John Dalton - Scientists, Life Achievements and Family
John Dalton's Personal Details
John Dalton was an English chemist, meteorologist and physicist who is best known for his work on ‘modern atomic theory’ and ‘colour blindness’
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | September 6, 1766 |
| Died on | July 27, 1844 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Scientists |
| Siblings | Jonathan |
| Universities |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Eaglesfield, Cumberland, England |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Eaglesfield, Cumberland, England |
| Died at Age | 77 |
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
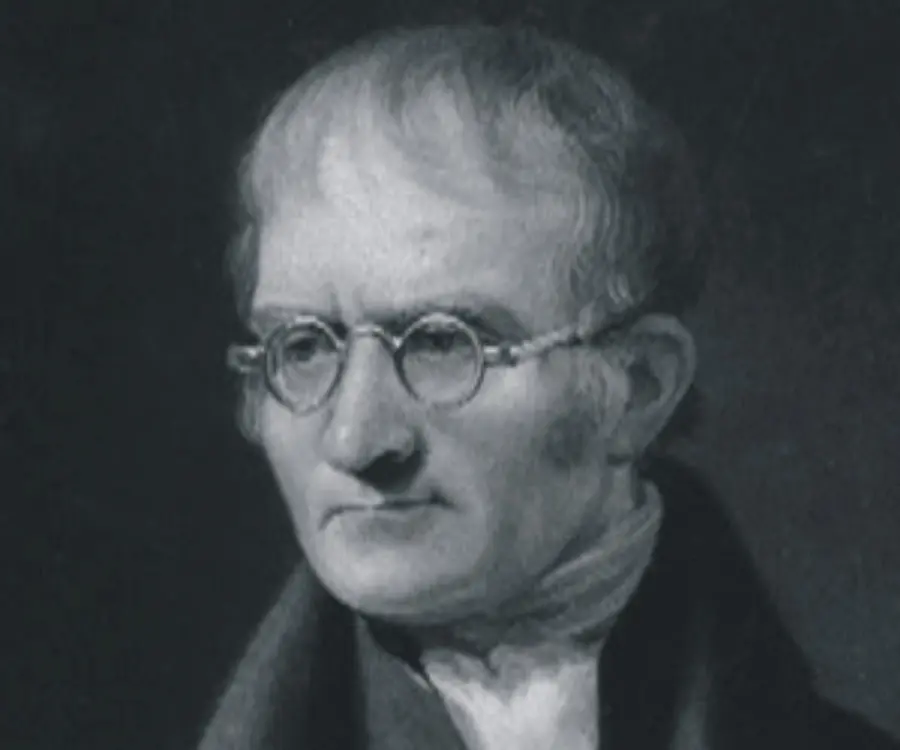
John Dalton's photo
Who is John Dalton?
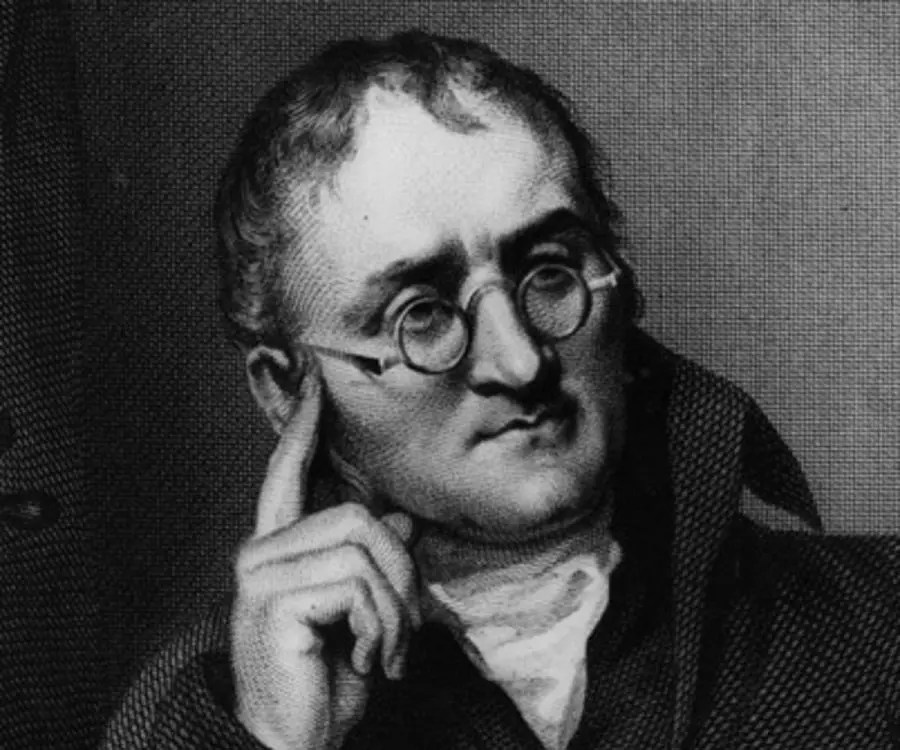
Considered to be the father of ‘modern atomic theory’, John Dalton was also a pioneer of weather forecast and was one of the first scientists to use homemade instruments to make weather observations. Much of his early works and observations using meteorological instruments laid the foundation for the study of weather forecasting. His fascination for the weather and atmosphere lead him to pursue research on ‘the nature of gases’, which in turn laid the ground on which he built the ‘atomic theory’. Today, he is known primarily for his work on atomic theory and although more than two centuries old, his theory still remains valid in the field of modern chemistry. Inquisitive by nature, his diligent research and meddlesome nature led him to make many discoveries in fields other than chemistry. He also made a study on colour-blindness, a condition from which he personally suffered. A non-conformist and ‘dissenter’, Dalton refused to accept much of his deserved fame and recognition and chose to live a simple and modest life. Today, his theories help modern scuba divers gauge oceanic pressure levels and have also facilitated cost-effective manufacturing of chemical compounds. To learn more interesting facts about his personal life and professional achievements, scroll down and continue to read this biography.
// Famous Virgo Celebrities peoples
Temple Grandin
Temple Grandin is a well-known American writer, autistic activist and animal expert. This biography profiles her childhood, life, achievements, career and timeline
Alex Holtti
Check out all that you wanted to know about Alex Holtti, the famous Danish Viner & YouTuber; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Benjamin Atkinson
Benjamin Atkinson is the son of the world-renowned British actor and comedian, Rowan Atkinson. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, personal life, including his age, birthday, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
John Dalton was born in the small settlement of Eaglesfield in Cumberland, England to Joseph Dalton, a poor weaver and Deborah Greenup, who belonged to a prosperous Quaker family in England.
His family was ‘Quaker’, a member of a Christian Movement, whose ideology was derived from a verse in the New Testament. At the age of 15, he helped his older brother Jonathan run a Quaker school in Kenda, Cumbria.
From 1787, he kept a meteorological diary and through his lifetime he recorded over 20,000 weather observations over a period of 57 years.
Sometime around 1790, he planned to pursue law or medicine but since he was a ‘dissenter’, a member of an organisation that opposed the Church of England, he was not allowed to study at English Universities.
Career
In 1793, he moved to Manchester, where he was appointed as a teacher of mathematics and natural philosophy at the New College, a dissenting academy that provided jobs to religious non-conformists with higher education.
All through his younger days, he looked up to Elihu Robinson, a prominent Quaker and accomplished meteorologist, who had a great influence in inculcating in him an interest for mathematics and meteorology.
In 1793, ‘Meteorological Observations and Essays’, his first book of essays on meteorological topics based on his own set of observations was published. This book laid the foundation for his later discoveries.
In 1794, he authored a paper titled ‘Extraordinary facts relating to the vision of colours’, one of his early works on colour perception of the eye.
In 1800, he gave an oral presentation titled ‘Experimental Essays’, that dealt with information on his experiments on gasses and the study of the nature and chemical makeup of air in relation to atmospheric pressures.
In 1801, his second book titled ‘Elements of English Grammar’ was published and in the same year he discovered ‘Daltons Law’, an empirical law coined by him related to the gases.
By 1803, his experiments on the ‘pressure of a mixture of gasses’ came to be known as the ‘Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures’.
During the early 1800s he formulated a theory on ‘thermal expansion’ and the ‘heating and cooling reaction of gasses’ with respect to expansion and compression of air.
In 1803, he authored an article for the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society, in which he presented a chart on atomic weights, which was one of the first atomic charts to be created at that time.
In 1808, he further explained atomic theory and atomic weight in the book titled ‘A New System of Chemical Philosophy’. In this book, he introduced the concept of how different ‘elements’ can be distinguished based on their atomic weights.
In 1810, he authored an appendix for the book ‘A New System of Chemical Philosophy’, in which he elaborated on ‘atomic theory’ and ‘atomic weight’.
Major Works
In 1801, he came up with the ‘Dalton Law’ also known as Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures’. This theory is used by scuba divers today to gauge pressure levels at different depths of the ocean and its effect on air and nitrogen levels.
He coined the term ‘Daltonism’, which is a term for colour blindness and it became synonymous with his name. He elaborated on this topic in his 1798 paper titled ‘Extraordinary facts relating to the vision of colours, with observation’.
In his 1808 publication ‘A New System of Chemical Philosophy’, he coined the atomic theory and was the first scientist to prepare a table on atomic weights. This theory is considered valid even today and laid the foundation for further studies in this field.
Awards & Achievements
In 1794, he was elected as a member of the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society.
In 1800, he was appointed as the secretary of the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society and became the President of the society in 1817.
Personal Life & Legacy
He did not marry all his life and lived a modest life and socialised with a few friends from the Quaker group.
In 1837, he suffered a stroke and the following year he suffered another one that left him with a speech impediment.
After he suffered a third stroke, at the age of 77, he fell off from his bed and his attendant found him dead when he came to serve him tea. He was laid to rest at the Manchester Town Hall.
In honour of his achievements, many chemist and biochemists use ‘unit dalton’ to represent one atomic mass unit.
Trivia
A large statue of this scientist was erected in the Manchester Town Hall while he was still alive and probably he was the only scientist who got a statue in his lifetime.
// Famous British peoples
Wentworth Miller
Wentworth Miller is an American actor and screenwriter who achieved recognition for his role in the TV series ‘Prison Break’.
Sophie Reade
Sophie Victoria Reade is a British model and reality show star. Let’s take a look at her family and personal life, including her age, birthday, boyfriends, and some interesting facts.
Josh Temple
Check out all that you wanted to know about Josh Temple (Slogoman), the famous British YouTube Personality; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
John Dalton biography timelines
- // 6th Sep 1766John Dalton was born in the small settlement of Eaglesfield in Cumberland, England to Joseph Dalton, a poor weaver and Deborah Greenup, who belonged to a prosperous Quaker family in England.
- // 1790Sometime around 1790, he planned to pursue law or medicine but since he was a ‘dissenter’, a member of an organisation that opposed the Church of England, he was not allowed to study at English Universities.
- // 1793In 1793, he moved to Manchester, where he was appointed as a teacher of mathematics and natural philosophy at the New College, a dissenting academy that provided jobs to religious non-conformists with higher education.
- // 1793In 1793, ‘Meteorological Observations and Essays’, his first book of essays on meteorological topics based on his own set of observations was published. This book laid the foundation for his later discoveries.
- // 1794In 1794, he authored a paper titled ‘Extraordinary facts relating to the vision of colours’, one of his early works on colour perception of the eye.
- // 1794In 1794, he was elected as a member of the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society.
- // 1800In 1800, he gave an oral presentation titled ‘Experimental Essays’, that dealt with information on his experiments on gasses and the study of the nature and chemical makeup of air in relation to atmospheric pressures.
- // 1801In 1801, his second book titled ‘Elements of English Grammar’ was published and in the same year he discovered ‘Daltons Law’, an empirical law coined by him related to the gases.
- // 1803By 1803, his experiments on the ‘pressure of a mixture of gasses’ came to be known as the ‘Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures’.
- // 1803In 1803, he authored an article for the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society, in which he presented a chart on atomic weights, which was one of the first atomic charts to be created at that time.
- // 1808In 1808, he further explained atomic theory and atomic weight in the book titled ‘A New System of Chemical Philosophy’. In this book, he introduced the concept of how different ‘elements’ can be distinguished based on their atomic weights.
- // 1810In 1810, he authored an appendix for the book ‘A New System of Chemical Philosophy’, in which he elaborated on ‘atomic theory’ and ‘atomic weight’.
- // 1837In 1837, he suffered a stroke and the following year he suffered another one that left him with a speech impediment.
- // 27th Jul 1844After he suffered a third stroke, at the age of 77, he fell off from his bed and his attendant found him dead when he came to serve him tea. He was laid to rest at the Manchester Town Hall.
John Dalton's FAQ
What is John Dalton birthday?
John Dalton was born at 1766-09-06
When was John Dalton died?
John Dalton was died at 1844-07-27
Where was John Dalton died?
John Dalton was died in Manchester, England
Which age was John Dalton died?
John Dalton was died at age 77
Where is John Dalton's birth place?
John Dalton was born in Eaglesfield, Cumberland, England
What is John Dalton nationalities?
John Dalton's nationalities is British
Who is John Dalton siblings?
John Dalton's siblings is Jonathan
What was John Dalton universities?
John Dalton studied at Royal Institution
What is John Dalton's inventions/discoveries?
Atomic Theory, Law Of Multiple Proportions, Dalton's Law Of Partial Pressures, Daltonism was invented (or discovered) by John Dalton
What is John Dalton's sun sign?
John Dalton is Virgo