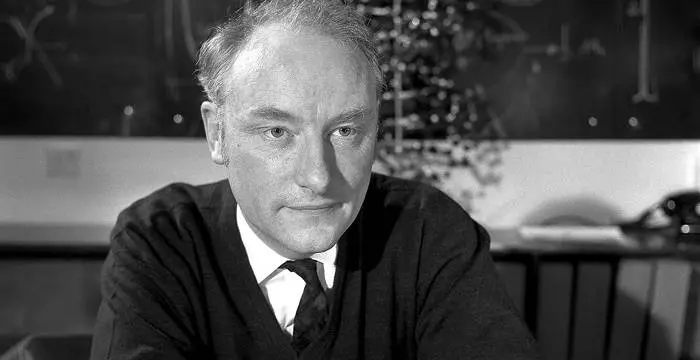J. J. Thomson - Nobel Prize Winner, Timeline and Facts
J. J. Thomson's Personal Details
J.J
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | December 18, 1856 |
| Died on | August 30, 1940 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Cambridge University, Trinity College, Cambridge, University Of Manchester, Scientists, Physicists, Nobel Prize Winner |
| Spouses | Rose Elisabeth Paget |
| Siblings | Frederick Vernon Thomson |
| Known as | Sir Joseph John Thomson |
| Childrens | George Paget Thomson |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Manchester, Lancashire, UK |
| Religion | Anglican/Episcopalian |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Joseph James Thomson |
| Mother | Emma Swindells |
| Sun Sign | Sagittarius |
| Born in | Manchester, Lancashire, UK |
| Famous as | Physicist, Nobel Prize Winner |
| Died at Age | 83 |
// Famous Nobel Prize Winner
Peter C. Doherty
Peter C Doherty is a renowned Australian scientist circle, who was received the Nobel Prize in Physiology for the discovery of how immune system recognizes virus-infected cells. Read this biography to know in details about his childhood, life, career
Francis Crick
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist, who received the Nobel Prize for Medicine. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
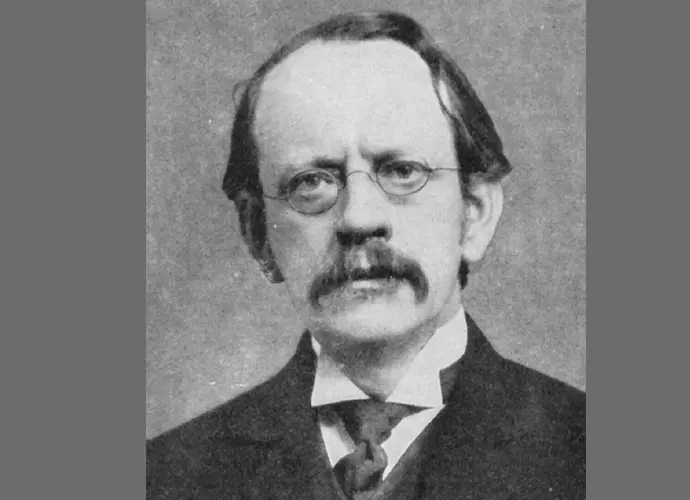
J. J. Thomson's photo
Who is J. J. Thomson?
J.J. Thomson was an English physicist and mathematician. Thomson was a child prodigy who first went to college at the age of 14 and continued his progression to become one of the most gifted scientists of his generation. Thomson became the Cavendish Professor of Experimental Physics at the University of Cambridge at a very young age but he made his greatest achievement when he did a detailed study of cathode rays and proved the existence of the electron in atoms; that would go on to have far reaching effects in the study of the natural sciences. Thomson also delivered lectures at some of the leading universities in the world like Princeton University and Yale University as a guest which further enhanced his reputation as a scientist of rare gift. Other than the Nobel Prize in Physics, Thomson went on to win several other important medals throughout a career that produced scientific discoveries that would shape scientific research for many years.
// Famous University Of Manchester
James Chadwick
Sir James Chadwick CH was an English physicist, who won the 1935 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of neutron. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Milo Yiannopoulos
Milo Yiannopoulos is a British technology journalist. Let’s have a look at his family, personal life, career, achievements, controversies, and some facts.
Phil Collins
Phil Collins (Philip David Charles Collins) is an English musician, drummer, singer, and actor. This biography profiles his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
Joseph John Thomson was born to Joseph James Thomson and his wife Emma Swindells on 18 December, 1856 in the Cheetham Hill area of Manchester located in Lancashire, United Kingdom. His father was the owner of a bookshop that dealt in antiquarian books. J.J. Thomson had one younger brother.
Thomson was a child prodigy of sorts due to his remarkable grasp of the sciences from an early age. He was allowed to take admission to Owens College in 1870, when he was only 14 years old.
In 1876, at the age of 20 Thomson won a place at Trinity College, University of Cambridge to study mathematics. He received his bachelors degree 4 years later with first class honours and was one of the two students who won the Smith’s Prize, which is a prize meant for students of mathematics and theoretical physics who are engaged in research.
In 1881, he was made a Fellow of Trinity College and 2 years later he completed his MA from Cambridge University. Thomson was also bestowed with the prestigious Adams Prize, which is awarded by Cambridge University to outstanding research efforts.
Career
Thomson started his career at Trinity College, University of Cambridge, and further enhanced his reputation as one of the most gifted mathematicians through his efforts. It was in 1884 that the members of the Royal Society elected him as a member and by the end of the same year Thomson was appointed as the Cavendish Professor of ExperimentalPhysics at the University of Cambridge.
His earliest research work was based on the structure of atoms and his first published paper was titled ‘Motion of Vortex Rings’ and in that particular paper he used pure mathematics to describe the vortex theory in relation to atomic structure as propounded by William Thomson.
Much of Thomson’s early research centred on mathematical explanation of chemical phenomena and the result was the 1886 book ‘Applications of Dynamics to Physics and Chemistry’. Six years later he published ‘Researches in Electricity and Dynamism’.
In 1896, Princeton University invited him to deliver lectures on the subjects on which he had worked. The contents of those lectures were all documented in the book ‘Discharge of Electricity through Gases’ that was published the following year.
He undertook the most important original research of his career in the year 1897 when he started is seminal research on cathode rays that led him through different alleys and one of the most significant discoveries out of that research was the discovery of the electron in relation to atoms which changed the face of the natural sciences.
In a series of lectures delivered at the famous University of Yale in 1904, he demonstrated how an atom was structured and also explained the different principles of electricity. In addition to this, Thomson stated that positive rays could be used in order to separate atoms.
He spent the latter part of his career in conducting research on isotopes that led to the discovery of positive ions and later on he went on to make such important discoveries as the radioactivity of the element potassium. On the other hand he was also able to assert that hydrogen did not have more than one electron.
Major Works
J. J. Thomson’s most important work centred around the research on cathode rays that led to the discovery of the electron and he won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906 for this path breaking discovery.
Awards & Achievements
Thomson won the Royal Medal in 1894.
The Royal Society of London awarded J. J. Thomson the Hughes Medal in 1902.
In 1906, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the discovery of the electron.
The Franklin Institute awarded him the Elliott Cresson Medal in 1910 and 12 years later the same institute gave him the Franklin Medal.
The Royal Society awarded him the Copley Medal in 1914 and a year later the Royal School of Arts awarded him the Albert Medal.
In 1918, Thomson was made a ‘Master of Trinity College’.
Personal Life & Legacy
J. J. Thomson married Rose Elisabeth Paget in 1890. They had two children- a son named George Paget Thomson and a daughter named Joan Paget Thomson. The son went on to become a Nobel Prize winning physicist.
He died at the age of 83 on 30 August, 1940. His body was buried at the famous Westminster Abbey.
// Famous Cambridge University
Stephen Fry
Stephen Fry is a comedian, actor, author, television and radio presenter. Read the biography and know all about his childhood, career, profile and timeline.
Ludwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Wittgenstein is a renowned philosopher. Read on to know about the life, career, and works of the famous Austrian philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein.
Rupert Brooke
Rupert Brooke was an English poet who is widely known for his poem ‘The Soldier’, which was a part of five war sonnets. This biography of Rupert Brooke provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
J. J. Thomson's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize for Physics (1906) | |
| 0 | Elliott Cresson Medal (1910) | |
| 0 | Copley Medal (1914) | |
| 0 | Albert Medal (1915) | |
| 0 | Franklin Medal (1922) | |
| 0 | Faraday Medal (1925) | |
| 0 | Smith's Prize (1880) | |
| 0 | Royal Medal (1894) | |
| 0 | Hughes Medal (1902) | |
J. J. Thomson biography timelines
- // 18th Dec 1856Joseph John Thomson was born to Joseph James Thomson and his wife Emma Swindells on 18 December, 1856 in the Cheetham Hill area of Manchester located in Lancashire, United Kingdom. His father was the owner of a bookshop that dealt in antiquarian books. J.J. Thomson had one younger brother.
- // 1870Thomson was a child prodigy of sorts due to his remarkable grasp of the sciences from an early age. He was allowed to take admission to Owens College in 1870, when he was only 14 years old.
- // 1876In 1876, at the age of 20 Thomson won a place at Trinity College, University of Cambridge to study mathematics. He received his bachelors degree 4 years later with first class honours and was one of the two students who won the Smith’s Prize, which is a prize meant for students of mathematics and theoretical physics who are engaged in research.
- // 1881In 1881, he was made a Fellow of Trinity College and 2 years later he completed his MA from Cambridge University. Thomson was also bestowed with the prestigious Adams Prize, which is awarded by Cambridge University to outstanding research efforts.
- // 1884Thomson started his career at Trinity College, University of Cambridge, and further enhanced his reputation as one of the most gifted mathematicians through his efforts. It was in 1884 that the members of the Royal Society elected him as a member and by the end of the same year Thomson was appointed as the Cavendish Professor of ExperimentalPhysics at the University of Cambridge.
- // 1886Much of Thomson’s early research centred on mathematical explanation of chemical phenomena and the result was the 1886 book ‘Applications of Dynamics to Physics and Chemistry’. Six years later he published ‘Researches in Electricity and Dynamism’.
- // 1890J. J. Thomson married Rose Elisabeth Paget in 1890. They had two children- a son named George Paget Thomson and a daughter named Joan Paget Thomson. The son went on to become a Nobel Prize winning physicist.
- // 1894Thomson won the Royal Medal in 1894.
- // 1896In 1896, Princeton University invited him to deliver lectures on the subjects on which he had worked. The contents of those lectures were all documented in the book ‘Discharge of Electricity through Gases’ that was published the following year.
- // 1897He undertook the most important original research of his career in the year 1897 when he started is seminal research on cathode rays that led him through different alleys and one of the most significant discoveries out of that research was the discovery of the electron in relation to atoms which changed the face of the natural sciences.
- // 1902The Royal Society of London awarded J. J. Thomson the Hughes Medal in 1902.
- // 1904In a series of lectures delivered at the famous University of Yale in 1904, he demonstrated how an atom was structured and also explained the different principles of electricity. In addition to this, Thomson stated that positive rays could be used in order to separate atoms.
- // 1906J. J. Thomson’s most important work centred around the research on cathode rays that led to the discovery of the electron and he won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906 for this path breaking discovery.
- // 1906In 1906, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the discovery of the electron.
- // 1910The Franklin Institute awarded him the Elliott Cresson Medal in 1910 and 12 years later the same institute gave him the Franklin Medal.
- // 1914The Royal Society awarded him the Copley Medal in 1914 and a year later the Royal School of Arts awarded him the Albert Medal.
- // 1918In 1918, Thomson was made a ‘Master of Trinity College’.
- // 30th Aug 1940He died at the age of 83 on 30 August, 1940. His body was buried at the famous Westminster Abbey.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Robert Andrews Millikan
Robert Andrews Millikan was an eminent American experimental physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for his work on photoelectric effect. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton was an English scientist and mathematician, who discovered gravitation and Newtonian Mechanics. Read this biography to find more on his life.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie was a Physicist and Chemist, who was world renowned for her work on radioactivity. She also was the winner of two Nobel Prize. Read this biography to get info about her life and profile.
J. J. Thomson's FAQ
What is J. J. Thomson birthday?
J. J. Thomson was born at 1856-12-18
When was J. J. Thomson died?
J. J. Thomson was died at 1940-08-30
Where was J. J. Thomson died?
J. J. Thomson was died in Cambridge, UK
Which age was J. J. Thomson died?
J. J. Thomson was died at age 83
Where is J. J. Thomson's birth place?
J. J. Thomson was born in Manchester, Lancashire, UK
What is J. J. Thomson nationalities?
J. J. Thomson's nationalities is British
Who is J. J. Thomson spouses?
J. J. Thomson's spouses is Rose Elisabeth Paget
Who is J. J. Thomson siblings?
J. J. Thomson's siblings is Frederick Vernon Thomson
Who is J. J. Thomson childrens?
J. J. Thomson's childrens is George Paget Thomson
What was J. J. Thomson universities?
J. J. Thomson studied at Cambridge University,Trinity College, Cambridge,University Of Manchester, University of Cambridge, Trinity College, Cambridge, University of Manchester, Victoria University of Manchester
What was J. J. Thomson notable alumnis?
J. J. Thomson's notable alumnis is Cambridge University, Trinity College, Cambridge, University Of Manchester
What is J. J. Thomson's inventions/discoveries?
Electrons And Isotopes And Inventing The Mass Spectrometer was invented (or discovered) by J. J. Thomson
What is J. J. Thomson's religion?
J. J. Thomson's religion is Anglican/Episcopalian
Who is J. J. Thomson's father?
J. J. Thomson's father is Joseph James Thomson
Who is J. J. Thomson's mother?
J. J. Thomson's mother is Emma Swindells
What is J. J. Thomson's sun sign?
J. J. Thomson is Sagittarius
How famous is J. J. Thomson?
J. J. Thomson is famouse as Physicist, Nobel Prize Winner