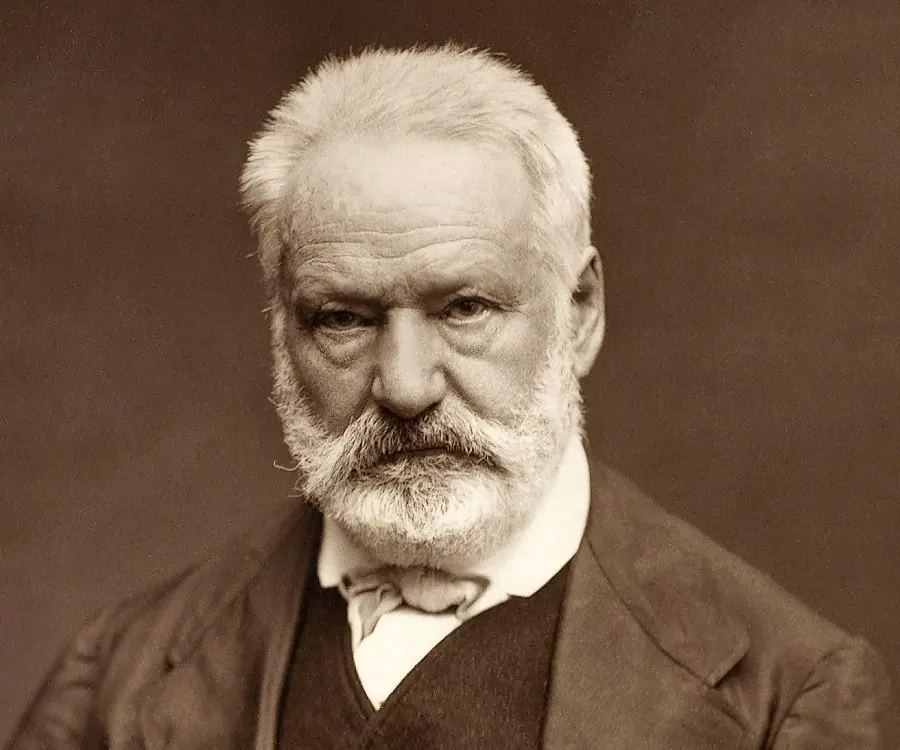Victor Hugo - Author, Birthday and Childhood
Victor Hugo's Personal Details
Victor Hugo was a French poet, novelist and a leading figure of the Romantic Movement in France
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | February 26, 1802 |
| Died on | May 22, 1885 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Activists, Human Rights Activists, Poets, Author, Poets |
| Spouses | Adèle Foucher |
| Siblings | Abel Joseph Hugo, Eugène Hugo |
| Childrens | Adèle |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | France |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Joseph Léopold Sigisbert Hugo |
| Mother | Sophie Trébuchet |
| Sun Sign | Pisces |
| Born in | France |
| Famous as | Author & Poet |
| Died at Age | 83 |
// Famous Poets
Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman was an American poet, journalist and humanist. Read this brief biography to find more on his life & timeline.
Sarojini Naidu
Sarojini Naidu was an Indian freedom fighter and poet. Read this brief biography to find more on her life.
Pablo Neruda
Pablo Neruda was a Chilean poet, politician and Nobel laureate. Go through this biography to learn more about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
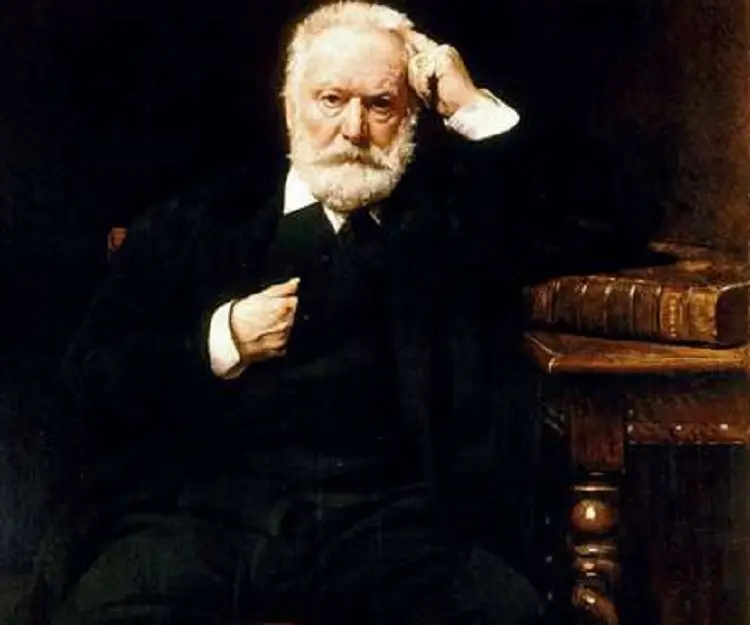
Victor Hugo's photo
Who is Victor Hugo?
Victor Hugo was a renowned poet, novelist and playwright of the Romantic Movement in 19th century France. He is considered by many as one of the greatest and best-known French authors of all times. He was also a political statesman and human rights activist, although he is primarily remembered for his literary creations like poetry and novels. In France, he is most revered for his poetry followed by his novels and dramas. Some examples of his outstanding poetry are ‘Les Contemplations’ and ‘Les Legende des siecles’. His most popular novels are ‘Les Misérables’, ‘Notre-Dame de Paris’ (‘The Hunchback of Notre Dame’), and ‘Les Travailleurs de la Mer’. His work explores the political and social issues of his time and his books have been translated to several foreign languages. He also produced more than 4,000 beautiful drawings. He grew up embracing the Catholic Royalist faith followed by his mother but gradually became a freethinking republican in the events leading to the French Revolution. He was the foremost supporter of the Romantic Movement in France and campaigned for social causes like the abolition of capital punishment. He also helped to establish the Third Republican and democracy in France.
// Famous Author
Joyce Meyer
Joyce Meyer is a Christian author and speaker. This biography provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Suze Orman
Suze Orman is an American television host, financial advisor, author and motivational speaker, famous for her ‘The Suze Orman Show’ on CNBC. This biography profiles her childhood, life, career, works, achievements and timeline.
Robert Graysmith
Robert Graysmith is an author best identified for his works on the ‘Zodiac Killer case’. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Childhood & Early Life
Victor Hugo was born on 26 February 1802 in Besancon, France, to Joseph Leopold Sigisbert Hugo and Sophie Trebuchet. He was the third-born and the youngest son of the family. His elder siblings were Abel Joseph Hugo and Eugene Hugo.
His father, Joseph was a freethinking republican. He was an important officer in the army of Napoleon and considered him his idol. On the other hand, his mother Sophie was a devoted Catholic Royalist. The political incompatibility of his parents adversely affected their family life.
Joseph’s job required him to move constantly from one place to another. Travelling with his father to different countries, young Hugo developed a liking for nature and beauty. By 1803, his mother was exhausted of travelling and decided to stay back in Paris while his father went to Italy. She took up the responsibility of Victor’s education and successfully imbibed in him the Catholic faith.
Career
Victor Hugo was inspired by François-René de Chateaubriand, the founder of Romanticism in French literature. In 1822 at the age of 20, his first volume of poetry ‘Odes et Poésies Diverses’ was published which established his reputation as a poet and earned him a royal pension from Louis XVIII. Four years later, his second collection of poetry ‘Odes et Ballades’ (1826) strengthened his reputation further.
Meanwhile, his first novel ‘Han d'Islande’ was published in 1823, followed by his second novel ‘Bug-Jargal’, published in 1826. From 1829 – 1840, he published five collections of poetry: ‘Les Orientales’ (1829); ‘Les Feuilles d'automne’ (1831); ‘Les Chants du crépuscule’ (1835); ‘Les Voix intérieures’ (1837); and ‘Les Rayons et les ombres’ (1840).
In 1829, he also published a fiction ‘Le Dernier jour d'un condamné’ (The Last Day of a Condemned Man), his first mature work. The work was based upon the real life story of a murderer and reflected the acute social conscience.
His first full-length book was ‘Notre- Dame de Paris’ (The Hunchback of Notre Dame), published in 1831. It was immensely successful and was promptly translated to a number of foreign languages. It made the Cathedral of Notre Dame and other Renaissance buildings popular among the people of Europe and encouraged their preservation.
Around 1830, he embarked on writing the most important novel of his literary career: ‘Les Misérables’. The work explored social misery and injustice. After several years of writing followed by planned marketing campaigns by the Belgian publishing house Lacroix and Verboeckh, the novel was finally published in 1862. The success of the novel turned his fortune.
In 1841, after three futile attempts, he was elected to the Académie française. Thereafter, he became more and more involved in French politics, supporting the Republic form of government. King Louis-Philippe promoted him and made him a part of the Higher Chamber as a ‘pair de France’.
After the Revolution of 1848 and the establishment of the Second Republic, he was elected to the Parliament as a conservative. A few years later, when Napoleon III seized power in 1851 and established an anti-parliamentary constitution, he objected openly calling him a traitor. As a result he was exiled; he settled in Guernsey and lived there until 1870.
During his exile, he published two famous political pamphlets against Napoleon III, ‘Napoléon le Petit’ and ‘Histoire d'un crime’. Although the pamphlets were banned in France, they managed to create a strong impact there nonetheless.
In 1859, when amnesty was granted to all political exiles by Napoleon III, he chose not to return to France and imposed upon himself a self-exile. He was determined to return only when the Napoleon dynasty was removed from power.
Meanwhile on the literary front, he published his next novel ‘Les Travailleurs de la Mer’ (Toilers of the Sea) in 1866. The story portrayed a man's battle with the sea and its deadly creatures, a symbolic theme not far removed from the political turmoil prevailing at the moment. The success of his previous novel, ‘Les Misérables’ ensured that ‘Les Travailleurs de la Mer’ was also a success.
With his next novel ‘L'Homme Qui Rit’ (The Man Who Laughs), he again returned to social issues. The book published in 1869, depicted a critical image of the upper class. It, however, failed to secure a distinctive position in French literature.
After the fall of Napoleon III and the establishment of the Third Republic in France, Victor Hugo returned to his country in 1870 and was soon appointed to the National Assembly and the Senate. He also became a founding member of the Association Littéraire et Artistique Internationale. Two years later in 1872, he lost the National Assembly election.
The writings of his last few years were murky, highlighting themes like God, Satan, and death. His last novel ‘Quatrevingt-treize’ (Ninety-Three) was published in 1874. The book presented a picture of the atrocities committed during the French Revolution. Regardless of the completely new subject matter, it failed to achieve success.
Major Works
In 1831, Victor Hugo published the Gothic novel, ‘Notre-Dame de Paris’ (The Hunchback of Notre Dame). The story is set in the late medieval period of Paris, France, and presents a grim picture of the society that humiliates and rejects the hunchback Quasimodo. The novel was immensely successful.
Another of his famous novels, ‘Les Misérables’ was published in 1862 after several years of hard work. The story involving several characters primarily unravels the destiny of a convict Jean Valjean, a victim of the society who had been imprisoned for 19 years for stealing a loaf of bread. The novel was an instant success and was quickly translated into several languages.
Personal Life & Legacy
Victor Hugo’s education in his childhood was largely supervised by his mother who was a devout Catholic Royalist. Hence his early literary works reflect his commitment to both the King and Faith. Later however, during the events leading up to France's 1848 Revolution, he began to rebel against the Catholic beliefs and championed Republicanism and Free-thought instead.
Much against his mother's approval, he got secretly engaged to his childhood sweetheart Adèle Foucher and married her later in 1822, after his mother’s death. The couple had their first child, Léopold in 1823 but the boy did not survive. In August 1824, the couple's second child, Léopoldine was born followed by Charles in November 1826, François-Victor in October 1828, and Adèle in August 1830.
His daughter Léopoldine died in 1843 at the young age of 19, shortly after her marriage to Charles Vacquerie. She drowned in the Seine at Villequier when her boat overturned; her husband also died trying to save her. Her death left Hugo devastated.
He lost his wife in 1868. In the next decade, he lost two sons between 1871 and 1873. His mistress, Juliet Drouet died in 1883.
In 1878, he began suffering from cerebral congestion. On 22 May 1885 at the age of 83, Victor Hugo breathed his last. His death was lamented by the whole country. His body was rested in state beneath the Arc de Triomphe before burial in the Panthéon.
His residences - Hauteville House, Guernsey and 6, Place des Vosges, Paris have been preserved as museums. The house where he stayed in Vianden, Luxembourg, in 1871 has also become a memorial museum.
Trivia
To honor his entering his 80th year in 1881, celebrations across France were organized which included the largest parade in French history. Thereafter, several streets and roads all over France were named after him. His portrait was also placed on French Franc banknotes.
He is respected as a saint in the Vietnamese religion of Cao Đài.
// Famous Human Rights Activists
Michael Bolton
Michael Bolton is a Grammy Award winning singer and songwriter. Read this biography to learn more about his childhood, profile, life and timeline.
Maggie McGuane
Maggie McGuane is the daughter of Canadian-American actress and activist Margot Kidder. Check out this biography to know about her family, personal life, age, birthday, etc.
Anita Roddick
Anita Roddick was the founder of ‘The Body Shop’, the popular cosmetic brand. This article offers detailed information about her life, career, profile, humanitarian works and timeline
Victor Hugo biography timelines
- // 26th Feb 1802Victor Hugo was born on 26 February 1802 in Besancon, France, to Joseph Leopold Sigisbert Hugo and Sophie Trebuchet. He was the third-born and the youngest son of the family. His elder siblings were Abel Joseph Hugo and Eugene Hugo.
- // 1822 To 1826Victor Hugo was inspired by François-René de Chateaubriand, the founder of Romanticism in French literature. In 1822 at the age of 20, his first volume of poetry ‘Odes et Poésies Diverses’ was published which established his reputation as a poet and earned him a royal pension from Louis XVIII. Four years later, his second collection of poetry ‘Odes et Ballades’ (1826) strengthened his reputation further.
- // 1822 To 1830Much against his mother's approval, he got secretly engaged to his childhood sweetheart Adèle Foucher and married her later in 1822, after his mother’s death. The couple had their first child, Léopold in 1823 but the boy did not survive. In August 1824, the couple's second child, Léopoldine was born followed by Charles in November 1826, François-Victor in October 1828, and Adèle in August 1830.
- // 1823 To 1840Meanwhile, his first novel ‘Han d'Islande’ was published in 1823, followed by his second novel ‘Bug-Jargal’, published in 1826. From 1829 – 1840, he published five collections of poetry: ‘Les Orientales’ (1829); ‘Les Feuilles d'automne’ (1831); ‘Les Chants du crépuscule’ (1835); ‘Les Voix intérieures’ (1837); and ‘Les Rayons et les ombres’ (1840).
- // 1829In 1829, he also published a fiction ‘Le Dernier jour d'un condamné’ (The Last Day of a Condemned Man), his first mature work. The work was based upon the real life story of a murderer and reflected the acute social conscience.
- // 1830Around 1830, he embarked on writing the most important novel of his literary career: ‘Les Misérables’. The work explored social misery and injustice. After several years of writing followed by planned marketing campaigns by the Belgian publishing house Lacroix and Verboeckh, the novel was finally published in 1862. The success of the novel turned his fortune.
- // 1831His first full-length book was ‘Notre- Dame de Paris’ (The Hunchback of Notre Dame), published in 1831. It was immensely successful and was promptly translated to a number of foreign languages. It made the Cathedral of Notre Dame and other Renaissance buildings popular among the people of Europe and encouraged their preservation.
- // 1831In 1831, Victor Hugo published the Gothic novel, ‘Notre-Dame de Paris’ (The Hunchback of Notre Dame). The story is set in the late medieval period of Paris, France, and presents a grim picture of the society that humiliates and rejects the hunchback Quasimodo. The novel was immensely successful.
- // 1832Another of his famous novels, ‘Les Misérables’ was published in 1862 after several years of hard work. The story involving several characters primarily unravels the destiny of a convict Jean Valjean, a victim of the society who had been imprisoned for 19 years for stealing a loaf of bread. The novel was an instant success and was quickly translated into several languages.
- // 1841In 1841, after three futile attempts, he was elected to the Académie française. Thereafter, he became more and more involved in French politics, supporting the Republic form of government. King Louis-Philippe promoted him and made him a part of the Higher Chamber as a ‘pair de France’.
- // 1843His daughter Léopoldine died in 1843 at the young age of 19, shortly after her marriage to Charles Vacquerie. She drowned in the Seine at Villequier when her boat overturned; her husband also died trying to save her. Her death left Hugo devastated.
- // 1848 To 1870After the Revolution of 1848 and the establishment of the Second Republic, he was elected to the Parliament as a conservative. A few years later, when Napoleon III seized power in 1851 and established an anti-parliamentary constitution, he objected openly calling him a traitor. As a result he was exiled; he settled in Guernsey and lived there until 1870.
- // 1859In 1859, when amnesty was granted to all political exiles by Napoleon III, he chose not to return to France and imposed upon himself a self-exile. He was determined to return only when the Napoleon dynasty was removed from power.
- // 1868 To 1883He lost his wife in 1868. In the next decade, he lost two sons between 1871 and 1873. His mistress, Juliet Drouet died in 1883.
- // 1870After the fall of Napoleon III and the establishment of the Third Republic in France, Victor Hugo returned to his country in 1870 and was soon appointed to the National Assembly and the Senate. He also became a founding member of the Association Littéraire et Artistique Internationale. Two years later in 1872, he lost the National Assembly election.
- // 1871His residences - Hauteville House, Guernsey and 6, Place des Vosges, Paris have been preserved as museums. The house where he stayed in Vianden, Luxembourg, in 1871 has also become a memorial museum.
- // 1874The writings of his last few years were murky, highlighting themes like God, Satan, and death. His last novel ‘Quatrevingt-treize’ (Ninety-Three) was published in 1874. The book presented a picture of the atrocities committed during the French Revolution. Regardless of the completely new subject matter, it failed to achieve success.
- // 1878 To 22nd May 1885In 1878, he began suffering from cerebral congestion. On 22 May 1885 at the age of 83, Victor Hugo breathed his last. His death was lamented by the whole country. His body was rested in state beneath the Arc de Triomphe before burial in the Panthéon.
- // 1881To honor his entering his 80th year in 1881, celebrations across France were organized which included the largest parade in French history. Thereafter, several streets and roads all over France were named after him. His portrait was also placed on French Franc banknotes.
// Famous Poets
Charles Bukowski
Charles Bukowski was a German-born American novelist, short story writer and poet. With this biography, learn in details about his childhood, life, works, career and timeline
Seamus Heaney
Nobel Laureate Seamus Heaney was an Irish poet, playwright and translator. Know about his profile, childhood, life and timeline in the biography below.
Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman was an American poet, journalist and humanist. Read this brief biography to find more on his life & timeline.
Francesco Petrarch
Fêted as the “Father of Humanism”, Francesco Petrarch is one of the most influential literary figures the world has ever had. Explore this biography to know about his childhood, life and timeline.
Sarojini Naidu
Sarojini Naidu was an Indian freedom fighter and poet. Read this brief biography to find more on her life.
Abdolkarim Soroush
Abdolkarim Soroush is a reformer, thinker, and Rumi scholar belonging to Iran. Soroush is also a prominent figure in Iran’s religious movement. This biography provides detailed information about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Victor Hugo's FAQ
What is Victor Hugo birthday?
Victor Hugo was born at 1802-02-26
When was Victor Hugo died?
Victor Hugo was died at 1885-05-22
Where was Victor Hugo died?
Victor Hugo was died in Paris, France
Which age was Victor Hugo died?
Victor Hugo was died at age 83
Where is Victor Hugo's birth place?
Victor Hugo was born in France
What is Victor Hugo nationalities?
Victor Hugo's nationalities is French
Who is Victor Hugo spouses?
Victor Hugo's spouses is Adèle Foucher
Who is Victor Hugo siblings?
Victor Hugo's siblings is Abel Joseph Hugo, Eugène Hugo
Who is Victor Hugo childrens?
Victor Hugo's childrens is Adèle
What was Victor Hugo universities?
Victor Hugo studied at Lycée Louis-le-Grand
Who is Victor Hugo's father?
Victor Hugo's father is Joseph Léopold Sigisbert Hugo
Who is Victor Hugo's mother?
Victor Hugo's mother is Sophie Trébuchet
What is Victor Hugo's sun sign?
Victor Hugo is Pisces
How famous is Victor Hugo?
Victor Hugo is famouse as Author & Poet