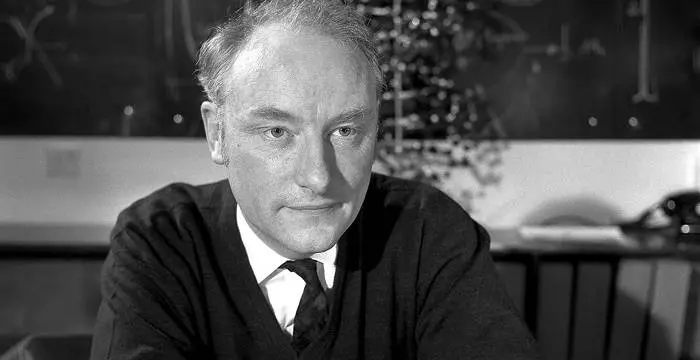Sir John Eccles - Neurophysiologist, Birthday and Family
Sir John Eccles's Personal Details
Sir John Carew Eccles was a neurophysiologist from Australia who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | January 27, 1903 |
| Died on | May 2, 1997 |
| Nationality | Australian |
| Famous | University Of Melbourne, Scientists, Neuroscientists, Neurophysiologist |
| Spouses | Helena Taborikova, Irene Frances Miller |
| Known as | Sir John Carew Eccles |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Melbourne, Australia |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | William James Eccles |
| Mother | Mary Carew |
| Sun Sign | Aquarius |
| Born in | Melbourne, Australia |
| Famous as | Neurophysiologist |
| Died at Age | 94 |
// Famous Neurophysiologist
Charles Scott Sherrington
Charles Sherrington was a Nobel Prize winning English scientist who explained the function of neurons in the human body. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Torsten Wiesel
Torsten Wiesel is a Nobel Prize winning Swedish neurophysiologist who was one of the co-recipients of the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
David H. Hubel
David Hunter Hubel was a Nobel Prize winning Canadian neurophysiologist noted for his work on the structure and function of the visual cortex. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
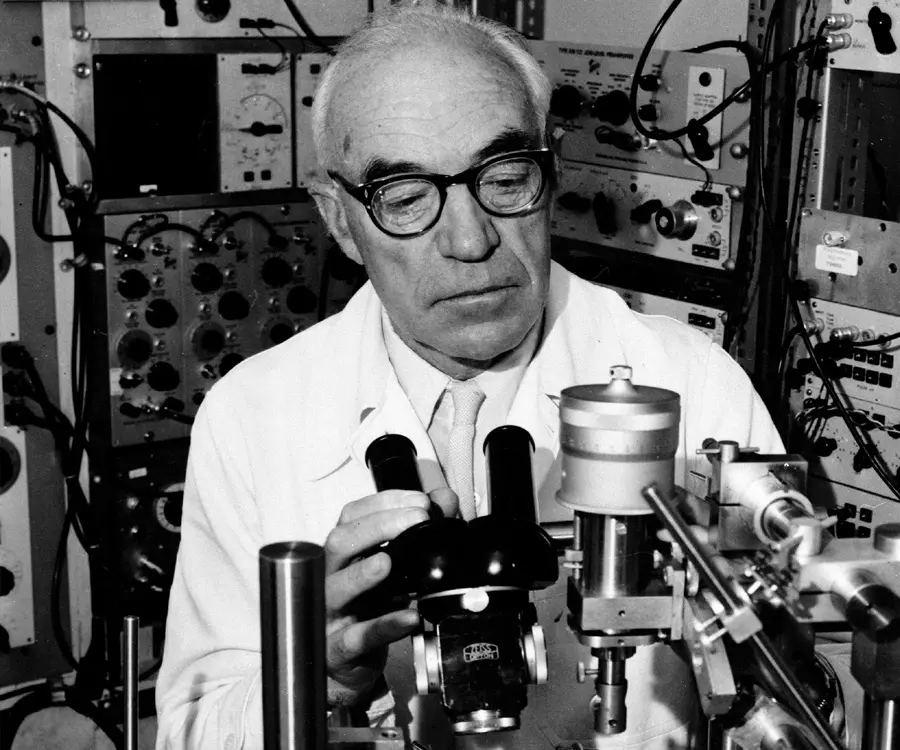
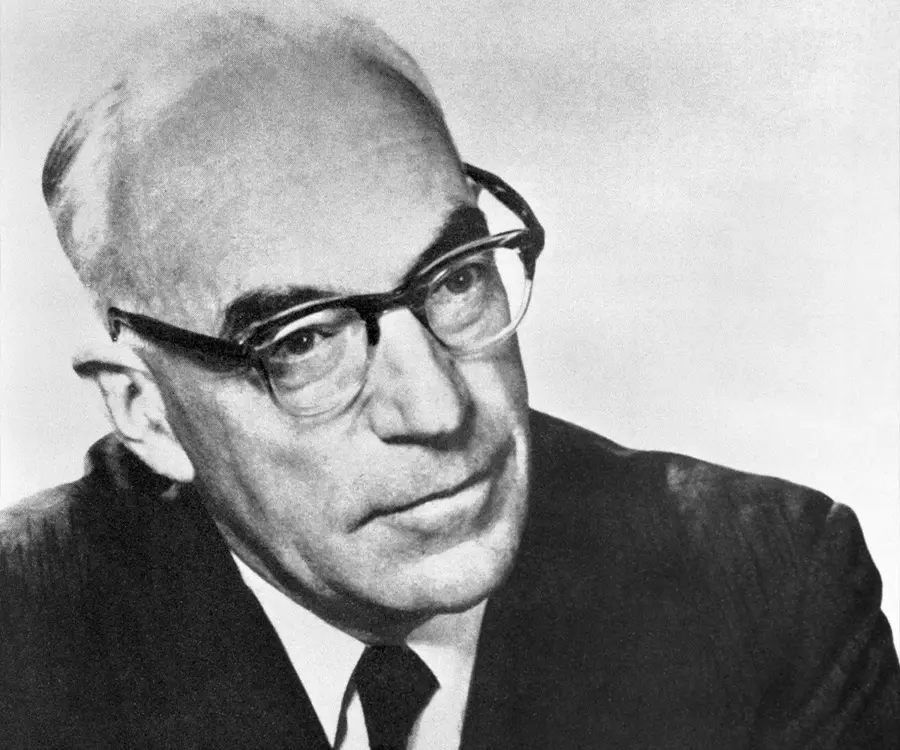
Sir John Eccles's photo
Who is Sir John Eccles?
Sir John Carew Eccles was a neurophysiologist from Australia who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his research on synapse in the central nervous system. He shared the prize with two other scientists, Alan Lloyd Hodgkin and Andrew Fielding Huxley. His research centered on the complex way in which the human brain works and the neurophysiologic processes which control thought processes. He discovered the chemical reactions allow or suppress the impulses sent to the nerve cells or neurons in the brain. Though he believed till 1949 that the synaptic transmission was mainly due to electrical impulses rather than chemical, his experiments later proved his hypothesis otherwise. After conducting various experiments with Bernard Katz, he came to the conclusion that these transmissions had a chemical side too. He proved that the communication between two adjacent nerve cells is done by the release of chemicals into the synapse or the gap between the two cells. Every reaction of the brain was caused by a distinct chemical reaction which caused an electrical impulse to be passed from one cell to another. Apart from the research on synapses he also played an important role in the development of neuroscience. His experiments helped in the future treatment of nervous diseases and brain, heart and kidney research.
// Famous Neuroscientists
Seymour Kety
Seymour Kety was a popular American neuroscientist who made great inroads in diverse fields such as psychiatry, physiology and neuroscience. Read on to learn more about Seymour Kety’s profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Francis Crick
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist, who received the Nobel Prize for Medicine. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Santiago Ramón y Cajal
Santiago Ramón y Cajal was a famous Spanish pathologist, neuroscientist and histologist. This biography profiles his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Sir John Eccles was born in Melbourne, Australia on January 27, 1903. Both his father William James Eccles and his mother Mary Carew were school teachers.
He was schooled at home by his parents till he was twelve years of age. He grew up with two sisters.
He initially attended the ‘Warrnambool High School’ which is currently known as the ‘Warrnambool College’.
He completed his schooling from the ‘Melbourne High School’.
At the age of 17, he received a senior scholarship for studying medicine at the ‘University of Melbourne’.
He graduated from the ‘Melbourne University’ in 1925 with a first class honors in Medicine.
He was awarded the ‘Victorian Rhodes Scholarship’ for the year 1925 and attended the ‘Magdalen College, Oxford’.
In 1927 he received first class honors in ‘Natural Sciences’, the ‘Christopher Welch Scholarship’ and a ‘Junior Research Fellowship’ and joined the ‘Exeter College, Oxford’.
He received his D.Phil in Philosophy in 1929 from the Oxford University.
He received a ‘Staines Medical Fellowship’ in 1932 for doing research at Exeter College, Oxford after completing his doctorate.
He also received a tutorial fellowship at the Magdalen College and a University Demonstratorship in 1934.
Career
He returned to Australia in 1937 as the Director of a small medical research center in Sydney named ‘Kanematsu Institute’ under the ‘Sydney Medical School’.
During the period 1937 to 1943 he was engaged in research on the neuromuscular reactions in frogs and cats. He devoted the later part of this period on experiments to help the war effort.
He was appointed at the ‘University of Otago’ in New Zealand after the war ended and spent the period from 1944 to 1951 doing his own experiments on the central nervous system.
In 1951 Eccles, Brock and Coombs were successful in inserting microelectrodes for the first time into the nerve cells of the central nervous system and were able to record the electrical impulses created by synaptic transmissions.
He worked from 1952 to 1966 at the ‘John Curtin School of Medical Research’ under the ‘Australian National University’ in Canberra as a Professor of Physiology.
In 1966 he moved to the United States and joined the ‘Institute for Biomedical Research’ located in Chicago where he carried on his research on synapses.
He was not happy with the working conditions prevailing at the institute in Chicago and joined the ‘State University of New York’ in Buffalo in the United States in 1968. He remained with this university until he retired in 1975.
After retirement he left the United States for Switzerland and wrote on the problems regarding the relationship between the mind and the body.
Major Works
Sir John Eccles’ book ‘The Self and its Brain’ written in collaboration with Karl Popper and Karl Raimund was published in 1977.
His two main works ‘The Human Mystery. Gifford Lectures’ and the ‘The Human Psyche. Gifford Lectures’ were published in 1979 and 1980 respectively.
His book ‘The Wonder of being Human: Our Brain and our Mind’ written in collaboration with Daniel N. Robinson and his own book ‘Mind and Brain: The Many-Faceted Problems’ came out in 1984 and 1985 respectively while his last book ‘How the Self Controls its Brain’ was published in 1994.
Awards & Achievements
Sir John Carew Eccles received a ‘Fellowship of the Royal Society’ in 1941.
He received a ‘Fellowship of the Australian Academy of Science’ and honorary doctorates from nine different universities.
He was honored with knighthood in 1958.
He was declared ‘Australian of the Year’ in 1963.
He received the Nobel Prize in 1963.
In 1964 he was made an honorary member of the ‘American Philosophical Society’.
In 1990 he was appointed as a ‘Companion of the Order of Australia’.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married his first wife Irene Frances Miller in 1928 and divorced her in 1968. He had four sons and five daughters from this marriage.
He married his second wife Helena Taborikova in 1968 after divorcing Irene. Helena was a neurophysiologist with an M.D. and worked with him at the Charles University during his research work.
Sir John Eccles died in Tenero-Contra, Locarno, Switzerland, on May 2, 1997.
Trivia
Unlike other scientists, Sir John Eccles believed that science alone could not explain everything in the universe.
He had a deep spiritual sense about the reality of every unexplained matter in this world and believed in unraveled mysteries.
He tried to reconcile science and faith.
// Famous University Of Melbourne
Nicole Kidman
Nicole Kidman is one of the most talented actors that the Hollywood film industry can boast of. Browse through this biography to get detailed information regarding her life, childhood, profile & timeline
Peter Singer
Peter Singer is an Australian moral philosopher who has challenged traditional notions of applied ethics throughout his philosophical and literary career. Check out this biography to get detailed information on his life.
Julia Gillard
Julia Gillard is a former Prime Minister of Australia and the first woman to hold the position. To know more about her childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Sir John Eccles's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Knight Bachelor (1958) | |
| 0 | Royal Medal (1962) | |
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1963) | |
| 0 | Companion of the Order of Australia (1990) | |
Sir John Eccles biography timelines
- // 27th Jan 1903Sir John Eccles was born in Melbourne, Australia on January 27, 1903. Both his father William James Eccles and his mother Mary Carew were school teachers.
- // 1925He graduated from the ‘Melbourne University’ in 1925 with a first class honors in Medicine.
- // 1925He was awarded the ‘Victorian Rhodes Scholarship’ for the year 1925 and attended the ‘Magdalen College, Oxford’.
- // 1927In 1927 he received first class honors in ‘Natural Sciences’, the ‘Christopher Welch Scholarship’ and a ‘Junior Research Fellowship’ and joined the ‘Exeter College, Oxford’.
- // 1928 To 1968He married his first wife Irene Frances Miller in 1928 and divorced her in 1968. He had four sons and five daughters from this marriage.
- // 1929He received his D.Phil in Philosophy in 1929 from the Oxford University.
- // 1932He received a ‘Staines Medical Fellowship’ in 1932 for doing research at Exeter College, Oxford after completing his doctorate.
- // 1934He also received a tutorial fellowship at the Magdalen College and a University Demonstratorship in 1934.
- // 1937He returned to Australia in 1937 as the Director of a small medical research center in Sydney named ‘Kanematsu Institute’ under the ‘Sydney Medical School’.
- // 1937 To 1943During the period 1937 to 1943 he was engaged in research on the neuromuscular reactions in frogs and cats. He devoted the later part of this period on experiments to help the war effort.
- // 1941Sir John Carew Eccles received a ‘Fellowship of the Royal Society’ in 1941.
- // 1944 To 1951He was appointed at the ‘University of Otago’ in New Zealand after the war ended and spent the period from 1944 to 1951 doing his own experiments on the central nervous system.
- // 1951In 1951 Eccles, Brock and Coombs were successful in inserting microelectrodes for the first time into the nerve cells of the central nervous system and were able to record the electrical impulses created by synaptic transmissions.
- // 1952 To 1966He worked from 1952 to 1966 at the ‘John Curtin School of Medical Research’ under the ‘Australian National University’ in Canberra as a Professor of Physiology.
- // 1958He was honored with knighthood in 1958.
- // 1963He was declared ‘Australian of the Year’ in 1963.
- // 1963He received the Nobel Prize in 1963.
- // 1964In 1964 he was made an honorary member of the ‘American Philosophical Society’.
- // 1966In 1966 he moved to the United States and joined the ‘Institute for Biomedical Research’ located in Chicago where he carried on his research on synapses.
- // 1968 To 1975He was not happy with the working conditions prevailing at the institute in Chicago and joined the ‘State University of New York’ in Buffalo in the United States in 1968. He remained with this university until he retired in 1975.
- // 1968He married his second wife Helena Taborikova in 1968 after divorcing Irene. Helena was a neurophysiologist with an M.D. and worked with him at the Charles University during his research work.
- // 1977Sir John Eccles’ book ‘The Self and its Brain’ written in collaboration with Karl Popper and Karl Raimund was published in 1977.
- // 1979 To 1980His two main works ‘The Human Mystery. Gifford Lectures’ and the ‘The Human Psyche. Gifford Lectures’ were published in 1979 and 1980 respectively.
- // 1990In 1990 he was appointed as a ‘Companion of the Order of Australia’.
- // 2nd May 1997Sir John Eccles died in Tenero-Contra, Locarno, Switzerland, on May 2, 1997.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Gabe Newell
Gabe Newell is an American computer programmer and businessman, best known as the co-founder of ‘Valve Corporation.’ This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Grigori Perelman
Grigori Perelman is a Russian mathematician who is best known for his contributions to Riemannian geometry and geometric topology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Eduardo Saverin
Eduardo Luiz Saverin is a Brazilian internet entrepreneur and investor. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements, and timeline
Sir John Eccles's FAQ
What is Sir John Eccles birthday?
Sir John Eccles was born at 1903-01-27
When was Sir John Eccles died?
Sir John Eccles was died at 1997-05-02
Which age was Sir John Eccles died?
Sir John Eccles was died at age 94
Where is Sir John Eccles's birth place?
Sir John Eccles was born in Melbourne, Australia
What is Sir John Eccles nationalities?
Sir John Eccles's nationalities is Australian
Who is Sir John Eccles spouses?
Sir John Eccles's spouses is Helena Taborikova, Irene Frances Miller
What was Sir John Eccles universities?
Sir John Eccles studied at University Of Melbourne
What was Sir John Eccles notable alumnis?
Sir John Eccles's notable alumnis is University Of Melbourne
Who is Sir John Eccles's father?
Sir John Eccles's father is William James Eccles
Who is Sir John Eccles's mother?
Sir John Eccles's mother is Mary Carew
What is Sir John Eccles's sun sign?
Sir John Eccles is Aquarius
How famous is Sir John Eccles?
Sir John Eccles is famouse as Neurophysiologist