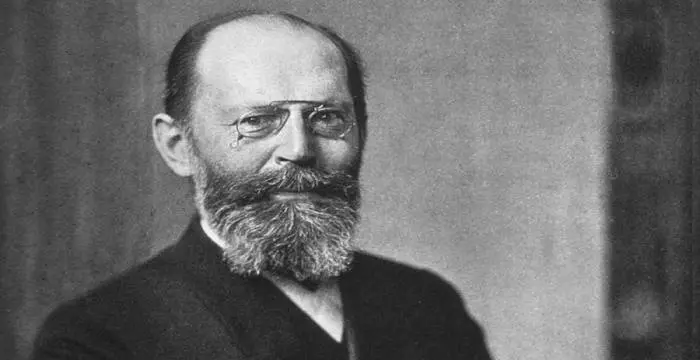Jean-Marie Lehn - Organic Chemists, Life Achievements and Life
Jean-Marie Lehn's Personal Details
Jean-Marie Lehn is an eminent French chemist who was one of the joint recipients of the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1987
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | September 30, 1939 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Chemists, Organic Chemists |
| Spouses | Sylvie Lederer |
| Childrens | David, Mathias |
| Birth Place | Rosheim, France |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Pierre Lehn |
| Mother | Marie Lehn |
| Sun Sign | Libra |
| Born in | Rosheim, France |
| Famous as | Chemist |
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
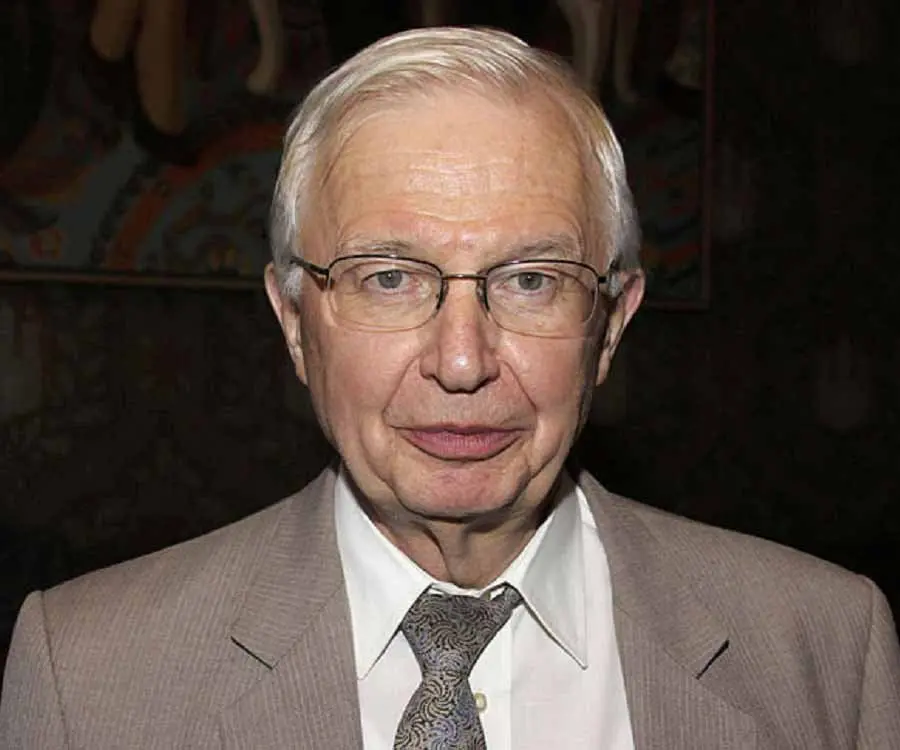
Jean-Marie Lehn's photo
Who is Jean-Marie Lehn?
Jean-Marie Lehn is an eminent French chemist who, together with Charles J. Pedersen and Donald J. Cram, won the prestigious Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1987 “for their development and use of molecules with structure-specific interactions of high selectivity”. He synthesized molecules that replicated the essential chemical functions of molecules in living organisms. Lehn received his doctoral degree in Chemistry in 1963 from the University of Strasbourg and within a few years, became Professor of Chemistry at the Louis Pasteur University in Strasbourg. A decade later, he also became Professor of Chemistry at the Collège de France in Paris. He amplified Pedersen’s discovery of ‘crown ethers’, molecules that are able to attract certain metallic atoms. Lehn found related molecules that he called ‘Cryptands’, which made it possible to create chemical compounds through chemical reactions, which had a considerable impact on biological processes. The molecule could combine with the chemical acetylcholine, which is an important neurotransmitter in the brain. Thus he was an early innovator in the field of ‘supramolecular chemistry’ and continues to innovate in this field. His team has published over 900 scientific peer-reviewed papers and he has authored three books.
// Famous Organic Chemists
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist who is best known for his discovery of the periodic law. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Aleksandr Borodin
Aleksandr Borodin was a prodigal Russian music composer and scientist. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
Hermann Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer was a Nobel Prize winning chemist from Germany who is known for inventing the ‘Fischer Projection’ method. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Childhood & Early Life
Jean-Marie Lehn was born on 30 September 1939, in Rosheim, a small medieval city of Alsace in France, to Pierre and Marie Lehn. He was the eldest of four sons in the family.
Pierre Lehn was a baker. However, he was quite interested in music and played the piano and the organ. Eventually, he became the city organist. Marie, on the other hand, took care of the shop with assistance from her eldest son.
He spent his childhood years during World War II in Rosheim and attended a primary school after the war ended. In 1950, he joined Collège Freppel high school in Obernai, a small town a little away from Rosheim. He studied Latin, Greek, English, German, French, Philosophy and Science, especially Chemistry.
Simultaneously, he also learnt to play the piano and the organ, and eventually music became an important part of his being. In July 1957, he left high school with a Baccalauréat in Philosophy, and in September 1957, he earned a Baccalauréat in Experimental Sciences as well.
He then joined the University of Strasbourg and initially considered studying Philosophy. However, he was undecided and hence began classes with courses in physical, chemical and natural sciences.
In the initial year, he cultivated an interest in organic chemistry to the extent that he set up a small laboratory at home and performed various experiments. In the second year, he attended the motivating lectures of a young professor named Guy Ourisson, and realized that research in organic chemistry was his true calling.
Career
After he received his Licencié-ès-Sciences (Bachelor degree), in October 1960, Jean-Marie Lehn joined Ourisson's laboratory as a member of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. There, he worked towards completing his Ph.D. research.
At Ourisson's laboratory, he was responsible for the lab’s first NMR spectrometer. He worked on conformational and physico-chemical properties of triterpenes. In 1961, he published his first scientific paper, which reported an additivity rule for substituent induced shifts of proton NMR signals in steroid derivatives.
He received his Ph.D degree in 1963 from the University of Strasbourg and soon after joined the laboratory of Robert Burns Woodward at Harvard University for a year, as a post-doctoral research fellow. Among other things, he worked on the synthesis of Vitamin B12.
At Woodward’s lab, he also followed a course in Quantum Mechanics and performed his first computations with Roald Hoffmann. In 1964, he had the opportunity to witness the initial stages of the Woodward-Hoffmann rules.
After he returned to Strasbourg in 1964, he started working in the field of physical organic chemistry, wherein he could combine the knowledge acquired in organic chemistry on physical methods and in quantum theory.
In 1966, he was appointed Maître de Conférences (Assistant Professor) at the Chemistry Department of the University of Strasbourg. Soon after, he set up his own laboratory. He continued in the position till 1969.
His main research topics were NMR studies of conformational rate processes, nitrogen inversion, quadrupolar relaxation, molecular motions and liquid structure, electronic structures, stereo electronic effects, etc. He further explored the physical properties of molecules, synthesizing compounds based on particular characteristic requirement.
In 1968, he was able to synthesize cage-like molecules, consisting of a hollow space inside where another molecule could be lodged. Moving forward, with the help of organic chemistry, he could create cages of desired shape, thus allowing only a certain type of molecule to fit itself inside. This was the foundation of a new field in chemistry, sensors.
Amplifying on Pedersen’s ‘crown ethers’, he discovered similar molecules that he called ‘Cryptands’. This led to the invention of ‘Supramolecular Chemistry’, which studied intermolecular attractions as compared to the bonds inside a molecule.
He was promoted to the position of Associate Professor in early 1970 at University Louis Pasteur of Strasbourg, followed by Full Professor of Chemistry in October same year. He continued in the position till 1979.
Meanwhile, he was Visiting Professor of Chemistry at Harvard University in 1972 (spring), 1974 (spring), and on a part time basis till 1980. He was also Visiting Professor of Chemistry at the E.T.H. Zürich (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich) in 1977.
In October 1979, he was elected to the chair of ‘Chimie des Interactions Moléculaires’ at the prestigious Collège de France in Paris. Following Alain Horeau’s retirement in 1980, he became in charge of the chemistry laboratory at Collège de France, and subsequently divided his time between the two laboratories in Strasbourg and in Paris.
He was Alexander Todd Visiting Professor of Chemistry at Cambridge University in 1984, Visiting Professor of Chemistry at University of Barcelona in 1985, and the Rolf-Sammet Gastprofessor at Frankfurt University in 1985-86. .
In 1987, he shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Donald J. Cram and Charles J. Pedersen “for their development and use of molecules with structure-specific interactions of high selectivity”.
He was Heinrich-Hertz Gastprofessor at Karlsruhe University in November and December 1989, Robert Burns Woodward Visiting Professor at Harvard University in 1997 and again in 2000, and Newton Abraham Professor at Lincoln College, Oxford University in 1999-2000. He was also Adjunct Professor at the Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok in 2005.
Throughout his long illustrious research career, along with his talented team, he has published over 900 scientific peer-reviewed papers and has authored three books.
Major Works
After Charles Pedersen discovered crown ethers, molecules that can attract certain metallic atoms, Jean-Marie Lehn discovered related molecules in 1969 that he called ‘Cryptands’. The cryptands could capture particular types of molecules, which made it possible to create chemical compounds through chemical reactions that had a considerable impact on biological processes. This area of research gradually developed into ‘supramolecular chemistry’, which studied intermolecular attractions instead of the bonds inside one molecule.
Awards & Achievements
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1987 was awarded jointly to Jean-Marie Lehn, Donald J. Cram and Charles J. Pedersen “for their development and use of molecules with structure-specific interactions of high selectivity”..
Personal Life & Legacy
Jean-Marie Lehn married Sylvie Lederer in 1965 and together they have two sons - David (born 1966) and Mathias (born 1969).
He studied music in his youth, and eventually it became his major interest after science.
He is known to be an atheist.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Jean-Marie Lehn's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1987) | |
| 0 | Davy Medal (1997) | |
| 0 | ForMemRS (1993) | |
Jean-Marie Lehn biography timelines
- // 30th Sep 1939Jean-Marie Lehn was born on 30 September 1939, in Rosheim, a small medieval city of Alsace in France, to Pierre and Marie Lehn. He was the eldest of four sons in the family.
- // 1950He spent his childhood years during World War II in Rosheim and attended a primary school after the war ended. In 1950, he joined Collège Freppel high school in Obernai, a small town a little away from Rosheim. He studied Latin, Greek, English, German, French, Philosophy and Science, especially Chemistry.
- // Sep 1957Simultaneously, he also learnt to play the piano and the organ, and eventually music became an important part of his being. In July 1957, he left high school with a Baccalauréat in Philosophy, and in September 1957, he earned a Baccalauréat in Experimental Sciences as well.
- // Oct 1960After he received his Licencié-ès-Sciences (Bachelor degree), in October 1960, Jean-Marie Lehn joined Ourisson's laboratory as a member of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. There, he worked towards completing his Ph.D. research.
- // 1961At Ourisson's laboratory, he was responsible for the lab’s first NMR spectrometer. He worked on conformational and physico-chemical properties of triterpenes. In 1961, he published his first scientific paper, which reported an additivity rule for substituent induced shifts of proton NMR signals in steroid derivatives.
- // 1963He received his Ph.D degree in 1963 from the University of Strasbourg and soon after joined the laboratory of Robert Burns Woodward at Harvard University for a year, as a post-doctoral research fellow. Among other things, he worked on the synthesis of Vitamin B12.
- // 1964At Woodward’s lab, he also followed a course in Quantum Mechanics and performed his first computations with Roald Hoffmann. In 1964, he had the opportunity to witness the initial stages of the Woodward-Hoffmann rules.
- // 1964After he returned to Strasbourg in 1964, he started working in the field of physical organic chemistry, wherein he could combine the knowledge acquired in organic chemistry on physical methods and in quantum theory.
- // 1965Jean-Marie Lehn married Sylvie Lederer in 1965 and together they have two sons - David (born 1966) and Mathias (born 1969).
- // 1966 To 1969In 1966, he was appointed Maître de Conférences (Assistant Professor) at the Chemistry Department of the University of Strasbourg. Soon after, he set up his own laboratory. He continued in the position till 1969.
- // 1968In 1968, he was able to synthesize cage-like molecules, consisting of a hollow space inside where another molecule could be lodged. Moving forward, with the help of organic chemistry, he could create cages of desired shape, thus allowing only a certain type of molecule to fit itself inside. This was the foundation of a new field in chemistry, sensors.
- // 1969After Charles Pedersen discovered crown ethers, molecules that can attract certain metallic atoms, Jean-Marie Lehn discovered related molecules in 1969 that he called ‘Cryptands’. The cryptands could capture particular types of molecules, which made it possible to create chemical compounds through chemical reactions that had a considerable impact on biological processes. This area of research gradually developed into ‘supramolecular chemistry’, which studied intermolecular attractions instead of the bonds inside one molecule.
- // 1970 To 1979He was promoted to the position of Associate Professor in early 1970 at University Louis Pasteur of Strasbourg, followed by Full Professor of Chemistry in October same year. He continued in the position till 1979.
- // Oct 1979 To 1980In October 1979, he was elected to the chair of ‘Chimie des Interactions Moléculaires’ at the prestigious Collège de France in Paris. Following Alain Horeau’s retirement in 1980, he became in charge of the chemistry laboratory at Collège de France, and subsequently divided his time between the two laboratories in Strasbourg and in Paris.
- // 1984He was Alexander Todd Visiting Professor of Chemistry at Cambridge University in 1984, Visiting Professor of Chemistry at University of Barcelona in 1985, and the Rolf-Sammet Gastprofessor at Frankfurt University in 1985-86. .
- // 1987In 1987, he shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Donald J. Cram and Charles J. Pedersen “for their development and use of molecules with structure-specific interactions of high selectivity”.
- // 1987The Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1987 was awarded jointly to Jean-Marie Lehn, Donald J. Cram and Charles J. Pedersen “for their development and use of molecules with structure-specific interactions of high selectivity”..
- // Dec 1989He was Heinrich-Hertz Gastprofessor at Karlsruhe University in November and December 1989, Robert Burns Woodward Visiting Professor at Harvard University in 1997 and again in 2000, and Newton Abraham Professor at Lincoln College, Oxford University in 1999-2000. He was also Adjunct Professor at the Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok in 2005.
// Famous Libra Celebrities peoples
Melissa Brim
Melissa Brim is the ex-girlfriend of former professional boxer Floyd Mayweather Jr. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jacob Tremblay
Jacob Tremblay is a Canadian child actor. Let’s have a look at his family & personal life including age, birthday, relationships, net worth and fun facts.
Sierra Furtado
Check out all that you wanted to know about Sierra Furtado, the famous YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriend, fun trivia facts and more.
Sexxy Lexxy
Alexis Smith Walker, popularly known as Sexxy Lexxy, is an African-American singer. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements, and fun facts about her.
Benjamin Keough
Benjamin Keough is an American socialite who is best known as the grandson and look-alike of legendary musician Elvis Presley.
Lizzie LDShadowLady
Check out all that you wanted to know about Lizzie LDShadowLady, the famous YouTuber and gamer; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriend, fun trivia facts and more.
Jean-Marie Lehn's FAQ
What is Jean-Marie Lehn birthday?
Jean-Marie Lehn was born at 1939-09-30
Where is Jean-Marie Lehn's birth place?
Jean-Marie Lehn was born in Rosheim, France
What is Jean-Marie Lehn nationalities?
Jean-Marie Lehn's nationalities is French
Who is Jean-Marie Lehn spouses?
Jean-Marie Lehn's spouses is Sylvie Lederer
Who is Jean-Marie Lehn childrens?
Jean-Marie Lehn's childrens is David, Mathias
Who is Jean-Marie Lehn's father?
Jean-Marie Lehn's father is Pierre Lehn
Who is Jean-Marie Lehn's mother?
Jean-Marie Lehn's mother is Marie Lehn
What is Jean-Marie Lehn's sun sign?
Jean-Marie Lehn is Libra
How famous is Jean-Marie Lehn?
Jean-Marie Lehn is famouse as Chemist