Alexandre Yersin - Discoverer of Yersinia Pestis, Family and Facts
Alexandre Yersin's Personal Details
Alexandre Émile John Yersin, popularly known as Alexandre Yersin was a Franco-Swiss bacteriologist and physician
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | September 22, 1863 |
| Died on | March 1, 1943 |
| Nationality | French, Swiss, Vietnamese |
| Famous | Physicians, Bacteriologists, Discoverer of Yersinia Pestis |
| Known as | Alexandre Emile Jean Yersin |
| Birth Place | Aubonne, Canton of Vaud, Switzerland |
| Born Country | Switzerland |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Alexandre Yersin |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Aubonne, Canton of Vaud, Switzerland |
| Famous as | Discoverer of Yersinia Pestis |
| Died at Age | 79 |
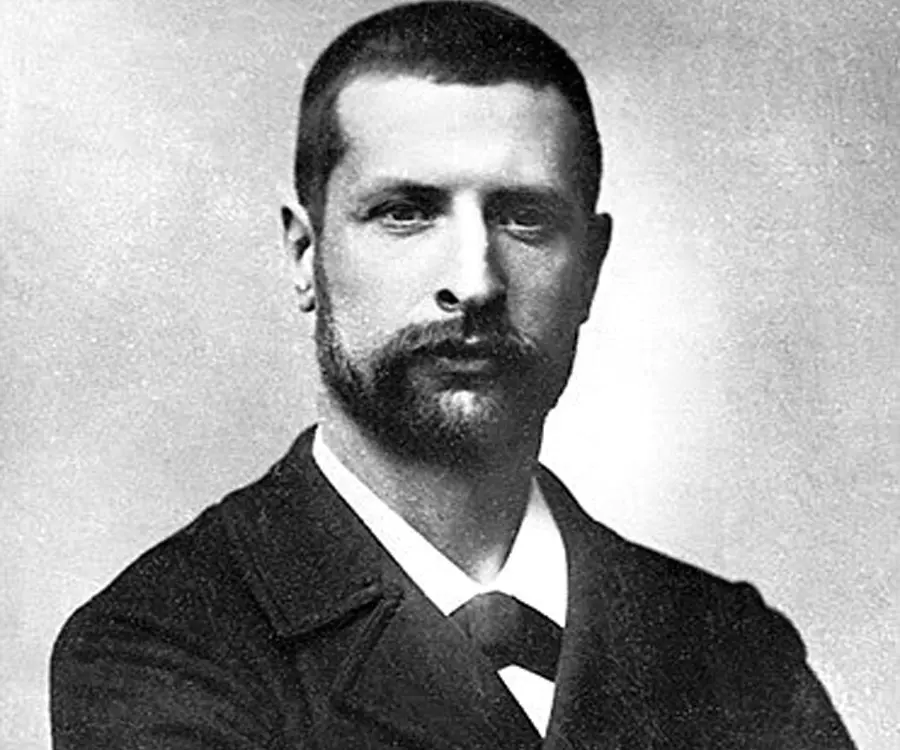
Alexandre Yersin's photo
Who is Alexandre Yersin?
Alexandre Émile John Yersin, popularly known as Alexandre Yersin was a Franco-Swiss bacteriologist. He is best remembered for discovering the bubonic plague bacillus, ‘Pasteurellapestis’, which is now known as ‘Yersinia pestis’. With his persistent effort, he helped to eradicate an epidemic disease like the plague that claimed lives of millions of people over the century. A nature lover and bright student since childhood, he spent most of his life in France and French Indochina, researching the bubonic plague. Together with fellow bacteriologist Émile Roux, Albert Calmette and Amédée Borrel, he prepared the first ever anti-plague serum to combat the disease. Later on, based on his research in this field, further investigation was directed towards antiserum treatment, use of antibiotics, and the deterrence of infection through the improvement of vaccines. These measures eventually led to the complete eradication of plague. The technique he used to make the discovery is relevant even to this day and is often used by scientists whenever they are confronted with a new contagious disease. In the last few years, a similar approach has been adapted to study the treatment and cure of diseases like AIDS, SARS, Chikungunya, and more recently, the Ebola virus.
// Famous Physicians
Al-Zahrawi
Al-Zahrawi, was an illustrious medieval Arab Muslim physician and surgeon. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and interesting facts about him.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Maria Montessori
Maria Montessori was a physician and educator who developed the approach of Montessori education. This biography of Maria Montessori provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Yersin was born on September 22, 1863 in Aubonne, Canton of Vaud, Switzerland. His family originally belonged to France. His father, also named Alexandre Yersin, was a teacher of natural sciences in Aubonne and Morges. Unfortunately, he passed away two weeks before the birth of his son.
As a child, Yersin was interested in nature and gathered various tiny organisms like insects that he studied carefully. He grew up in Morges and received his secondary education in Lausanne, before entering the university there.
He later attended the University of Marburg and the Paris Faculty of Medicine in the late 1980s. There he worked in Professor André Victor Cornil's laboratory at the Hôtel-Dieu.
Career
He met fellow bacteriologist Pierre-Paul-Émile Roux by accident. While performing an autopsy on a dead rabies patient, he incidentally cut himself. It was Roux who saved his life by injecting a new therapeutic serum.
In 1886, upon an invitation by Roux, he joined the Louis Pasteur's research laboratory of École Normale Supérieure. Soon after, he joined Roux in the development of the anti-rabies serum.
In 1888, he received his PhD degree submitting a thesis titled ‘Étudesur le Développement du Tubercule Expérimental’ following which he spent a couple of months with Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch in Berlin and continued his studies on the tubercle bacillus. He also obtained French nationality the same year.
In 1889, together with Roux, he isolated a toxin secreted by the diphtheria bacillus (bacterium) and revealed that the toxin, and not the microorganism, was the main cause of the disease.
In 1890, he served as a physician aboard steamships operating off the coast of French Indochina. This marked the beginning of his four-year exploration of the central region of Southeast Asia.
In 1894, he visited Hong Kong to investigate the Manchurian Pneumonic Plague epidemic. While in Hong Kong, he discovered the pathogen that causes plague. Incidentally, a few days earlier in Hong Kong, Dr Kitasato Shibasaburōhad had also identified a bacterium of the disease.
Yersin was able to demonstrate, for the first time in history, that the same bacillus was present in both rodents and humans, thus highlighting the probable means of transmission of the disease.
In 1895, he returned to the Institute Pasteur in Paris and prepared the first anti-plague serum in association with Émile Roux, Albert Calmette, and Amédée Borrel. Later that year, he revisited Indochina and established a small laboratory at Nha Trang to produce the serum. The laboratory later became a branch of the Pasteur Institute.
From 1895 to 1897, he continued his research on the bubonic plague. He tried the serum received from Paris in Canton and Amoy in 1896 and in 1897 he tried the same in Bombay, India, as well but got unsatisfactory results.
He decided to settle permanently in Indochina and actively participated in the advancement of medical science. He helped to establish the Hanoi Medical University in 1902 and became the institute’s first medical director, holding office for the next two years.
Meanwhile, to finance the laboratory at Nha Trang, he took up agriculture and initiated the cultivation of rubber trees, imported from Brazil to Indochina. He also cultivated corn (maize), rice, and coffee. At Honba in 1915, he tried to cultivate the quinine tree imported from South America, as quinine had malaria healing properties.
In 1934, he was nominated Honorary Director of Pasteur Institute and a member of its Board of Administration.
Major Works
In 1894, he discovered the pathogen that causes plague. It is now known as ‘Yersinia pestis’ in his honor. Through this ground-breaking discovery, he demonstrated that the same bacillus was present in both rodents and humans, leading to the identification of the probable carrier of the disease.
Awards & Achievements
His discovery, the bubonic plague bacillus, is named as ‘Yersinia pestis’ in his honour. He was honored with the Leconte Prize in 1927, in recognition of the important discovery.
On 8 January, 1902 he was appointed the first Headmaster of Hanoi Medical University by Paul Doumer, the then Governor-General of French Indochina.
After Indochina’s independence, streets named in his memory kept their name.
His house in Nha Trang has been converted into the ‘Yersin Museum’.
A private university in Da Lat, founded in 2004, has been named the ‘Yersin University’ in his memory.
Personal Life & Legacy
He died at his home in Nha Trang, Vietnam, on 1 March, 1943, during World War II. His grave in Suoi Dau has been beautified by a pagoda where rites are performed. The epitaph on his tombstone reads “Benefactor and humanist, venerated by the Vietnamese people”.
Because of his immense contribution to the field of public health, he is fondly and affectionately remembered by the people of Vietnam as ‘Ông Năm’.
// Famous Bacteriologists
Alexander Fleming
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish biologist and pharmacologist who discovered enzyme lysozyme and antibiotic penicillin. This biography of Alexander Fleming profiles his childhood, life, research, discoveries, achievements and timeline.
Ferdinand Cohn
Ferdinand Cohn was a German biologist who is considered as the father of bacteriology and microbiology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. This biography of Louis Pasteur provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Alexandre Yersin biography timelines
- // 22nd Sep 1863Yersin was born on September 22, 1863 in Aubonne, Canton of Vaud, Switzerland. His family originally belonged to France. His father, also named Alexandre Yersin, was a teacher of natural sciences in Aubonne and Morges. Unfortunately, he passed away two weeks before the birth of his son.
- // 1886In 1886, upon an invitation by Roux, he joined the Louis Pasteur's research laboratory of École Normale Supérieure. Soon after, he joined Roux in the development of the anti-rabies serum.
- // 1888In 1888, he received his PhD degree submitting a thesis titled ‘Étudesur le Développement du Tubercule Expérimental’ following which he spent a couple of months with Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch in Berlin and continued his studies on the tubercle bacillus. He also obtained French nationality the same year.
- // 1889In 1889, together with Roux, he isolated a toxin secreted by the diphtheria bacillus (bacterium) and revealed that the toxin, and not the microorganism, was the main cause of the disease.
- // 1890In 1890, he served as a physician aboard steamships operating off the coast of French Indochina. This marked the beginning of his four-year exploration of the central region of Southeast Asia.
- // 1894In 1894, he visited Hong Kong to investigate the Manchurian Pneumonic Plague epidemic. While in Hong Kong, he discovered the pathogen that causes plague. Incidentally, a few days earlier in Hong Kong, Dr Kitasato Shibasaburōhad had also identified a bacterium of the disease.
- // 1894In 1894, he discovered the pathogen that causes plague. It is now known as ‘Yersinia pestis’ in his honor. Through this ground-breaking discovery, he demonstrated that the same bacillus was present in both rodents and humans, leading to the identification of the probable carrier of the disease.
- // 1895In 1895, he returned to the Institute Pasteur in Paris and prepared the first anti-plague serum in association with Émile Roux, Albert Calmette, and Amédée Borrel. Later that year, he revisited Indochina and established a small laboratory at Nha Trang to produce the serum. The laboratory later became a branch of the Pasteur Institute.
- // 1902He decided to settle permanently in Indochina and actively participated in the advancement of medical science. He helped to establish the Hanoi Medical University in 1902 and became the institute’s first medical director, holding office for the next two years.
- // 8th Jan 1902On 8 January, 1902 he was appointed the first Headmaster of Hanoi Medical University by Paul Doumer, the then Governor-General of French Indochina.
- // 1915Meanwhile, to finance the laboratory at Nha Trang, he took up agriculture and initiated the cultivation of rubber trees, imported from Brazil to Indochina. He also cultivated corn (maize), rice, and coffee. At Honba in 1915, he tried to cultivate the quinine tree imported from South America, as quinine had malaria healing properties.
- // 1927His discovery, the bubonic plague bacillus, is named as ‘Yersinia pestis’ in his honour. He was honored with the Leconte Prize in 1927, in recognition of the important discovery.
- // 1934In 1934, he was nominated Honorary Director of Pasteur Institute and a member of its Board of Administration.
- // 1st Mar 1943He died at his home in Nha Trang, Vietnam, on 1 March, 1943, during World War II. His grave in Suoi Dau has been beautified by a pagoda where rites are performed. The epitaph on his tombstone reads “Benefactor and humanist, venerated by the Vietnamese people”.
- // 2004A private university in Da Lat, founded in 2004, has been named the ‘Yersin University’ in his memory.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Alex Lange
Alex Lange is a French-South African model, who is quite popular on Instagram. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Tina Kunakey
Tina Kunakey Di Vita is a model and wife of the French actor Vincent Cassel. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jeanne Calment
Jeanne Calment was a French supercentenarian who had the longest confirmed lifespan in human history. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, death, etc.
Alexandre Yersin's FAQ
What is Alexandre Yersin birthday?
Alexandre Yersin was born at 1863-09-22
When was Alexandre Yersin died?
Alexandre Yersin was died at 1943-03-01
Where was Alexandre Yersin died?
Alexandre Yersin was died in Nha Trang, Vietnam
Which age was Alexandre Yersin died?
Alexandre Yersin was died at age 79
Where is Alexandre Yersin's birth place?
Alexandre Yersin was born in Aubonne, Canton of Vaud, Switzerland
What is Alexandre Yersin nationalities?
Alexandre Yersin's nationalities is French, Swiss, Vietnamese
Who is Alexandre Yersin's father?
Alexandre Yersin's father is Alexandre Yersin
What is Alexandre Yersin's sun sign?
Alexandre Yersin is Virgo
How famous is Alexandre Yersin?
Alexandre Yersin is famouse as Discoverer of Yersinia Pestis