Wallace Carothers - Nylon, Timeline and Life
Wallace Carothers's Personal Details
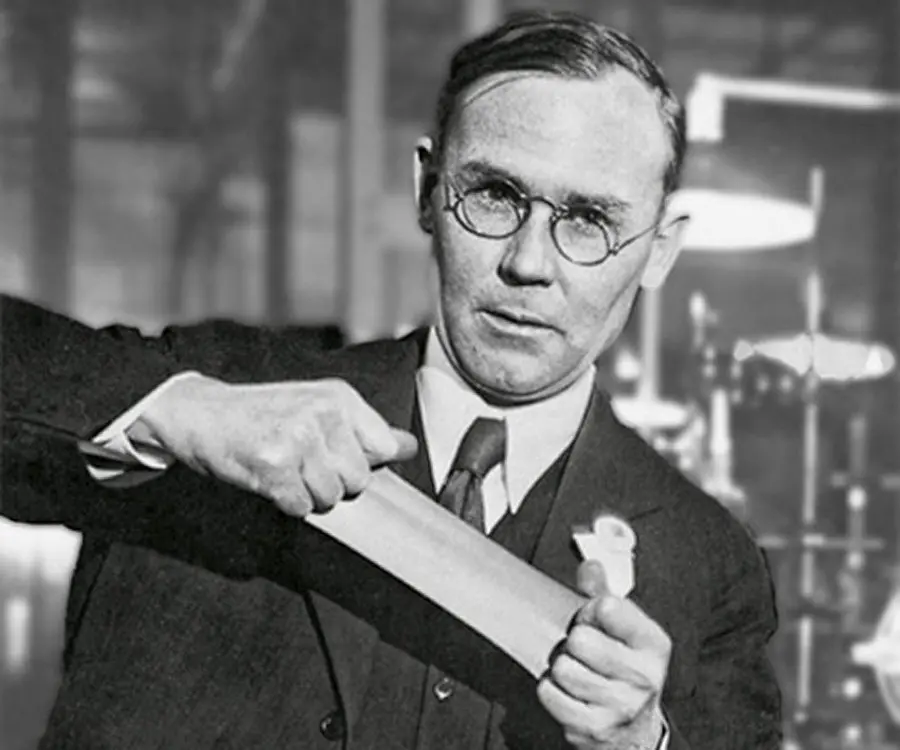
Wallace Hume Carothers was an American chemist who invented nylon and neoprene
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | April 27, 1896 |
| Died on | April 29, 1937 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | University Of Illinois, Inventors & Discoverers, Chemists, Organic Chemists, Inventor of Neoprene, Nylon |
| Known as | Wallace Hume Carothers |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Cause of death |
|
| Birth Place | Burlington, Iowa, United States |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Taurus |
| Born in | Burlington, Iowa, United States |
| Famous as | Inventor of Neoprene & Nylon |
| Died at Age | 41 |
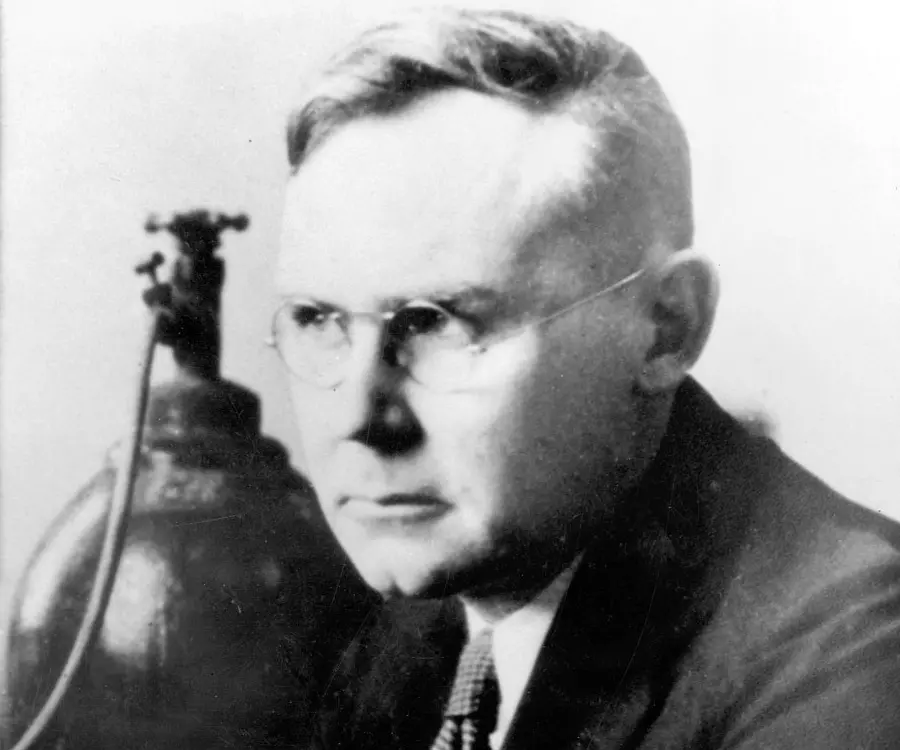
Wallace Carothers's photo
Who is Wallace Carothers?
Wallace Hume Carothers was an American chemist who invented nylon and neoprene. The name of Wallace Carothers stands out from the list of the world’s greatest inventors. His contributions to organic chemistry were recognized as outstanding and, in spite of the relatively short span of time for his productive accomplishments, he became a leader in his field with an enviable international reputation. He was a brilliant scientist but a melancholic man who was happiest out of the limelight, beavering away in his laboratory. Carothers made the breakthrough that would change the very fabric of the modern world.Carothers called it nylon and, thanks to its myriad uses, he was responsible for a 20th century industrial revolution. Clothes, ropes, weapons and machines could all be manufactured from this versatile and durable first form of plastic. It was the material that helped the Allies win the Second World War and, even now, nylon and its spin-offs surround us. Yet its inventor never lived to see the remarkable impact of nylon. Carothers was a tortured soul who struggled to cope away from his beloved test tubes and took his own life at the age of just 41.
Childhood & Early Life
Carothers was born on April 27, 1937 in Burlington, Iowa. Wallace carothers was the first scientist in the family.
His father, Ira Hume Carothers, taught at a country school. Later he entered the field of commercial education and for forty-five years engaged himself in that type of work as teacher and vice-president in the Capital City Commercial College, Des Moines, Iowa.
His mother, Mary Evalina McMullin of Burlington, Iowa, exerted a powerful influence and guidance in the earlier years of Carothers’s life.
Carothers was especially devoted to his sister, Isobel. Her death in January, 1936, was a shock to him and he was never able to reconcile himself completely to her loss.
Carothers was the oldest of four children. His education began in the public schools of Des Moines, Iowa, where his parents moved when he was just five. In 1914 he graduated from the North High School. As a growing boy he had zest for work as well as play. He enjoyed tools and mechanical things and spent much time in experimenting.
His school work was characterized by thoroughness. It was his habit to leave no task unfinished or done in a careless manner.
He entered the Capital City Commercial College in the fall of 1914 and graduated in the accountancy and secretarial curriculum in July, 1915, taking considerably less time than the average.
Career
He entered Tarkio College, Tarkio, Missouri, in September, 1915, to pursue a scientific course, and simultaneously accepted a position of an assistant in the Commercial Department.
He continued in this capacity for two years and then was made an assistant in English, although he had specialized in chemistry from the time he entered college.
During the World War the head of the department of chemistry, Dr. Arthur M. Pardee, was called to another institution, and Tarkio College found it impossible to secure a fully equipped teacher of chemistry. Carothers, who previously had taken all of the chemistry courses offered, was appointed to take over the instruction.
Leaving Tarkio College in 1920 with his bachelor of science degree, he enrolled in the chemistry department of the University of Illinois where he completed the requirements for the master of arts degree in the summer of 1921.
His former instructor at Tarkio College, then head of the chemistry department at the University of South Dakota, desired a young instructor to handle courses in analytical and physical chemistry and was fortunate in securing Carothers for this position during the year, 1921-1922.
He went to South Dakota only with the intention of securing sufficient funds to enable him to complete his graduate work, but the careful and adequate preparation of his courses, as well as his care of the students under his direction, showed that he could be a very successful teacher of chemistry.
He returned to the University of Illinois in 1922 to complete his studies for the degree of doctor of philosophy, which he received in 1924. His major work was in organic chemistry with a thesis under the direction of Dr. Roger Adams, on the catalytic reduction of aldehydes with platinum-oxide platinumblack and on the effect of promoters and poisons on this catalyst in the reduction of various organic compounds. His minors were physical chemistry and mathematics.
In 1920-1921 he held an assistantship for one semester in inorganic chemistry and for one semester in organic chemistry.
He was a research assistant during 1922-1923, and during 1923-1924 held the Carr Fellowship, the highest award offered at that time by the department of chemistry at Illinois.
At graduation he was considered by the staff as one of the most brilliant students who had ever been awarded the doctor's degree. A vacancy on the staff of the chemistry department in the University of Illinois made it possible to appoint him as an instructor in organic chemistry in the fall of 1924. In this capacity he continued with unusual success for two years, teaching qualitative organic analysis and two organic laboratory courses, one for premedical students and the other for chemists.
In 1926 Harvard University was in need of an instructor in organic chemistry. After carefully surveying the available candidates from the various universities of the country, Carothers was selected. In this new position he taught during the first year a course in experimental organic chemistry and an advanced course in structural chemistry, and during the second year he gave the lectures and laboratory instruction in elementary organic chemistry.
In 1928 the du Pont Company had completed plans to embark on a new program of fundamental research at their central laboratory, the Experimental Station at Wilmington, Delaware. Carothers was selected to head the research in organic chemistry.
Major Works
It was his discovery that it was possible to add hydrogen chloride to monovinylacetylene with formation of 2-chloro-i, 3-butadiene, called chloroprene. This substance is analogous structurally to isoprene but polymerizes several hundreds of times more rapidly and leads to a product much superior to all previously known synthetic rubbers. Carothers' work laid the foundation for the development by other chemists and by chemical engineers of the du Pont Company of the commercial product which has found wide industrial use and which is marketed as neoprene.
He investigated the means by which polymers structurally analogous to cellulose and silk could be prepared, and synthesized a large number. These materials constituted the first completely synthetic fibres with a degree of strength, orientation, and pliability comparable with natural fibres. This investigation led du Pont to set up a plant in Seaford, Delaware, which cost upwards of eight million dollars, for producing a new textile yarn to be known as nylon.
Awards & Achievements
In 1929 he was elected Associate Editor of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
His achievements were recognized by his election to the National Academy of Sciences in 1936—the first organic chemist associated with industry to be elected to that organization.
Personal Life & Legacy
On February 21, 1936, he married Helen Everett Sweetman of Wilmington, Delaware. A daughter, Jane, was born November 27, 1937, after the death of Carothers.
Carothers committed suicide on April 29, 1937. In 1937, his sister had died suddenly and this loss cast him into a depression, which ultimately resulted into his suicide.
// Famous Organic Chemists
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist who is best known for his discovery of the periodic law. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Aleksandr Borodin
Aleksandr Borodin was a prodigal Russian music composer and scientist. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
Hermann Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer was a Nobel Prize winning chemist from Germany who is known for inventing the ‘Fischer Projection’ method. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Wallace Carothers biography timelines
- // 1914Carothers was the oldest of four children. His education began in the public schools of Des Moines, Iowa, where his parents moved when he was just five. In 1914 he graduated from the North High School. As a growing boy he had zest for work as well as play. He enjoyed tools and mechanical things and spent much time in experimenting.
- // 1914 To 1915He entered the Capital City Commercial College in the fall of 1914 and graduated in the accountancy and secretarial curriculum in July, 1915, taking considerably less time than the average.
- // 1915He entered Tarkio College, Tarkio, Missouri, in September, 1915, to pursue a scientific course, and simultaneously accepted a position of an assistant in the Commercial Department.
- // 1920 To 1921Leaving Tarkio College in 1920 with his bachelor of science degree, he enrolled in the chemistry department of the University of Illinois where he completed the requirements for the master of arts degree in the summer of 1921.
- // 1920 To 1921In 1920-1921 he held an assistantship for one semester in inorganic chemistry and for one semester in organic chemistry.
- // 1921 To 1922His former instructor at Tarkio College, then head of the chemistry department at the University of South Dakota, desired a young instructor to handle courses in analytical and physical chemistry and was fortunate in securing Carothers for this position during the year, 1921-1922.
- // 1922 To 1924He returned to the University of Illinois in 1922 to complete his studies for the degree of doctor of philosophy, which he received in 1924. His major work was in organic chemistry with a thesis under the direction of Dr. Roger Adams, on the catalytic reduction of aldehydes with platinum-oxide platinumblack and on the effect of promoters and poisons on this catalyst in the reduction of various organic compounds. His minors were physical chemistry and mathematics.
- // 1924At graduation he was considered by the staff as one of the most brilliant students who had ever been awarded the doctor's degree. A vacancy on the staff of the chemistry department in the University of Illinois made it possible to appoint him as an instructor in organic chemistry in the fall of 1924. In this capacity he continued with unusual success for two years, teaching qualitative organic analysis and two organic laboratory courses, one for premedical students and the other for chemists.
- // 1926In 1926 Harvard University was in need of an instructor in organic chemistry. After carefully surveying the available candidates from the various universities of the country, Carothers was selected. In this new position he taught during the first year a course in experimental organic chemistry and an advanced course in structural chemistry, and during the second year he gave the lectures and laboratory instruction in elementary organic chemistry.
- // 1928In 1928 the du Pont Company had completed plans to embark on a new program of fundamental research at their central laboratory, the Experimental Station at Wilmington, Delaware. Carothers was selected to head the research in organic chemistry.
- // 1929In 1929 he was elected Associate Editor of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
- // 1936Carothers was especially devoted to his sister, Isobel. Her death in January, 1936, was a shock to him and he was never able to reconcile himself completely to her loss.
- // 1936His achievements were recognized by his election to the National Academy of Sciences in 1936—the first organic chemist associated with industry to be elected to that organization.
- // 21st Feb 1936 To 27th Nov 1937On February 21, 1936, he married Helen Everett Sweetman of Wilmington, Delaware. A daughter, Jane, was born November 27, 1937, after the death of Carothers.
- // 27th Apr 1937Carothers was born on April 27, 1937 in Burlington, Iowa. Wallace carothers was the first scientist in the family.
- // 29th Apr 1937Carothers committed suicide on April 29, 1937. In 1937, his sister had died suddenly and this loss cast him into a depression, which ultimately resulted into his suicide.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie was a Physicist and Chemist, who was world renowned for her work on radioactivity. She also was the winner of two Nobel Prize. Read this biography to get info about her life and profile.
Amedeo Avogadro
Amedeo Avogadro was an Italian scientist who formulated what is now known as Avogadro's law. This biography of Amedeo Avogadro provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn was a Nobel Prize winning German scientist who discovered the phenomenon of nuclear fission and the element protactinium. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Wallace Carothers's FAQ
What is Wallace Carothers birthday?
Wallace Carothers was born at 1896-04-27
When was Wallace Carothers died?
Wallace Carothers was died at 1937-04-29
Where was Wallace Carothers died?
Wallace Carothers was died in Philadelphia
Which age was Wallace Carothers died?
Wallace Carothers was died at age 41
Where is Wallace Carothers's birth place?
Wallace Carothers was born in Burlington, Iowa, United States
What is Wallace Carothers nationalities?
Wallace Carothers's nationalities is American
What was Wallace Carothers universities?
Wallace Carothers studied at University Of Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Tarkio College
What was Wallace Carothers notable alumnis?
Wallace Carothers's notable alumnis is University Of Illinois
What is Wallace Carothers's inventions/discoveries?
Nylon was invented (or discovered) by Wallace Carothers
What is Wallace Carothers's cause of dead?
Wallace Carothers dead because of Suicide
What is Wallace Carothers's sun sign?
Wallace Carothers is Taurus
How famous is Wallace Carothers?
Wallace Carothers is famouse as Inventor of Neoprene & Nylon