Charles Thomson Rees Wilson - Physicists, Family and Childhood
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's Personal Details
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was a Scottish meteorologist and physicist
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | February 14, 1869 |
| Died on | November 15, 1959 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Cambridge University, University Of Manchester, Scientists, Physicists, Meteorologists |
| Spouses | Jessie Fraser |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Midlothian, Scotland |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | John Wilson |
| Mother | Annie Clerk Harper |
| Sun Sign | Aquarius |
| Born in | Midlothian, Scotland |
| Famous as | Physicist |
| Died at Age | 90 |
// Famous Cambridge University
Stephen Fry
Stephen Fry is a comedian, actor, author, television and radio presenter. Read the biography and know all about his childhood, career, profile and timeline.
Ludwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Wittgenstein is a renowned philosopher. Read on to know about the life, career, and works of the famous Austrian philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein.
Rupert Brooke
Rupert Brooke was an English poet who is widely known for his poem ‘The Soldier’, which was a part of five war sonnets. This biography of Rupert Brooke provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
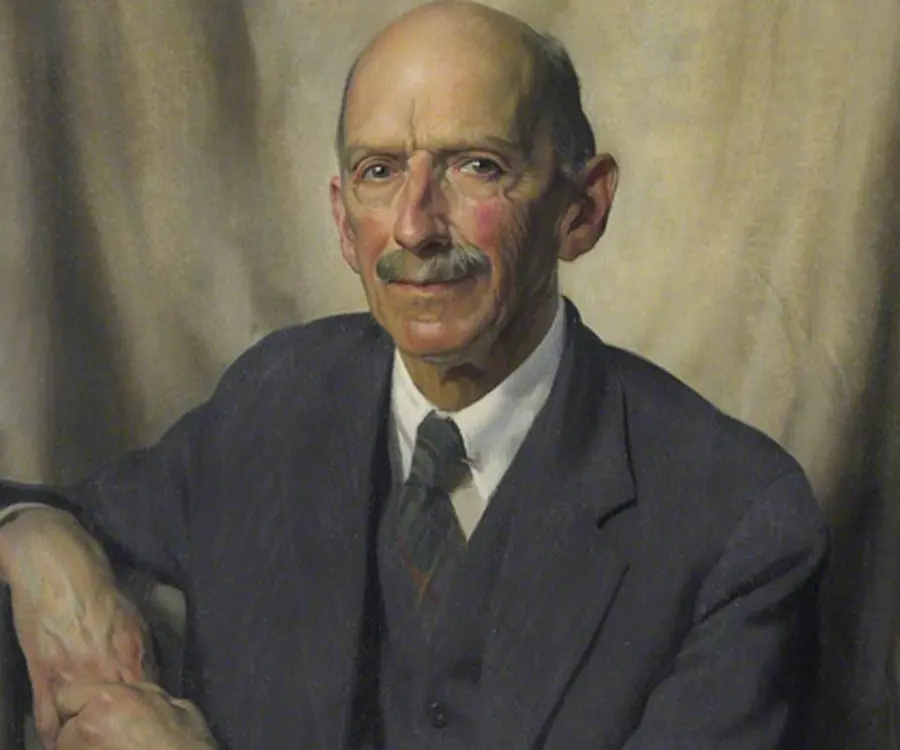
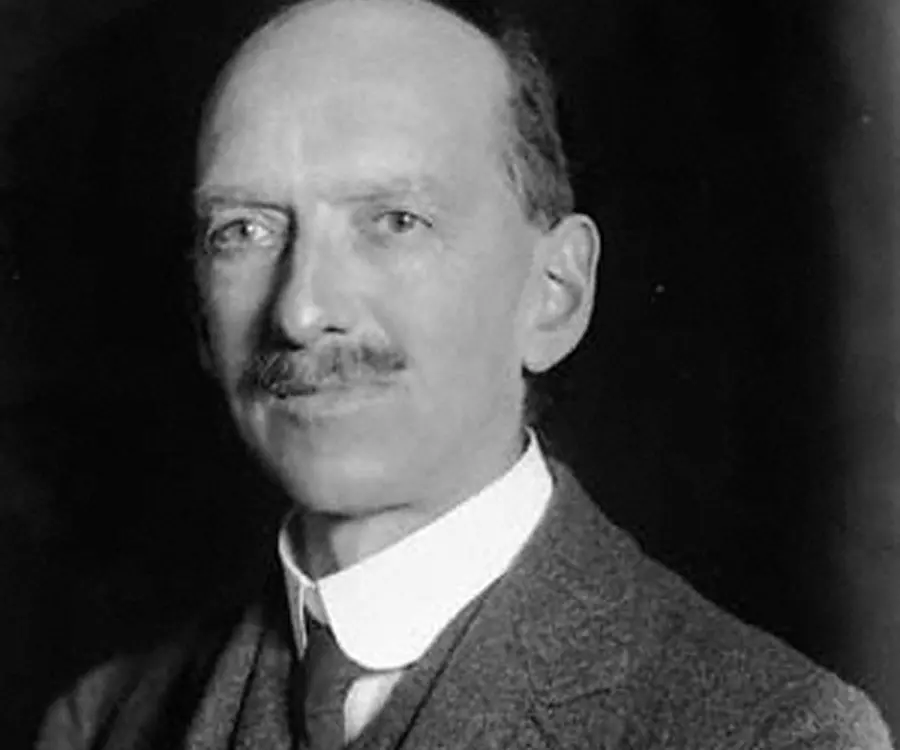
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's photo
Who is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was a Scottish meteorologist and physicist. Early in his life, he was interested in natural science and studied to become a doctor. However, he later grew interested in physics and chemistry and went on to complete his graduation. Throughout his career, he got the opportunity to conduct research, teach and work as a reader and demonstrator at the Cambridge university. His most significant works include his observation on the formation of clouds and subsequent development of the cloud chamber, research on the behaviour of ions and so on. He received the prestigious Nobel Prize for Physics in 1927 for ‘for his method of making the paths of electrically charged particles visible by condensation of vapour’. He was honored with several other awards and recognitions for his research and contribution to physics. Throughout his life, he remained active in the field of science and during his final years, he worked on documenting on the ‘theory of thundercloud electricity’.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was born on 14 February 1869 at Midlothian in Scotland to farmer John Wilson and Annie Clerk Harper.
His father died in 1873 and his family shifted to Manchester. He completed his primary education at Greenheyes Collegiate School in Manchester.
Later he enrolled in the Owen’s College and took up majors in Biology, with the intent to pursue a career in medicine. In 1888, he received a scholarship and went to Sidney Sussex College in Cambridge. While studying here he grew interested in physics and chemistry.
Career
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson taught at the Bradford Grammar School in Yorkshire for a brief period, but since he had keen interest in science so he soon joined Cambridge as a demonstrator for medical students.
He was interested in studying meteorology and in 1893 he began his research on clouds and their various properties. During this time, he worked at an observatory at Ben Nevis where he used to conduct his observations. He tried to create a similar formation in his Cambridge laboratory with humid air and sealed containers.
He further conducted research on cloud formations due to radiation and ions at his chamber. By 1896, it was proved that the ions in gases could be detected, photographed and recorded for later studies.
The same year he was awarded with a scholarship, ‘Clerk Maxwell Student’, that allowed him to engage in research for the next three years. Between the years 1896 and 1900, he focused on studying the behaviour of ions as condensation nuclei.
In 1900, he was appointed a lecturer, demonstrator and fellow at the Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge. Until 1918 he taught advanced practical physics at the Cavendish Laboratory. In 1901, he also carried out studies on atmospheric electricity.
By 1912, Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was able to optimize his creation, cloud chamber, a particle detector that was used to detect ionizing radiation. This creation proved significant for scientists during the 1920s and 1930s as many theories and ideas were supported and proved by its use. Some of the most important accomplishments include proving the ‘Compton Effect’ by Arthur Compton, discovery of positron by Anderson, the demonstration of ‘pair creation’ and ‘annihilation’ of electrons and positrons by Blackett and Occhialini, transmutation of atomic nucleiby Cockcroft and Walton.
He was appointed an observer in the Meteorological Physics at the Solar Physics in 1913. While working here, he was able to study the tracks of ionizing particles and research on thunderstorm electricity. In 1918, he was made a Reader in Electrical Meteorology.
A few years later in 1925, he took up the post of Jacksonian Professor of Natural Philosophy, where he remained until 1934. While working here, he created a method of protecting the British wartime barrage balloons from lightning by using his understanding of thunderstorms. In 1956, he published his theory on thunderstorm electricity.
Post his retirement, he shifted to Edinburgh, and later to the village of Carlops at Glencorse. During this time, he worked on his manuscript on the ‘theory of thundercloud electricity’.
Major Works
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was an eminent physicist who became well-known for his research on clouds and his creation, ‘cloud chamber’.
Awards & Achievements
In 1900, he was appointed a Fellow of the Royal Society.
He was awarded the Royal Medal by the Royal Society in 1922.
He received the Howard N. Potts Medal by the by the Franklin Institute of Philadelphia in 1925.
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1927.
In 1929 he was awarded the Franklin Medal by the Franklin Institute of Philadelphia.
He received the Duddell Medal and Prize by the Institute of Physics in 1931.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1908 Charles Thomson Rees Wilson married Jessie Fraser who was daughter of Minister Rev. G. H. Dick at Glasgow. The couple had four children – two sons and two daughters.
He died on 15 November 1959 at Edinburgh in Scotland. He was 90 at the time of his death.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physics (1927) | |
| 0 | Franklin Medal (1929) | |
| 0 | Duddell Medal and Prize (1931) | |
| 0 | Royal Medal (1922) | |
| 0 | Howard N. Potts Medal (1925) | |
| 0 | FRS (1900) | |
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson biography timelines
- // 14th Feb 1869Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was born on 14 February 1869 at Midlothian in Scotland to farmer John Wilson and Annie Clerk Harper.
- // 1873His father died in 1873 and his family shifted to Manchester. He completed his primary education at Greenheyes Collegiate School in Manchester.
- // 1888Later he enrolled in the Owen’s College and took up majors in Biology, with the intent to pursue a career in medicine. In 1888, he received a scholarship and went to Sidney Sussex College in Cambridge. While studying here he grew interested in physics and chemistry.
- // 1893He was interested in studying meteorology and in 1893 he began his research on clouds and their various properties. During this time, he worked at an observatory at Ben Nevis where he used to conduct his observations. He tried to create a similar formation in his Cambridge laboratory with humid air and sealed containers.
- // 1896He further conducted research on cloud formations due to radiation and ions at his chamber. By 1896, it was proved that the ions in gases could be detected, photographed and recorded for later studies.
- // 1896 To 1900The same year he was awarded with a scholarship, ‘Clerk Maxwell Student’, that allowed him to engage in research for the next three years. Between the years 1896 and 1900, he focused on studying the behaviour of ions as condensation nuclei.
- // 1900In 1900, he was appointed a Fellow of the Royal Society.
- // 1908In 1908 Charles Thomson Rees Wilson married Jessie Fraser who was daughter of Minister Rev. G. H. Dick at Glasgow. The couple had four children – two sons and two daughters.
- // 1912By 1912, Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was able to optimize his creation, cloud chamber, a particle detector that was used to detect ionizing radiation. This creation proved significant for scientists during the 1920s and 1930s as many theories and ideas were supported and proved by its use. Some of the most important accomplishments include proving the ‘Compton Effect’ by Arthur Compton, discovery of positron by Anderson, the demonstration of ‘pair creation’ and ‘annihilation’ of electrons and positrons by Blackett and Occhialini, transmutation of atomic nucleiby Cockcroft and Walton.
- // 1913 To 1918He was appointed an observer in the Meteorological Physics at the Solar Physics in 1913. While working here, he was able to study the tracks of ionizing particles and research on thunderstorm electricity. In 1918, he was made a Reader in Electrical Meteorology.
- // 1922He was awarded the Royal Medal by the Royal Society in 1922.
- // 1925He received the Howard N. Potts Medal by the by the Franklin Institute of Philadelphia in 1925.
- // 1927Charles Thomson Rees Wilson won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1927.
- // 1929In 1929 he was awarded the Franklin Medal by the Franklin Institute of Philadelphia.
- // 1931He received the Duddell Medal and Prize by the Institute of Physics in 1931.
- // 15th Nov 1959He died on 15 November 1959 at Edinburgh in Scotland. He was 90 at the time of his death.
// Famous University Of Manchester
James Chadwick
Sir James Chadwick CH was an English physicist, who won the 1935 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of neutron. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
J. J. Thomson
J.J. Thomson was an English physicist and mathematician. This biography profiles his childhood, life, academic career, research and timeline.
Milo Yiannopoulos
Milo Yiannopoulos is a British technology journalist. Let’s have a look at his family, personal life, career, achievements, controversies, and some facts.
Phil Collins
Phil Collins (Philip David Charles Collins) is an English musician, drummer, singer, and actor. This biography profiles his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Norman Foster
Norman Robert Foster often referred to as the ‘hero of high-tech’ is one of the most distinguished British architects. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, works, achievements and timeline.
Henry Moseley
Henry Moseley was a renowned English physicist who developed the Moseley’s Law in the field of x-ray spectroscopy. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on.
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's FAQ
What is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson birthday?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was born at 1869-02-14
When was Charles Thomson Rees Wilson died?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was died at 1959-11-15
Where was Charles Thomson Rees Wilson died?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was died in Edinburgh
Which age was Charles Thomson Rees Wilson died?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was died at age 90
Where is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's birth place?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson was born in Midlothian, Scotland
What is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson nationalities?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's nationalities is British
Who is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson spouses?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's spouses is Jessie Fraser
What was Charles Thomson Rees Wilson universities?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson studied at Cambridge University,University Of Manchester, University of Cambridge, University of Manchester, Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge, Victoria University of Manchester
What was Charles Thomson Rees Wilson notable alumnis?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's notable alumnis is Cambridge University, University Of Manchester
What is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's inventions/discoveries?
Cloud Chamber was invented (or discovered) by Charles Thomson Rees Wilson
Who is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's father?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's father is John Wilson
Who is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's mother?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's mother is Annie Clerk Harper
What is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson's sun sign?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson is Aquarius
How famous is Charles Thomson Rees Wilson?
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson is famouse as Physicist