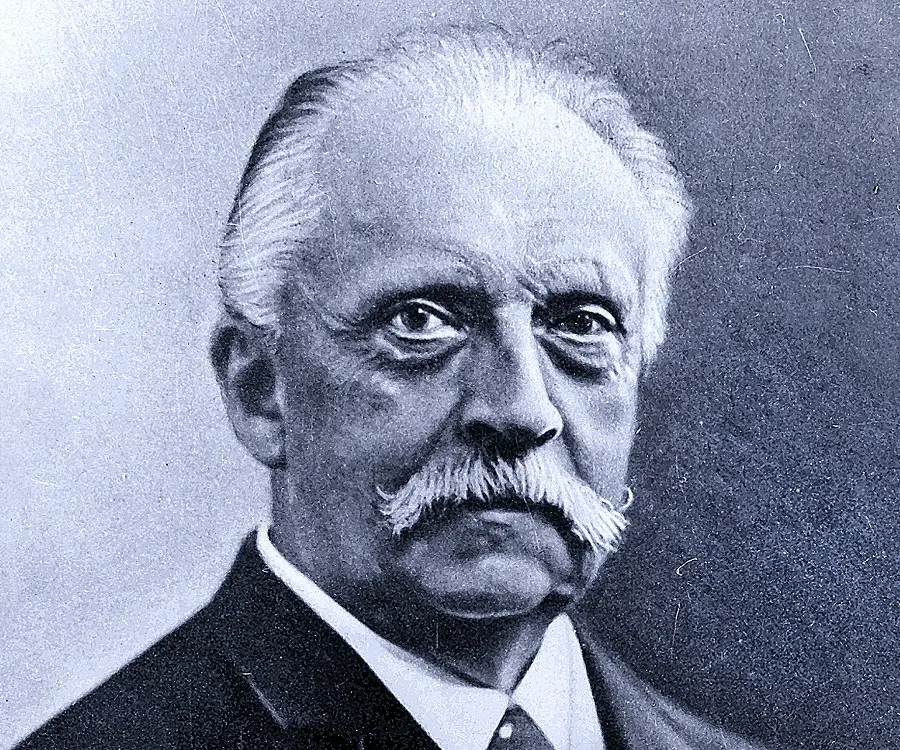
Hermann von Helmholtz - Physicians, Family and Facts
Hermann von Helmholtz's Personal Details
Hermann von Helmholtz was a German physician and physicist, best known for his statement of the law of the conservation of energy.
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | August 31, 1821 |
| Died on | September 8, 1894 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Inventors & Discoverers, Physicians, Physicists, Physicians, Physicists |
| Known as | Hermann Helmholtz, Dr. Hermann von Helmholtz |
| Universities |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Potsdam |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Potsdam |
| Famous as | Physicist and Physician |
| Died at Age | 73 |
// Famous Physicists
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Gabriel Lippmann
Gabriel Lippmann was a French physicist and inventor. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1908. This biography of Lippmann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Hermann von Helmholtz's photo
Who is Hermann von Helmholtz?
Hermann von Helmholtz was a German physician and physicist, best known for his statement of the law of the conservation of energy. A highly versatile individual, he made notable contributions to several areas of modern science including physiology, psychology, electrodynamics, and chemical thermodynamics. In addition, he was also an esteemed philosopher known for his philosophy of science and ideas on the laws of nature and the science of aesthetics. Born as the son of a teacher, Helmholtz developed an early interest in natural sciences. He also inherited a love for philosophy from his father. The prominent philosopher Immanuel Hermann Fichte was known to the family, and he cast a lasting influence on the young boy. Helmholtz was intelligent and curious from an early age and displayed interest in several different fields. He studied medicine as a young man at the behest of his father and trained primarily in physiology. He worked as an army doctor for a few years before embarking on a teaching career as a professor. He began his research while serving as an army doctor, and continued with his relentless scientific research works throughout his career. He started out as a physician but went on to make significant contributions to several varied fields of science including physiology, optics, electrodynamics, mathematics, and meteorology.
// Famous Physicians
Maria Montessori
Maria Montessori was a physician and educator who developed the approach of Montessori education. This biography of Maria Montessori provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Severo Ochoa
Severo Ochoa was a Spanish physician and biochemist who won the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Virginia Apgar
Known for inventing a novel newborn scoring system, Virginia Apgar was a reputed Physician. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Childhood & Early Life
Hermann von Helmholtz was born on 31 August 1821, in Potsdam, Kingdom of Prussia, as the eldest of four children of Ferdinand Helmholtz. His father was a teacher of philosophy and literature at the Potsdam Gymnasium.
He grew up in an intellectually stimulating environment and was taught classical languages, as well as French, English, and Italian by his father. His father was a close friend of the philosopher Immanuel Hermann Fichte, and introduced the boy to the philosophy of Immanuel Kant and Johann Gottlieb Fichte. His upbringing greatly influenced the development of his own philosophical views.
Helmholtz received his primary education from Potsdam Gymnasium and wanted to study natural science. However, his father did not have the funds to send him to the university and instead asked him to study medicine as the government provided financial support for medical students.
He obtained a government stipend for five years’ study at the Königlich Medizinisch-chirurgische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Institut in Berlin. In return he had to commit himself to eight years of service as an army surgeon. At the institute he studied clinical medicine under Lucas Schönlein, and physiology under Johannes Müller.
He also took courses in chemistry and privately read the mathematical works of Laplace, Biot, and Daniel Bernoulli as well as the philosophical works of Kant. While working on his dissertation under Johannes Muller, he became acquainted with Muller’s other students including Ernst Brücke and Emil du Bois-Reymond. He graduated from medical school in 1843.
Career
Following his graduation, he was appointed an army surgeon at the regiment at Potsdam. His army duties were few and thus he had ample time to devote to his research. He had varied interests in a number of fields and his job left him with enough time to explore his interests.
Hermann von Helmholtz’s first important scientific achievement came in 1847 with the publication of his theories in his book ‘Über die Erhaltung der Kraft’ (On the Conservation of Force). He drew inspiration for his research from the earlier work of Sadi Carnot, Émile Clapeyron and James Prescott Joule.
In 1848, he was appointed assistant at the Anatomical Museum and lecturer at the Academy of Fine Arts in Berlin. The very next year he moved to Königsberg, in East Prussia, to become assistant professor and director of the Physiological Institute.
While working at Königsberg in 1849, Helmholtz measured the speed at which the signal is carried along a nerve fiber. He used a recently dissected sciatic nerve of a frog and the calf muscle to which it attached to perform the experiment, and used a galvanometer as a sensitive timing device. He reported transmission speeds in the range of 24.6–38.4 meters per second.
He was also an inventor and revolutionized the field of ophthalmology with the invention of the ophthalmoscope in 1851. The instrument he developed could be used to examine the inside of the human eye. This invention proved to be an extremely popular one and earned him considerable fame and acclaim.
He became professor of anatomy and physiology at the University of Bonn in 1855 and moved to the University of Heidelberg in 1858 where he served as professor of physiology.
He also had a keen interest in physics and published ‘On the Sensations of Tone’ in 1863. The book is said to have influenced musicologists well into the 20th century. Among his various inventions in this time period was the Helmholtz resonator which could identify the various frequencies or pitches of the pure sine wave components of complex sounds containing multiple tones.
In 1870, Gustav Magnus, who held the chair of physics at Berlin, died. Helmholtz was offered the position, which he accepted in 1871. He now focused on electromagnetism and theories of electrodynamic action. Over the ensuing years he published several papers on the galvanic cell, the thermodynamics of chemical processes, and meteorology.
By the 1880s he had become one of the best known figures of German science and the country’s foremost adviser on scientific affairs. In 1887 Helmholtz was made the president of the newly founded Physikalisch-technische Reichsanstalt for research in the exact sciences and precision technology.
Major Works
One of Hermann von Helmholtz’s major contributions to science was his work in the law of conservation of energy. He drew inspiration from the previous works of Joule, Sadi Carnot and Émile Clapeyron, and arrived at conclusions similar to Grove's. He then published his findings in the book ‘Über die Erhaltung der Kraft’ (On the Conservation of Force) in 1847.
He revolutionized ophthalmology with the invention of the ophthalmoscope, an instrument that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures. The device is extensively used for determining the health of the retina, optic disc, and vitreous humor.
Awards & Achievements
Helmholtz was conferred with Honorary Membership of the Institution of Engineers and Shipbuilders in Scotland in 1884.
The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor.
Personal Life & Legacy
Hermann von Helmholtz married Olga von Velten, the daughter of a surgeon, on 26 August 1849. The couple had two children. His wife was of delicate health and she died on 28 December 1859, leaving Helmholtz with the young children.
In 1861 he married Anna von Mohl, the daughter of Heidelberg professor Robert von Mohl. This marriage produced three more children. Anna was an attractive woman, considerably younger than Helmholtz.
Hermann von Helmholtz suffered from ill health, including fits of depression, during his later years, and died on 8 September 1894.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Hermann von Helmholtz's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Copley Medal | |
Hermann von Helmholtz biography timelines
- // 31st Aug 1821Hermann von Helmholtz was born on 31 August 1821, in Potsdam, Kingdom of Prussia, as the eldest of four children of Ferdinand Helmholtz. His father was a teacher of philosophy and literature at the Potsdam Gymnasium.
- // 1843He also took courses in chemistry and privately read the mathematical works of Laplace, Biot, and Daniel Bernoulli as well as the philosophical works of Kant. While working on his dissertation under Johannes Muller, he became acquainted with Muller’s other students including Ernst Brücke and Emil du Bois-Reymond. He graduated from medical school in 1843.
- // 1847Hermann von Helmholtz’s first important scientific achievement came in 1847 with the publication of his theories in his book ‘Über die Erhaltung der Kraft’ (On the Conservation of Force). He drew inspiration for his research from the earlier work of Sadi Carnot, Émile Clapeyron and James Prescott Joule.
- // 1847One of Hermann von Helmholtz’s major contributions to science was his work in the law of conservation of energy. He drew inspiration from the previous works of Joule, Sadi Carnot and Émile Clapeyron, and arrived at conclusions similar to Grove's. He then published his findings in the book ‘Über die Erhaltung der Kraft’ (On the Conservation of Force) in 1847.
- // 1848In 1848, he was appointed assistant at the Anatomical Museum and lecturer at the Academy of Fine Arts in Berlin. The very next year he moved to Königsberg, in East Prussia, to become assistant professor and director of the Physiological Institute.
- // 1849While working at Königsberg in 1849, Helmholtz measured the speed at which the signal is carried along a nerve fiber. He used a recently dissected sciatic nerve of a frog and the calf muscle to which it attached to perform the experiment, and used a galvanometer as a sensitive timing device. He reported transmission speeds in the range of 24.6–38.4 meters per second.
- // 26th Aug 1849 To 28th Dec 1859Hermann von Helmholtz married Olga von Velten, the daughter of a surgeon, on 26 August 1849. The couple had two children. His wife was of delicate health and she died on 28 December 1859, leaving Helmholtz with the young children.
- // 1851He was also an inventor and revolutionized the field of ophthalmology with the invention of the ophthalmoscope in 1851. The instrument he developed could be used to examine the inside of the human eye. This invention proved to be an extremely popular one and earned him considerable fame and acclaim.
- // 1855 To 1858He became professor of anatomy and physiology at the University of Bonn in 1855 and moved to the University of Heidelberg in 1858 where he served as professor of physiology.
- // 1861In 1861 he married Anna von Mohl, the daughter of Heidelberg professor Robert von Mohl. This marriage produced three more children. Anna was an attractive woman, considerably younger than Helmholtz.
- // 1863He also had a keen interest in physics and published ‘On the Sensations of Tone’ in 1863. The book is said to have influenced musicologists well into the 20th century. Among his various inventions in this time period was the Helmholtz resonator which could identify the various frequencies or pitches of the pure sine wave components of complex sounds containing multiple tones.
- // 1870 To 1871In 1870, Gustav Magnus, who held the chair of physics at Berlin, died. Helmholtz was offered the position, which he accepted in 1871. He now focused on electromagnetism and theories of electrodynamic action. Over the ensuing years he published several papers on the galvanic cell, the thermodynamics of chemical processes, and meteorology.
- // 1884Helmholtz was conferred with Honorary Membership of the Institution of Engineers and Shipbuilders in Scotland in 1884.
- // 1887By the 1880s he had become one of the best known figures of German science and the country’s foremost adviser on scientific affairs. In 1887 Helmholtz was made the president of the newly founded Physikalisch-technische Reichsanstalt for research in the exact sciences and precision technology.
- // 8th Sep 1894Hermann von Helmholtz suffered from ill health, including fits of depression, during his later years, and died on 8 September 1894.
// Famous Inventors & Discoverers
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Thomas Newcomen
Thomas Newcomen was a British inventor who developed the world’s first steam engine. Browse through this biography to learn in details about his life, career, works and timeline.
Erno Rubik
The famous inventor and educationist, Erno Rubik is known world-wide for his invention the ‘Rubik’s Cube’. To know more about the childhood, profile, timeline and career of this famous architect-inventor read on.
Ernst Ruska
Ernst Ruska was a German physicist who invented the electron microscope. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Howard Hughes
Howard Hughes was an American aviator, business tycoon, philanthropist and also a film maker. This biography explores his childhood, career, achievements and timeline.
Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick was a British inventor who was the pioneer of steam-powered road and rail transport. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Hermann von Helmholtz's FAQ
What is Hermann von Helmholtz birthday?
Hermann von Helmholtz was born at 1821-08-31
When was Hermann von Helmholtz died?
Hermann von Helmholtz was died at 1894-09-08
Where was Hermann von Helmholtz died?
Hermann von Helmholtz was died in Charlottenburg
Which age was Hermann von Helmholtz died?
Hermann von Helmholtz was died at age 73
Where is Hermann von Helmholtz's birth place?
Hermann von Helmholtz was born in Potsdam
What is Hermann von Helmholtz nationalities?
Hermann von Helmholtz's nationalities is German
What was Hermann von Helmholtz universities?
Hermann von Helmholtz studied at Heidelberg University, University of Königsberg
What is Hermann von Helmholtz's inventions/discoveries?
Helmholtz Resonator was invented (or discovered) by Hermann von Helmholtz
What is Hermann von Helmholtz's sun sign?
Hermann von Helmholtz is Virgo
How famous is Hermann von Helmholtz?
Hermann von Helmholtz is famouse as Physicist and Physician