of Structural Biology at the University of Stanford and a Nobel Laureate. In 2006, he received the Nobel Prize for discovering how genetic information from DNA is copied to RNA.
- // 26th Oct 2007Kornberg died on 26 October, 2007 in Stanford of respiratory failure. He was survived by his third wife Carolyn and three sons.
// Famous Pisces Celebrities peoples
Christine Baumgartner
Christine Baumgartner is an American model and the wife of famous American actor Kevin Costner. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Galina Becker
Galina Becker is a former athlete and fitness model from America. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Nikkie De Jager
Check out all that you wanted to know about Nikkie De Jager, the famous Dutch Makeup artist; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Annie Bakes
Annie Bakes is an American adult model and the ex-wife of Dennis Rodman. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jordyn Jones
Jordyn Jones is an American dancer. Let’s have a look at her family & personal life including age, date of birth, boyfriends, net worth, and fun facts.
Oscar Rosenstroem
Oscar Rosenstroem is a Danish Musical.ly star. Let’s have a look at his family and personal life including age, date of birth, girlfriends, net worth and fun facts.
Arthur Kornberg's FAQ
What is Arthur Kornberg birthday?
Arthur Kornberg was born at 1918-03-03
When was Arthur Kornberg died?
Arthur Kornberg was died at 2007-10-26
Where was Arthur Kornberg died?
Arthur Kornberg was died in Stanford, United States
Which age was Arthur Kornberg died?
Arthur Kornberg was died at age 89
Where is Arthur Kornberg's birth place?
Arthur Kornberg was born in New York City, United States
What is Arthur Kornberg nationalities?
Arthur Kornberg's nationalities is American
Who is Arthur Kornberg spouses?
Arthur Kornberg's spouses is Carolyn Frey Dixon (1998–2007; his death), Charlene Walsh Levering (1988–1995; her death), Sylvy Ruth Levy (1943–1986; her death; 3 children)
Who is Arthur Kornberg's father?
Arthur Kornberg's father is Joseph
Who is Arthur Kornberg's mother?
Arthur Kornberg's mother is Lena (née Katz) Kornberg
What is Arthur Kornberg's sun sign?
Arthur Kornberg is Pisces
How famous is Arthur Kornberg?
Arthur Kornberg is famouse as Biochemist