Horace Mann - Politician, Timeline and Personal Life
Horace Mann's Personal Details
Horace Mann was an American education reformer and politician
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | May 4, 1796 |
| Died on | August 2, 1859 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Republicans, Brown University, Miscellaneous, Educators, Educators, Politician |
| Ideologies | Republicans |
| City/State | Massachusetts |
| Spouses | Charlotte Messer Mann (d. 1832), Mary Peabody Mann |
| Siblings | Louise Mann, Stephen Mann |
| Childrens | Benjamin Pickman, George Combe, Horace Jr. |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Franklin |
| Political Ideology | Whig Party |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Thomas Mann |
| Mother | Rebecca Stanley Mann |
| Sun Sign | Taurus |
| Born in | Franklin |
| Famous as | Educator & Politician |
| Died at Age | 63 |
// Famous Politician
Sebastian Coe
Sebastian Coe is a British former track and field athlete turned politician. This biography of Sebastian Coe provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Stephen Lewis
Stephen Lewis is a Canadian politician, broadcaster, diplomat and professor. This biography profiles his childhood, career, works, life, achievements and timeline.
Oswald Mosley
Sir Oswald Ernald Mosley was a British politician known for his pro-fascist beliefs. This biography profiles his childhood, family, personal life, opinions, career, etc.
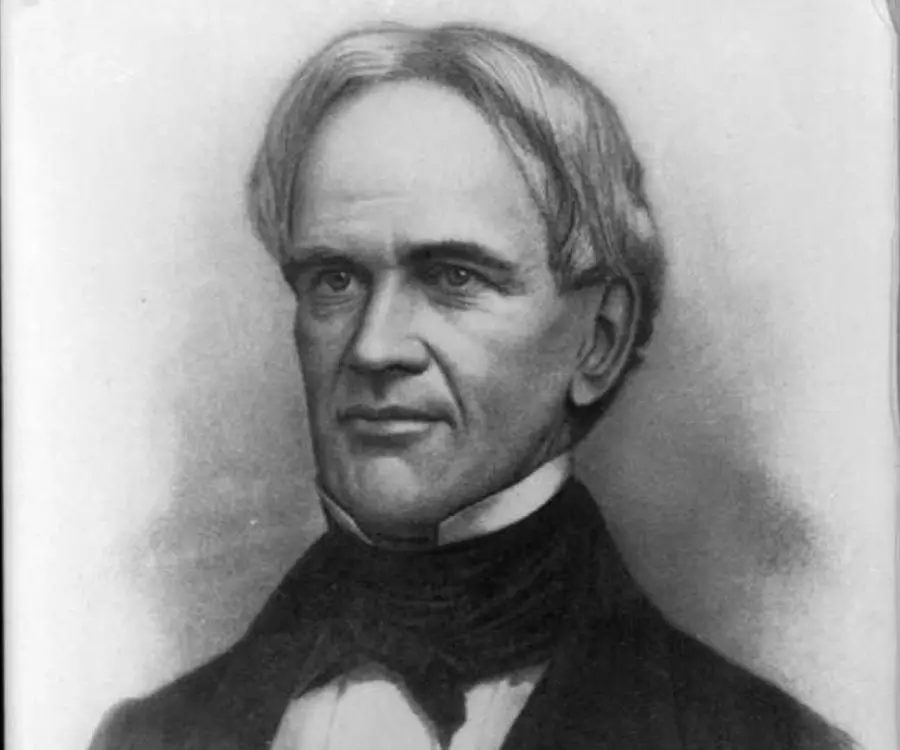
Horace Mann's photo
Who is Horace Mann?
Horace Mann renowned as the ‘Father of the Common School Movement’ was an American education reformer and politician. He was a pioneer of public education and argued that education in a democratic society should be universal, non-factional and reliable. He believed that unruly children of the country can be best transformed into disciplined, sensible and republican nationals through universal public education. He got extensive support from modernizers including the ones from his Whig Party for establishing public schools. Most of the states followed one of the systems he formed in Massachusetts, particularly the ‘normal school’ program for professional training of teachers. Mostly women were trained in normal schools enabling them to build a new career in teaching. He made effort for well equipped schools, longer school life for students till 16 years of age, elaborate curriculum and good pay for teachers. He served as the Secretary of the ‘Massachusetts State Board of Education’ since its inception. He served the ‘Massachusetts State Legislature’ as a dedicated Whig party member and promoted rapid modernization. He was also elected to the ‘United States House of Representatives’.
// Famous Educators
Maria Montessori
Maria Montessori was a physician and educator who developed the approach of Montessori education. This biography of Maria Montessori provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Paulo Freire
Paulo Freire was a Brazilian educator best known for his research on critical pedagogy. This biography of Paulo Freire provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Joshua Chamberlain
Joshua Chamberlain was an American college professor, war hero and Governor of Maine. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
On May 4, 1796, Horace Mann was born to Thomas Mannand Rebecca Stanley Mann in Franklin, Massachusetts. His father was a poor Yankee farmer.
As his family faced lots of hardships and poverty, Mann learned to be independent and self-reliant from an early age. From the age of 10 to 20 he could not attend school more than six weeks in any year. However, he self-studied by visiting the Franklin town library.
He was taught Greek and Latin by Samuel Barrett who later became a famous Unitarian minister.
At twenty years of age, he got admission at the ‘Brown University’. In 1819, he graduated as valedictorian. His valedictory address ‘The Progressive Character of the Human Race’ was a representation of philanthropic optimism showing how a combination of education, humanity and republicanism can allay an individual from the beset of wants and deficiencies. He studied law at Wrentham, Massachusetts for a brief period.
From 1820 to 1822 he worked as a teacher of Greek and Latin. He was the librarian of ‘Brown University’ during 1821-23. He studied at the ‘Litchfield Law School’ sometime around 1821-23. In 1823 he was enrolled in the bar of Norfolk County, Massachusetts.
Career
He began his career as a law practitioner and thereafter won a seat at the ‘Massachusetts House of Representatives’ from Dedham, Mass, in 1827 and served till 1833.
He took active interest in public charities, education and laws suppressing intemperance and lottery culture.
He made personal effort and established a lunatic asylum at Worcester and chaired the board of trustees in 1833. He was a member of the revision of the state statutes committee and remained its chairman for a while. Many of his suggestions were incorporated. He shifted to Boston in 1833.
He served as a majority leader in the ‘Massachusetts State Senate’ from 1835 to 1837 and as its president in 1836 after being elected from Boston. He took up different projects aiming at improvement of infrastructure including canals and railroads constructions.
The ‘Massachusetts State Board of Education’, the country’s first board of education, was created in 1837 following an intense reform movement for improving quality of education. He was made its first secretary. After he took responsibility as the secretary he withdrew himself from politics and other professional engagements.
He became a prominent proponent and spokesperson of education and held teacher’s conventions, delivered lectures and introduced several reforms. He visited all schools of the state. He initiated the Massachusetts ‘normal school’ system in Barre, Lexington and Bridgewater. He was not in favour of corporal punishment in schools which was in disagreement with some teachers in Boston. However, his views were later adopted.
In 1838 he started and edited a biweekly journal ‘The Common School Journal’ which focussed on public schools and their issues. His six main principles addressing public education and its problems are: (1) The public should not remain ignorant for long (2) public should take interest to pay for, control and maintain education (3) that best education can be provided in schools that welcome children from different socio-economic, religious and ethnic backgrounds; (4) this education should be free from sectarian influence; (5) tenets of a free society should prevail while parting education; and (6) that education should be provided by well-trained, professional teachers.
Since he had a huge fascination for German education system like many other American educators, he went to Germany in 1843 to see how the education system worked. After returning to the U.S., he emphatically lobbied for the adoption of the ‘Prussian model’.
In 1848, he resigned from his post as the secretary of the ‘Massachusetts State Board of Education’ to fill up the seat of John Quincy Adams in the ‘United States Congress’. He advocated exclusion of slavery in his first speech. He voluntarily counselled for Drayton and Sayres who were charged with stealing seventy-six slaves from the District of Columbia.
He was engaged in a controversy with Daniel Webster in 1850 on fugitive slave law and slavery extension. Though he was defeated by Webster’s supporters at the ensuing nominating convention by one vote, his appeal to people as an independent candidate of anti-slavery re-elected him and he served till March 1853.
He was supported by modernists including his Whig Party members for setting up public schools. He persuaded them to pass law in their states for tax-aided elementary public education.
In 1852, he backed the decision of adopting the Prussian education system in Massachusetts and after its adoption the New York Governor implemented the system on trial basis in twelve schools of New York.
In September 1852, the ‘Free Soil Party’ nominated him for the governor’s position in Massachusetts. He was also selected as the president of Antioch College which was newly set up at Yellow Springs in Ohio. Though he was unsuccessful in the election for the post of governor, he agreed to become the president of the college and remained so till he was alive. He taught philosophy, theology and economics in the college. His lectures advocating public schools were attended by lay audiences from all over Midwest.
He appointed his niece, Rebecca Pennell as the first woman faculty member who was paid equally compared to her male counterparts.
Some of the books of Horace Mann include ‘Lectures on Education’ (1845), ‘A Few Thoughts for a Young Man’ (1850) and ‘Slavery: Letters and Speeches’ (1851).
Most northern states followed one of the education systems Horace Mann implemented in Massachusetts, particularly the ‘normal school’ program for training teachers professionally.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1830, he married Charlotte Messer, daughter of Brown University’s president Asa Messer. His wife died on August 1, 1832.
Horace Mann married Mary Tyler Peabody in 1843. The couple had three sons - Horace Mann Jr., George Combe Mann and Benjamin Pickman Mann.
He died on August 2, 1859 at the age of 63 years at Yellow Springs, Ohio, U.S. He was buried by the side of his first wife Charlotte Messer Mann in the North Burial Ground, Providence, Rhode Island, U.S.
Trivia
His statue is erected in front of ‘Massachusetts State House’.
A monument at the Antioch College bears his quote, ‘’ Be Ashamed to Die Until You Have Won Some Victory for Humanity”.
Some of the schools named after him are ‘Horace Mann Elementary School’ in Dayton, Ohio, ‘Horace Mann Middle School’ in Franklin, Massachusetts and ‘Horace Mann School’ in Salem, Massachusetts.
// Famous Miscellaneous
Jason Simpson
Jason Simpson is the son of former NFL running back, broadcaster and actor O. J. Simpson. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, life, and little known facts about him.
Melissa Brim
Melissa Brim is the ex-girlfriend of former professional boxer Floyd Mayweather Jr. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Joyce Meyer
Joyce Meyer is a Christian author and speaker. This biography provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Horace Mann biography timelines
- // 4th May 1796On May 4, 1796, Horace Mann was born to Thomas Mannand Rebecca Stanley Mann in Franklin, Massachusetts. His father was a poor Yankee farmer.
- // 1819At twenty years of age, he got admission at the ‘Brown University’. In 1819, he graduated as valedictorian. His valedictory address ‘The Progressive Character of the Human Race’ was a representation of philanthropic optimism showing how a combination of education, humanity and republicanism can allay an individual from the beset of wants and deficiencies. He studied law at Wrentham, Massachusetts for a brief period.
- // 1827 To 1833He began his career as a law practitioner and thereafter won a seat at the ‘Massachusetts House of Representatives’ from Dedham, Mass, in 1827 and served till 1833.
- // 1830 To 1st Aug 1832In 1830, he married Charlotte Messer, daughter of Brown University’s president Asa Messer. His wife died on August 1, 1832.
- // 1833He made personal effort and established a lunatic asylum at Worcester and chaired the board of trustees in 1833. He was a member of the revision of the state statutes committee and remained its chairman for a while. Many of his suggestions were incorporated. He shifted to Boston in 1833.
- // 1837The ‘Massachusetts State Board of Education’, the country’s first board of education, was created in 1837 following an intense reform movement for improving quality of education. He was made its first secretary. After he took responsibility as the secretary he withdrew himself from politics and other professional engagements.
- // 1838In 1838 he started and edited a biweekly journal ‘The Common School Journal’ which focussed on public schools and their issues. His six main principles addressing public education and its problems are: (1) The public should not remain ignorant for long (2) public should take interest to pay for, control and maintain education (3) that best education can be provided in schools that welcome children from different socio-economic, religious and ethnic backgrounds; (4) this education should be free from sectarian influence; (5) tenets of a free society should prevail while parting education; and (6) that education should be provided by well-trained, professional teachers.
- // 1843Since he had a huge fascination for German education system like many other American educators, he went to Germany in 1843 to see how the education system worked. After returning to the U.S., he emphatically lobbied for the adoption of the ‘Prussian model’.
- // 1843Horace Mann married Mary Tyler Peabody in 1843. The couple had three sons - Horace Mann Jr., George Combe Mann and Benjamin Pickman Mann.
- // 1848In 1848, he resigned from his post as the secretary of the ‘Massachusetts State Board of Education’ to fill up the seat of John Quincy Adams in the ‘United States Congress’. He advocated exclusion of slavery in his first speech. He voluntarily counselled for Drayton and Sayres who were charged with stealing seventy-six slaves from the District of Columbia.
- // 1850 To Mar 1853He was engaged in a controversy with Daniel Webster in 1850 on fugitive slave law and slavery extension. Though he was defeated by Webster’s supporters at the ensuing nominating convention by one vote, his appeal to people as an independent candidate of anti-slavery re-elected him and he served till March 1853.
- // 1852In 1852, he backed the decision of adopting the Prussian education system in Massachusetts and after its adoption the New York Governor implemented the system on trial basis in twelve schools of New York.
- // Sep 1852In September 1852, the ‘Free Soil Party’ nominated him for the governor’s position in Massachusetts. He was also selected as the president of Antioch College which was newly set up at Yellow Springs in Ohio. Though he was unsuccessful in the election for the post of governor, he agreed to become the president of the college and remained so till he was alive. He taught philosophy, theology and economics in the college. His lectures advocating public schools were attended by lay audiences from all over Midwest.
- // 2nd Aug 1859He died on August 2, 1859 at the age of 63 years at Yellow Springs, Ohio, U.S. He was buried by the side of his first wife Charlotte Messer Mann in the North Burial Ground, Providence, Rhode Island, U.S.
// Famous Brown University
Ted Turner
Ted Turner is a media tycoon who founded the cable news network CNN. This biography of Ted Turner provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Marin Hinkle
Marin Hinkle is an actress known for her role in the sitcom ‘Two and a Half Men.’ Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Emma Watson
Emma Watson is a British actress and model, best-known for her role as ‘Hermione Granger’ in the Harry Potter series. Explore this biography to learn more about her profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Bess Armstrong
Bess Armstrong is an American actress known for her work in films, stage productions and television series. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
John D. Rockefeller Jr.
John D. Rockefeller, Jr. was a famous American businessman known for his philanthropic works. Read more about the life of this influential businessman in the following article.
Walter Dean Myers
Walter Dean Myers was a famous African-American author of novels for children and adolescents, renowned for his book ‘Monster’. This biography has detailed information about his childhood, profile, career and timeline
Horace Mann's FAQ
What is Horace Mann birthday?
Horace Mann was born at 1796-05-04
When was Horace Mann died?
Horace Mann was died at 1859-08-02
Where was Horace Mann died?
Horace Mann was died in Yellow Springs
Which age was Horace Mann died?
Horace Mann was died at age 63
Where is Horace Mann's birth place?
Horace Mann was born in Franklin
What is Horace Mann nationalities?
Horace Mann's nationalities is American
What is Horace Mann ideologies?
Horace Mann's ideologies is Republicans
Who is Horace Mann spouses?
Horace Mann's spouses is Charlotte Messer Mann (d. 1832), Mary Peabody Mann
Who is Horace Mann siblings?
Horace Mann's siblings is Louise Mann, Stephen Mann
Who is Horace Mann childrens?
Horace Mann's childrens is Benjamin Pickman, George Combe, Horace Jr.
What was Horace Mann universities?
Horace Mann studied at Brown University, Litchfield Law School, Brown University
What was Horace Mann notable alumnis?
Horace Mann's notable alumnis is Brown University
What is Horace Mann's political ideology?
Horace Mann's political ideology is Whig Party
Who is Horace Mann's father?
Horace Mann's father is Thomas Mann
Who is Horace Mann's mother?
Horace Mann's mother is Rebecca Stanley Mann
What is Horace Mann's sun sign?
Horace Mann is Taurus
How famous is Horace Mann?
Horace Mann is famouse as Educator & Politician