Otto Diels - Organic Chemists, Family and Family
Otto Diels's Personal Details
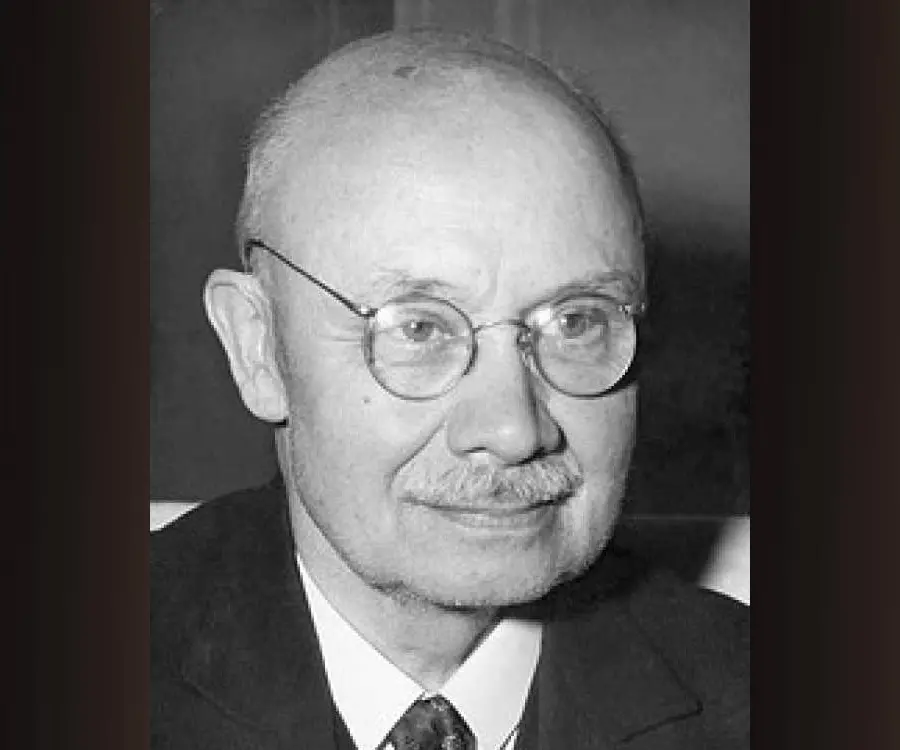
Otto Diels or Otto Paul Herman Diels was a German scientist who received the Nobel Prize in chemistry
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | January 23, 1876 |
| Died on | March 7, 1954 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Scientists, Chemists, Inorganic Chemists, Organic Chemists |
| Spouses | Paula Geyer |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Hamburg, German Empire |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Hermann Diels |
| Mother | Bertha Dubell |
| Sun Sign | Aquarius |
| Born in | Hamburg, German Empire |
| Famous as | Chemist |
| Died at Age | 78 |
// Famous Inorganic Chemists
William Ramsay
William Ramsay was a Nobel Prize winning chemist who discovered the ‘noble gases’. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Alfred Werner
Alfred Werner was a Swiss chemist and the founder of coordination chemistry. This biography of Werner provides detailed information about his childhood, life, research, work, achievements and timeline.
Paul Hermann Müller
Paul Hermann Muller was a Swiss Chemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery of a form of DDT. This biography profiles his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Otto Diels's photo
Who is Otto Diels?
Otto Diels or Otto Paul Herman Diels was a German scientist who received the Nobel Prize in chemistry for developing a process by which cyclic organic compounds could be obtained. This process was called the ‘diene synthesis’ or the ‘Diels-Alder reaction’. He shared the Nobel Prize with another scientist, Kurt Alder, who had worked jointly with him in developing the process. His work led to the production of synthetic plastics and rubber. His initial research was in the field of inorganic chemistry during which he discovered a highly reactive substance known as ‘carbon suboxide’. He later changed his research to encompass the domain of organic chemistry. His process of using selenium to remove hydrogen atoms from cyclic organic compounds not only helped the synthesis of plastics and rubber but also became a useful tool for finding out the complicated chemical structures of a series of steroids. He was successful in dehydrogenating cholesterol with the help of selenium which produced a skeletal structure of steroids. During the period when he was at the ‘University of Kiel’, he worked with Kurt Alder to develop the ‘Diels-Alder reaction’ which helped to synthesize unsaturated cyclic organic compounds leading to the production of synthetic plastic and rubber compounds, alkaloids and insecticides at a low cost without using any catalyst, reagent, high temperature or pressure.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Childhood & Early Life
Otto Diels was born on January 23, 1876 in Hamburg, Germany. His father, Hermann Diels, was a professor at the University of Berlin and taught classical philology. His mother, Bertha Dubell, was a district judge’s daughter.
He had two brothers named Ludwig and Paul who went on to become professors in the fields of botany and Slavic philology respectively.
When he was two-year-old his family moved from Hamburg to Berlin where his father was offered a professorship at the university.
He did his early schooling from 1882 to 1895 at the ‘Joachimsthalsches Gymnasium’ in Berlin.
In 1895 he enrolled at the University of Berlin to study chemistry along with other science subjects.
He received his doctoral degree from the university in 1899.
Career
Immediately after graduation from the University of Berlin in 1899, he was appointed an assistant at the Institute of Chemistry at the same university.
He progressed very fast through the ranks and soon became a lecturer in 1904 and was then promoted to professor in 1906.
In 1906 he discovered ‘carbon suboxide’ which is the anhydride acidic form of malonic acid. He found out the chemical composition and properties of this highly reactive substance. The information about its chemical structure helped him understand the composition of different carbon oxides.
In 1913 he was appointed the Head of the Department of chemistry at the Berlin University and became a full professor in 1915.
He was appointed as an associate professor at the Chemical Institute of the Royal Friedrich Wilhelm University in Kiel in 1914.
In 1916 he moved to the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel as the Professor and Director of the Institute of Chemistry and remained in the post till his retirement in 1945.
In 1927 he introduced the use of selenium as a reagent for removing hydrogen atoms from hydroaromatic compounds. The process he devised could be used to remove the hydrogen atoms from the molecules of certain organic compounds under external control by using metallic selenium producing a completely new structure.
In 1928 he and one of his students, Kurt Alder, developed a method known as the ‘Diels-Alder reaction’ which helped him synthesize a large number of organic compounds. In this experiment simple ‘dienes’ such as ‘butadiene’ could be converted into cyclic ‘dienes’ which lead to the production of new organic compounds. New types of polymers, alkaloids, and plastics could be obtained in this way. This was his most important discovery and won him the Nobel Prize.
He became a member of the ‘Bavarian Academy of Sciences’ and the scientific academies of Gottingen and Halle during this period and an Emeritus Professor in 1945.
During the end of the Second World War the Chemical Institute was totally destroyed in Allied air raids. He had to stop work and applied for retirement in September 1944 and was granted the permission to retire in March 1945.
In 1946 he was again requested to continue as the director of the Chemical Institute operating from makeshift quarters which he agreed to.
Major Works
Otto Diels authored and published his work ‘Einfuhrung in die organische Chemie’ in 1907 which had nineteen editions by 1962. It is one of the most popular textbooks in the field of organic chemistry.
His papers were published in many scientific journals and magazines including the periodical ‘Liebigs Annalen der Chemie’.
Awards & Achievements
Otto Diels was awarded a gold medal at the International Exhibition held in St. Louis, USA, in 1904.
He was awarded the Adolf von Baeyer Memorial Medal in 1931 by the ‘Society of German Chemists’.
In 1946 he was awarded an honorary doctorate by the ‘Medical faculty of Christian Albrecht University’.
He won the Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1950.
In 1952 he was awarded the ‘Grosskreuz des Verdienstordens der Bundesrepublik Deutschland’.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married Paula Geyer in 1909 and had three sons and two daughters from the marriage.
He lost two of his sons at the eastern front during World War II.
His home was also razed to the ground by Allied bombing during the later stages of the World War II.
Otto Diels died of heart failure on March 7, 1954 in Kiel in West Germany, which is now part of unified Germany.
Trivia
Otto Diels was fond of music and reading and liked traveling. He was also fond of mountaineering in his younger days.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Otto Diels's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1950) | |
Otto Diels biography timelines
- // 23rd Jan 1876Otto Diels was born on January 23, 1876 in Hamburg, Germany. His father, Hermann Diels, was a professor at the University of Berlin and taught classical philology. His mother, Bertha Dubell, was a district judge’s daughter.
- // 1882 To 1895He did his early schooling from 1882 to 1895 at the ‘Joachimsthalsches Gymnasium’ in Berlin.
- // 1895In 1895 he enrolled at the University of Berlin to study chemistry along with other science subjects.
- // 1899He received his doctoral degree from the university in 1899.
- // 1899Immediately after graduation from the University of Berlin in 1899, he was appointed an assistant at the Institute of Chemistry at the same university.
- // 1904 To 1906He progressed very fast through the ranks and soon became a lecturer in 1904 and was then promoted to professor in 1906.
- // 1904Otto Diels was awarded a gold medal at the International Exhibition held in St. Louis, USA, in 1904.
- // 1906In 1906 he discovered ‘carbon suboxide’ which is the anhydride acidic form of malonic acid. He found out the chemical composition and properties of this highly reactive substance. The information about its chemical structure helped him understand the composition of different carbon oxides.
- // 1907 To 1962Otto Diels authored and published his work ‘Einfuhrung in die organische Chemie’ in 1907 which had nineteen editions by 1962. It is one of the most popular textbooks in the field of organic chemistry.
- // 1909He married Paula Geyer in 1909 and had three sons and two daughters from the marriage.
- // 1913 To 1915In 1913 he was appointed the Head of the Department of chemistry at the Berlin University and became a full professor in 1915.
- // 1914He was appointed as an associate professor at the Chemical Institute of the Royal Friedrich Wilhelm University in Kiel in 1914.
- // 1916 To 1945In 1916 he moved to the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel as the Professor and Director of the Institute of Chemistry and remained in the post till his retirement in 1945.
- // 1927In 1927 he introduced the use of selenium as a reagent for removing hydrogen atoms from hydroaromatic compounds. The process he devised could be used to remove the hydrogen atoms from the molecules of certain organic compounds under external control by using metallic selenium producing a completely new structure.
- // 1928In 1928 he and one of his students, Kurt Alder, developed a method known as the ‘Diels-Alder reaction’ which helped him synthesize a large number of organic compounds. In this experiment simple ‘dienes’ such as ‘butadiene’ could be converted into cyclic ‘dienes’ which lead to the production of new organic compounds. New types of polymers, alkaloids, and plastics could be obtained in this way. This was his most important discovery and won him the Nobel Prize.
- // 1931He was awarded the Adolf von Baeyer Memorial Medal in 1931 by the ‘Society of German Chemists’.
- // Sep 1944 To Mar 1945During the end of the Second World War the Chemical Institute was totally destroyed in Allied air raids. He had to stop work and applied for retirement in September 1944 and was granted the permission to retire in March 1945.
- // 1945He became a member of the ‘Bavarian Academy of Sciences’ and the scientific academies of Gottingen and Halle during this period and an Emeritus Professor in 1945.
- // 1946In 1946 he was again requested to continue as the director of the Chemical Institute operating from makeshift quarters which he agreed to.
- // 1946In 1946 he was awarded an honorary doctorate by the ‘Medical faculty of Christian Albrecht University’.
- // 1950He won the Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1950.
- // 1952In 1952 he was awarded the ‘Grosskreuz des Verdienstordens der Bundesrepublik Deutschland’.
- // 7th Mar 1954Otto Diels died of heart failure on March 7, 1954 in Kiel in West Germany, which is now part of unified Germany.
// Famous Organic Chemists
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist who is best known for his discovery of the periodic law. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Aleksandr Borodin
Aleksandr Borodin was a prodigal Russian music composer and scientist. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
Hermann Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer was a Nobel Prize winning chemist from Germany who is known for inventing the ‘Fischer Projection’ method. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Robert Burns Woodward
Robert Burns Woodward was a Nobel Prize winning American chemist known for his work on complex natural products. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Chaim Weizmann
The famous scientist is known for his discovery of the industrial fermentation. He was also the first President of Israel. To know more about the childhood, profile, career and timeline of Chaim Weizmann read on.
Charles J Pedersen
Charles J Pedersen was an American chemist who discovered the chemical compound, crown ethers. Explore this section to get details about his life, career and scientific discoveries.
Otto Diels's FAQ
What is Otto Diels birthday?
Otto Diels was born at 1876-01-23
When was Otto Diels died?
Otto Diels was died at 1954-03-07
Where was Otto Diels died?
Otto Diels was died in Kiel
Which age was Otto Diels died?
Otto Diels was died at age 78
Where is Otto Diels's birth place?
Otto Diels was born in Hamburg, German Empire
What is Otto Diels nationalities?
Otto Diels's nationalities is German
Who is Otto Diels spouses?
Otto Diels's spouses is Paula Geyer
What was Otto Diels universities?
Otto Diels studied at Humboldt University of Berlin
Who is Otto Diels's father?
Otto Diels's father is Hermann Diels
Who is Otto Diels's mother?
Otto Diels's mother is Bertha Dubell
What is Otto Diels's sun sign?
Otto Diels is Aquarius
How famous is Otto Diels?
Otto Diels is famouse as Chemist