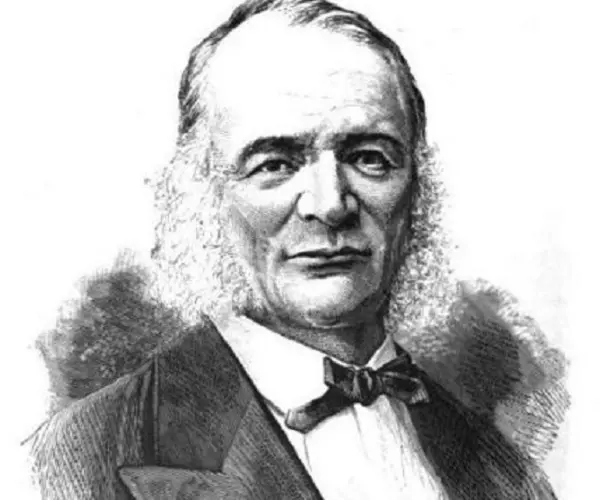Otto Wilhelm von Struve - Astronomers, Career and Facts
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's Personal Details
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was a 19th century Russian astronomer who pioneered the study of double stars
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | May 7, 1819 |
| Died on | April 16, 1905 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Scientists, Astronomers, Astrophysicists |
| Hobbies | Gem stones, Growing orchids |
| Childrens | Hermann Struve, Ludwig Struve |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Tartu |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve |
| Sun Sign | Taurus |
| Born in | Tartu |
| Famous as | Astronomer |
| Died at Age | 85 |
// Famous Astronomers
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton was an English scientist and mathematician, who discovered gravitation and Newtonian Mechanics. Read this biography to find more on his life.
Henrietta Swan Leavitt
Henrietta Swan Leavitt was an American astronomer. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, discoveries, achievements, etc.
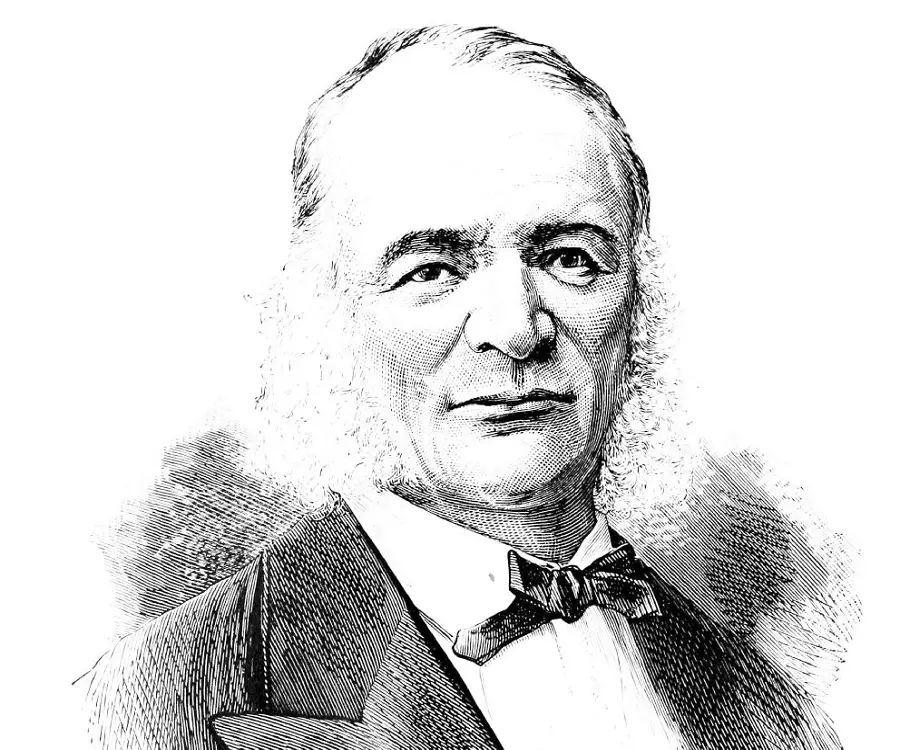
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's photo
Who is Otto Wilhelm von Struve?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was a 19th century Russian astronomer who pioneered the study of double stars and contributed greatly to our modern understanding of astrophysics. Son of the Russian astronomer Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, Otto followed in his father's footsteps. He was a genius in his time; completing school education at the age of 15 and university education at the age of 20. During his time at the Imperial University of Dorpat, Otto Wilhelm von Struve helped his father catalogue the northern skies. Otto Wilhelm alone is credited with discovering an estimated 500 double star systems along with detailed published measurements of their orbits. Throughout his prestigious career, he completed the most accurate measurement of the earth’s curve, known as the Struve Geodetic Arc, categorized the rings of Saturn and discovered the second moon of Uranus. Winner of a Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society and a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Otto Wilhelm’s contribution to the field of astronomy is unparalleled. After his death, the family’s name continued to be famous in astronomy. His sons: Ludwig and Hermann, both went on to become successful astronomers and his grandson, Otto Struve, too was a famous astronomer
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was born on May 7, 1819, in the then Russian Empire city of Dorpat (present day Tartu, Ukraine). He was the third of the eighteen children born to Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve and his wife Emilie Wall.
At the age of 15, he completed his primary education in Dorpat. While too young to attend university, he was invited to the Imperial University of Dorpat to listen in on lectures. While attending university, he assisted his father who worked at the Dorpat Observatory.
When he graduated at the age of 20 in 1839, he was appointed Assistant Director at the newly completed Pulkovo Observatory.
In 1841, he received a Masters of Astronomy from the University of St. Petersburg.
Career
In 1841, he began his first independent research, testing William Herschel’s theory of the solar system moving toward the Hercules constellation.
In 1842, he began his research on double stars for which he would later become famous.
From 1843 –1844, he was part of the team that carried out longitude measurements between Altona, Greenwich and Pulkovo, which were based on large displacement of chronometers over the Earth surface.
In 1844, he dedicated himself to studying the sun, measuring its speed to be 7.3 km/s. While the speed measured was found to be incorrect in a study carried out in 1901, Otto Wilhelm was correct in his observation that the sun was much slower than most stars in the night sky.
In 1851, he published notes of his observations of Uranus’s moons, Ariel and Umbriel, along with findings on Neptune.
When his father fell ill in 1858, Struve took on management of the Pulkovo Observatory. In 1862, he became Director of the observatory and remained so until his retirement in 1889.
In 1861, he presented his theory on how stars are formed from interstellar matter to the Academy of Sciences.
In 1872, he helped organize the newly opened Tashkent Observatory.
In 1874, he traveled across Asia, Persia and Egypt to observe Venus’s orbit.
From 1879-1884, he helped upgrade the Pulkovo Observatory. Upon its completion in 1885, the observatory held the world’s largest telescope with a 30 inch refracting lens.
Major Works
Continuing his father's work, Otto Wilhelm von Struve compiled the Pulkovo Catalogue of Stellar Coordinates, a catalogue of thousands of double stars.
In 1847, he co-discovered Uranus’s second moon, Umbriel, along with William Lassell.
In 1851, while studying a solar eclipse, he concluded that waves coming off the sun were in fact plasma, not an optical illusion. Solar corona was an unpopular idea at the time but was later proven true.
In 1852, he helped complete the triangulation of the Meridian arc from Hammerfest to Nekrasovka. This accurate measurement of distance, including the curvature of the earth, was named the Struve Geodetic Arc.
In the 1850s, he measured Saturn’s rings and helped discover its darker inner rings. The naming system he invented for the rings is still used today.
Awards & Achievements
In 1850, Otto Wilhelm von Struve was awarded the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society for his 1840 publication ‘The Determination of the Constant of Precession with Respect to the Proper Motion of the Solar System’.
From 1852 to 1889, he was a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences
In 1913, Asteroid 768 was named Struvena in honor of 3 astronomers of the Struve family, namely, Friedrich Georg Wilhelm, Otto Wilhelm and Otto.
Personal Life & Legacy
His first marriage was to Emilie Dyrssen. Together, they had six children, two daughters and four sons. Emilie died in 1863.
He married his second wife, Emma Jankowsky, in the mid-1860s. Together, they had one daughter.
Two of his sons, Ludwig and Hermann, continued the family legacy and became astronomers. Of the other two, one worked for the Ministry of Finances and the other as a geologist.
After retiring in 1889, Struve lived in St. Petersburg, compiling his notes and exchanging letters with other astronomers. He was fond of travel and often visited Italy and Switzerland.
In 1895, he traveled to Germany where he became ill and decided to stay there.
Otto Wilhelm von Struve died on April 14, 1905 in Karlsruhe, Germany.
Trivia
In 1865, he became ill, and local physicians said he would not recover. Struve decided to take a vacation in Italy over the winter, and when he returned, he was in perfect health.
In 1887, he was prepared to retire from the Pulkovo Observatory, but Tsar Alexander III convinced him to stay on until the Observatory’s 50th Anniversary celebration the next year.
// Famous Astrophysicists
Neil deGrasse Tyson
Neil deGrasse Tyson is an eminent astrophysicist and a popular science communicator. This biography of Neil deGrasse Tyson provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
J. Allen Hynek
Josef Allen Hynek was an American astronomer and ufologist. This biography of Josef Allen Hynek provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Carl Sagan
Carl Sagan was an American astronomer, astrophysicist, cosmology expert and author. This biography profiles his childhood, family life, facts, career, achievements and timeline.
Otto Wilhelm von Struve biography timelines
- // 7th May 1819Otto Wilhelm von Struve was born on May 7, 1819, in the then Russian Empire city of Dorpat (present day Tartu, Ukraine). He was the third of the eighteen children born to Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve and his wife Emilie Wall.
- // 1839When he graduated at the age of 20 in 1839, he was appointed Assistant Director at the newly completed Pulkovo Observatory.
- // 1840 To 1850In 1850, Otto Wilhelm von Struve was awarded the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society for his 1840 publication ‘The Determination of the Constant of Precession with Respect to the Proper Motion of the Solar System’.
- // 1841In 1841, he received a Masters of Astronomy from the University of St. Petersburg.
- // 1841In 1841, he began his first independent research, testing William Herschel’s theory of the solar system moving toward the Hercules constellation.
- // 1842In 1842, he began his research on double stars for which he would later become famous.
- // 1843 To 1844From 1843 –1844, he was part of the team that carried out longitude measurements between Altona, Greenwich and Pulkovo, which were based on large displacement of chronometers over the Earth surface.
- // 1844 To 1901In 1844, he dedicated himself to studying the sun, measuring its speed to be 7.3 km/s. While the speed measured was found to be incorrect in a study carried out in 1901, Otto Wilhelm was correct in his observation that the sun was much slower than most stars in the night sky.
- // 1847In 1847, he co-discovered Uranus’s second moon, Umbriel, along with William Lassell.
- // 1851In 1851, he published notes of his observations of Uranus’s moons, Ariel and Umbriel, along with findings on Neptune.
- // 1851In 1851, while studying a solar eclipse, he concluded that waves coming off the sun were in fact plasma, not an optical illusion. Solar corona was an unpopular idea at the time but was later proven true.
- // 1852In 1852, he helped complete the triangulation of the Meridian arc from Hammerfest to Nekrasovka. This accurate measurement of distance, including the curvature of the earth, was named the Struve Geodetic Arc.
- // 1852 To 1889From 1852 to 1889, he was a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences
- // 1858 To 1889When his father fell ill in 1858, Struve took on management of the Pulkovo Observatory. In 1862, he became Director of the observatory and remained so until his retirement in 1889.
- // 1861In 1861, he presented his theory on how stars are formed from interstellar matter to the Academy of Sciences.
- // 1863His first marriage was to Emilie Dyrssen. Together, they had six children, two daughters and four sons. Emilie died in 1863.
- // 1865In 1865, he became ill, and local physicians said he would not recover. Struve decided to take a vacation in Italy over the winter, and when he returned, he was in perfect health.
- // 1872In 1872, he helped organize the newly opened Tashkent Observatory.
- // 1874In 1874, he traveled across Asia, Persia and Egypt to observe Venus’s orbit.
- // 1879 To 1885From 1879-1884, he helped upgrade the Pulkovo Observatory. Upon its completion in 1885, the observatory held the world’s largest telescope with a 30 inch refracting lens.
- // 1887In 1887, he was prepared to retire from the Pulkovo Observatory, but Tsar Alexander III convinced him to stay on until the Observatory’s 50th Anniversary celebration the next year.
- // 1889After retiring in 1889, Struve lived in St. Petersburg, compiling his notes and exchanging letters with other astronomers. He was fond of travel and often visited Italy and Switzerland.
- // 1895In 1895, he traveled to Germany where he became ill and decided to stay there.
- // 14th Apr 1905Otto Wilhelm von Struve died on April 14, 1905 in Karlsruhe, Germany.
- // 1913In 1913, Asteroid 768 was named Struvena in honor of 3 astronomers of the Struve family, namely, Friedrich Georg Wilhelm, Otto Wilhelm and Otto.
// Famous German peoples
Jordan Carver
Jordan Carver is a famous German model. Let’s take a close look at her personal life, including her age, career, net worth, achievements and some fun facts.
Jürgen Klopp
Jürgen Klopp is a German football manager, and a former professional football player. Check out this biography to know more about his childhood, family, personal life, etc.
Irma Grese
Irma Grese was a notorious German Nazi concentration camp guard during the Second World War. This biography profiles her childhood, life, horrifying acts, death and other facts.
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Jawed Karim
Jawed Karim is a German-American internet entrepreneur, technologist and co-founder of the video-sharing website, YouTube. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, personal life, achievements, age, etc.
Charles Bukowski
Charles Bukowski was a German-born American novelist, short story writer and poet. With this biography, learn in details about his childhood, life, works, career and timeline
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's FAQ
What is Otto Wilhelm von Struve birthday?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was born at 1819-05-07
When was Otto Wilhelm von Struve died?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was died at 1905-04-16
Where was Otto Wilhelm von Struve died?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was died in Karlsruhe
Which age was Otto Wilhelm von Struve died?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was died at age 85
Where is Otto Wilhelm von Struve's birth place?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve was born in Tartu
What is Otto Wilhelm von Struve nationalities?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's nationalities is German
What is Otto Wilhelm von Struve hobbies?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's hobbies is Gem stones, Growing orchids
Who is Otto Wilhelm von Struve childrens?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's childrens is Hermann Struve, Ludwig Struve
What was Otto Wilhelm von Struve universities?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve studied at University of Tartu
Who is Otto Wilhelm von Struve's father?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve's father is Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve
What is Otto Wilhelm von Struve's sun sign?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve is Taurus
How famous is Otto Wilhelm von Struve?
Otto Wilhelm von Struve is famouse as Astronomer