Alexander Fleming - Discovered Penicillin, Timeline and Life
Alexander Fleming's Personal Details
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish biologist and pharmacologist who discovered enzyme lysozyme and antibiotic penicillin
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | August 6, 1881 |
| Died on | March 11, 1955 |
| Nationality | British, Scottish |
| Famous | Imperial College London, Scientists, Biologists, Pharmacologists, Bacteriologists, Discovered Penicillin |
| Spouses | Dr. Amalia Koutsouri-Vourekas, Sarah |
| Siblings | Tom |
| Childrens | Robert Fleming |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Lochfield, Ayrshire, Scotland |
| Born Country | Scotland |
| Religion | Roman Catholic |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Hugh Fleming |
| Mother | Grace Stirling Morton |
| Sun Sign | Leo |
| Born in | Lochfield, Ayrshire, Scotland |
| Famous as | Biologist, Pharmacologist, Discovered Penicillin |
| Died at Age | 73 |
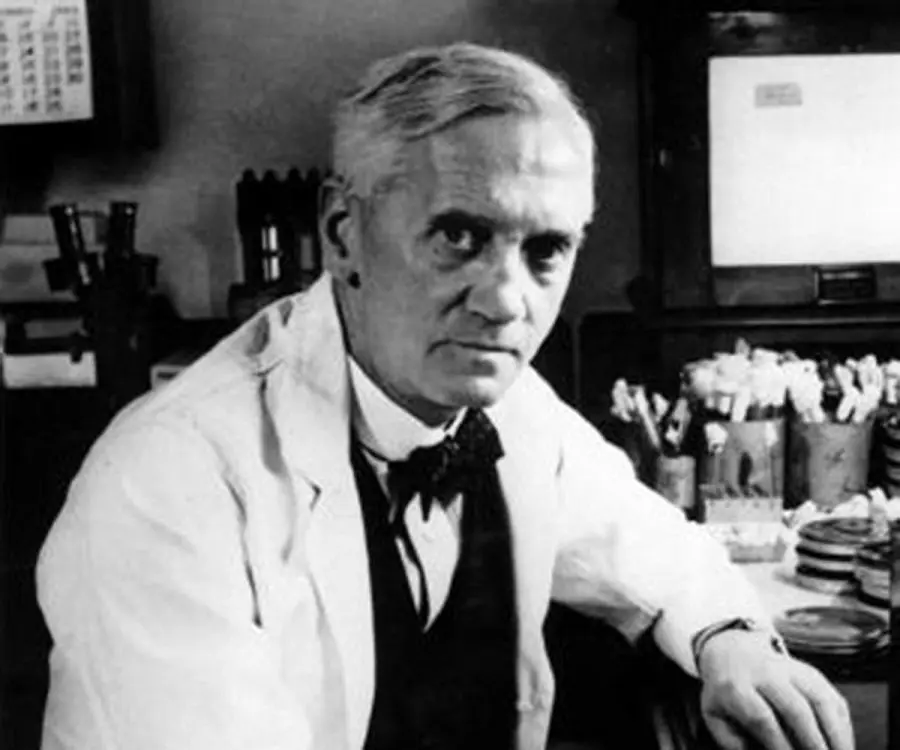
Alexander Fleming's photo
Who is Alexander Fleming?
Alexander Fleming was a great Scottish biologist and pharmacologist who made way for antibiotic medicines with his discovery of penicillin from the mould “Penicillium notatum”. Fleming’s discoveries brought new hope to mankind in battling certain diseases and treating bacterial infections. Fleming’s various works are recorded in his articles on bacteriology, immunology, and chemotherapy. He won Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945 for his outstanding and breakthrough discovery. Such is the impact of the great man that his name had even featured in the list of 100 Most Important People of the 20th Century as recently as in 1999. Present day penicillin upgrades carried put by the medicine world stand on one man’s quest and that is none other than Fleming. By discovering synthetic penicillin Fleming paved the way for preventing and fighting serious illnesses like syphilis, gangrene and tuberculosis which were never imagined of being treated before Fleming’s discoveries.
// Famous Bacteriologists
Ferdinand Cohn
Ferdinand Cohn was a German biologist who is considered as the father of bacteriology and microbiology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. This biography of Louis Pasteur provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Alexandre Yersin
Alexandre Émile John Yersin, popularly known as Alexandre Yersin was a Franco-Swiss bacteriologist and physician. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Alexander Fleming was born in Lochfield farm, Avrshire, Scotland, UK on 6th August 1881. He was born to farmer parents Hugh Fleming and Grace Stirling Morton (second wife of Hugh Fleming). He lost his father due to ill health at a tender age of seven only.
Fleming studied at Loudoun Moor School and Darvel School and moved to London at the age of thirteen to attend the Royal Polytechnic institution after attaining two scholarships for Kilmarnock Academy.
Following his elder brother Tom’s footsteps he also joined St. Mary’s Hospital Medical School (Paddington) in 1903 to study medicine which he completed with an MBBS degree in 1906.
Career
Alexander Fleming joined the Research department at St Mary's and worked as an assistant bacteriologist to Sir Almroth Wright who was a master in vaccine therapy and immunology.
In1908 Fleming joined St Mary's as a lecturer after being awarded a gold medal in bacteriology, and served there till 1914.
Fleming practiced as a venereologist between 1909 and 1914. He became the first doctor to administer a drug against syphilis called arsphenamine (Salvarsan).
In 1928 he became a professor of bacteriology at the University of London.
He was a part of the Royal Army Medical Corps as a captain during the World War I and served in the war field hospitals in France where he studied the effect of antiseptics on the wounds.
He returned to St. Mary’s as assistant director of the inoculation department and later became the principal of the same in 1946 which was later renamed as Wright-Fleming Institute.
In 1951, he joined the University Of Edinburg as rector for three years.
Major Works
Antiseptics do more harm than good: While serving the field hospitals during the World War I in 1914 he reached the conclusion that antiseptics such as carbolic acid, boric acid and hydrogen peroxide (used to treat wounds) do more harm than cure. He found that they only cured surface wounds and failed to heal deeper. Along with Almroth Wright, he suggested an alternative of saline water for treatment.
Discovery Of Lysozyme
November 1921 saw the discovery of the antiseptic enzyme lysozyme. It happened when Fleming dropped a drop of mucus from his nose on a culture of bacteria. In the quest of finding its effect on the bacterial growth, he mixed it and studied for a few days, thus leading to this significant discovery for mankind.
Other body fluids such as saliva and tears were studied with these bacteria and observed the failure of bacterial growth, thus rendering natural immunity from a number of health issues.
Today lysozyme is used in treating cold and throat infections, athlete’s foot and also as a preservative in food.
Discovery Of Penicillin
Having seen many soldiers succumbing to death due to Sepsis during the World War, Fleming got deeply involved in his search for antibacterial agents after having realized that antiseptics harmed the immunity system in the longer run.
Since 1927 Fleming had engrossed himself in studying about staphylococci. It was an accidental finding on September 3, 1928, wherein one on his fungus contaminated staphylococci culture destroyed all the surrounding staphylococci culture while other staphylococci colonies somewhat away were normal.
After further investigations and experiments, he identified this mould as being from was known to be Penicillium genus which hampered bacterial growth.
He initially called it “mould juice” but finally named the substance it produced Penicillin on 7th March 1929.
Though he had discovered penicillin but the challenge of stabilizing, purifying and producing it in large quantity still troubled Fleming. He continued experimenting until 1940 and then abandoned penicillin.
Just after Fleming abandoned his further research on penicillin, Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain at the Radcliffe Infirmary in Oxford started working on it with aim from the U.S. and the British government.
The mass production finally started after the Pearl Harbor accident leading to a level of production that changed the face of battlefield treatment and infection control since 1944.
Awards & Achievements
Alexander Fleming, Florey and Chain collectively received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1945.
He was also awarded the Hunterian Professorship by the Royal College of Surgeons of England and has a number of other honorary degrees from various universities in America and Europe.
He became the president of the Society for general microbiology and also a member of the pontifical academy of science. Fleming had made it to almost every medical and scientific society in the world as an honorary member.
The laboratory where Fleming discovered penicillin is preserved as the Alexander Fleming Laboratory Museum in St. Mary's Hospital, Paddington.
The Imperial College School of Medicine has ‘The Sir Alexander Fleming Building’ as one of its main preclinical teaching areas.
The Royal Polytechnic Institution (presently the University of Westminster) has named one of its residential halls as Alexander Fleming House.
By the year 2000, penicillin was marked as the most important discovery of the millennium by three major Swedish magazines.
Personal Life and Legacy
On 24 December 1915, Alexander Fleming married Sarah Marion McElroy of Ireland, a trained nurse. Their only son Robert, born in 1924, followed his father to become a medical practitioner.
Fleming was knighted as Knight Bachelor by King George VI to become Sir Alexander Fleming in 1944.
Post Sarah's death in 1949, Fleming remarried a colleague at St. Mary’s, Dr.Amalia Koutsouri-Vourekas, on 9 April 1953 who died in 1986.
Fleming succumbed to a heart attack at the age of 73 on 11 March 1955 and was cremated at St. Paul’s Catheral.
Fleming was always modest in accepting his role in the discovery of Penicillin and described his popularity as ‘Fleming Myth". Nonetheless, he always praised Florey and Chain but still turned out to become the hero of modern healthcare.
Sir Henry Harris’ remark says it all: "Without Fleming, no Chain; without Chain, no Florey; without Florey, no Heatley; without Heatley, no penicillin”.
On his tour to America, this great scientist and Nobel Prize winner was offered a gift of $100,000 as a token of respect which he did not accept rather donated to the laboratories at St. Mary’s Hospital Medical School.
// Famous Imperial College London
Roger Bannister
Roger Bannister is an English doctor, academic and a former athlete. Check out this biography to get detailed information on his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Brian May
Brian May is a legendary and prolific guitarist from the famous rock band ‘Queen’. Explore this biography to learn more about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
John Wilkinson
John Wilkinson was a British entrepreneur who pioneered the manufacture of cast iron’. This biography of John Wilkinson provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Alexander Fleming's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1945) | |
Alexander Fleming biography timelines
- // 6th Aug 1881Alexander Fleming was born in Lochfield farm, Avrshire, Scotland, UK on 6th August 1881. He was born to farmer parents Hugh Fleming and Grace Stirling Morton (second wife of Hugh Fleming). He lost his father due to ill health at a tender age of seven only.
- // 1903 To 1906Following his elder brother Tom’s footsteps he also joined St. Mary’s Hospital Medical School (Paddington) in 1903 to study medicine which he completed with an MBBS degree in 1906.
- // 1908 To 1914In1908 Fleming joined St Mary's as a lecturer after being awarded a gold medal in bacteriology, and served there till 1914.
- // 1909 To 1914Fleming practiced as a venereologist between 1909 and 1914. He became the first doctor to administer a drug against syphilis called arsphenamine (Salvarsan).
- // 1914Antiseptics do more harm than good: While serving the field hospitals during the World War I in 1914 he reached the conclusion that antiseptics such as carbolic acid, boric acid and hydrogen peroxide (used to treat wounds) do more harm than cure. He found that they only cured surface wounds and failed to heal deeper. Along with Almroth Wright, he suggested an alternative of saline water for treatment.
- // 24th Dec 1915 To 1924On 24 December 1915, Alexander Fleming married Sarah Marion McElroy of Ireland, a trained nurse. Their only son Robert, born in 1924, followed his father to become a medical practitioner.
- // Nov 1921November 1921 saw the discovery of the antiseptic enzyme lysozyme. It happened when Fleming dropped a drop of mucus from his nose on a culture of bacteria. In the quest of finding its effect on the bacterial growth, he mixed it and studied for a few days, thus leading to this significant discovery for mankind.
- // 1927 To 3rd Sep 1928Since 1927 Fleming had engrossed himself in studying about staphylococci. It was an accidental finding on September 3, 1928, wherein one on his fungus contaminated staphylococci culture destroyed all the surrounding staphylococci culture while other staphylococci colonies somewhat away were normal.
- // 1928In 1928 he became a professor of bacteriology at the University of London.
- // 7th Mar 1929He initially called it “mould juice” but finally named the substance it produced Penicillin on 7th March 1929.
- // 1940Though he had discovered penicillin but the challenge of stabilizing, purifying and producing it in large quantity still troubled Fleming. He continued experimenting until 1940 and then abandoned penicillin.
- // 1944The mass production finally started after the Pearl Harbor accident leading to a level of production that changed the face of battlefield treatment and infection control since 1944.
- // 1944Fleming was knighted as Knight Bachelor by King George VI to become Sir Alexander Fleming in 1944.
- // 1945Alexander Fleming, Florey and Chain collectively received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1945.
- // 1946He returned to St. Mary’s as assistant director of the inoculation department and later became the principal of the same in 1946 which was later renamed as Wright-Fleming Institute.
- // 1951In 1951, he joined the University Of Edinburg as rector for three years.
- // 11th Mar 1955Fleming succumbed to a heart attack at the age of 73 on 11 March 1955 and was cremated at St. Paul’s Catheral.
- // 2000By the year 2000, penicillin was marked as the most important discovery of the millennium by three major Swedish magazines.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Gabe Newell
Gabe Newell is an American computer programmer and businessman, best known as the co-founder of ‘Valve Corporation.’ This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Grigori Perelman
Grigori Perelman is a Russian mathematician who is best known for his contributions to Riemannian geometry and geometric topology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Eduardo Saverin
Eduardo Luiz Saverin is a Brazilian internet entrepreneur and investor. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements, and timeline
Alexander Fleming's FAQ
What is Alexander Fleming birthday?
Alexander Fleming was born at 1881-08-06
When was Alexander Fleming died?
Alexander Fleming was died at 1955-03-11
Where was Alexander Fleming died?
Alexander Fleming was died in London
Which age was Alexander Fleming died?
Alexander Fleming was died at age 73
Where is Alexander Fleming's birth place?
Alexander Fleming was born in Lochfield, Ayrshire, Scotland
What is Alexander Fleming nationalities?
Alexander Fleming's nationalities is British, Scottish
Who is Alexander Fleming spouses?
Alexander Fleming's spouses is Dr. Amalia Koutsouri-Vourekas, Sarah
Who is Alexander Fleming siblings?
Alexander Fleming's siblings is Tom
Who is Alexander Fleming childrens?
Alexander Fleming's childrens is Robert Fleming
What was Alexander Fleming universities?
Alexander Fleming studied at Imperial College London, Kilmarnock Academy (1900), University of Westminster, Imperial College London
What was Alexander Fleming notable alumnis?
Alexander Fleming's notable alumnis is Imperial College London
What is Alexander Fleming's inventions/discoveries?
Discovery Of Penicillin was invented (or discovered) by Alexander Fleming
What is Alexander Fleming's religion?
Alexander Fleming's religion is Roman Catholic
Who is Alexander Fleming's father?
Alexander Fleming's father is Hugh Fleming
Who is Alexander Fleming's mother?
Alexander Fleming's mother is Grace Stirling Morton
What is Alexander Fleming's sun sign?
Alexander Fleming is Leo
How famous is Alexander Fleming?
Alexander Fleming is famouse as Biologist, Pharmacologist, Discovered Penicillin