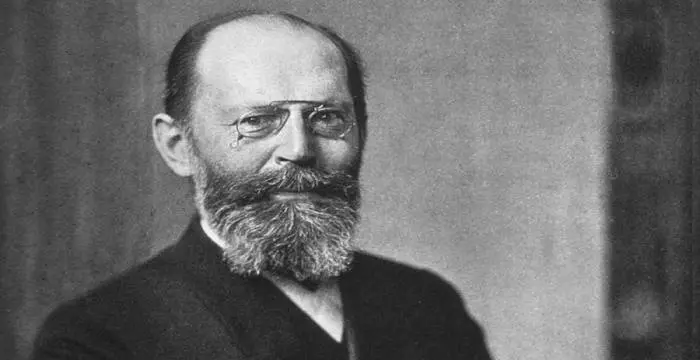Hermann Staudinger - Scientists, Facts and Childhood
Hermann Staudinger's Personal Details
Hermann Staudinger was a German chemist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1953
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | March 23, 1881 |
| Died on | September 8, 1965 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Scientists, Chemists, Organic Chemists |
| Spouses | Magda Woit |
| Siblings | Hans Wilhelm Staudinger, Karl August Friedrich Staudinger, Luise Federn, Wilhelm Staudinger |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Worms, Grand Duchy of Hesse, German Empire |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Dr. Franz Gottfried Christian Karl Georg Staudinger |
| Mother | Auguste Staudinger |
| Sun Sign | Aries |
| Born in | Worms, Grand Duchy of Hesse, German Empire |
| Famous as | Chemist |
| Died at Age | 84 |
// Famous Organic Chemists
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist who is best known for his discovery of the periodic law. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Aleksandr Borodin
Aleksandr Borodin was a prodigal Russian music composer and scientist. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
Hermann Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer was a Nobel Prize winning chemist from Germany who is known for inventing the ‘Fischer Projection’ method. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
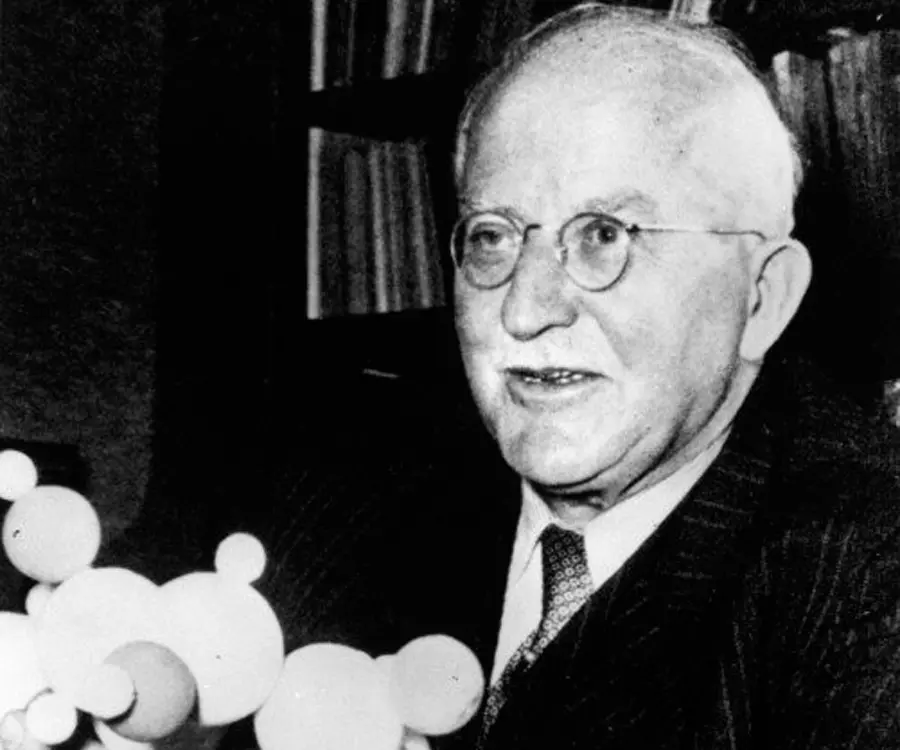
Hermann Staudinger's photo
Who is Hermann Staudinger?
Hermann Staudinger was a German chemist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1953 for his modern concept of polymers, which he demonstrated as covalently bonded macromolecular or giant molecular structures. He as well as J. Fritschi suggested the concept in the early 1920s but met with initial resistance. The term ‘macromolecule’ (macro + molecule) was coined by him. He began to examine polymers while conducting his research on the synthesis of isoprene, monomer of natural rubber, for the German chemical company ‘BASF’. Staudinger as well as other researchers displayed that polymers are long-chain molecules that are created out of chemical interaction of small molecules and not by physical aggregation, as was perceived at that time. He demonstrated that synthesis of these chain like molecules could be attained by applying different procedures and that their identity could be retained even after being subjected to chemical alterations. This pioneering work of Staudinger not only led to the theoretical foundation of polymer chemistry but also paved way for development of modern plastics, thus greatly contributing to the development of the plastics industry. This research also contributed to the advancement of molecular biology that dealt with comprehending the structure of proteins as well as other macromolecules present in living things. He is also noted for his discovery of the organic compound called ketenes and the ‘Staudinger reduction’ or the ‘Staudinger reaction’.
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Childhood & Early Life
He was born on March 23, 1881, in Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany to Dr. Franz Gottfried Christian Karl Georg Staudinger and his wife Auguste Staudinger. His father was a neo-Kantian philosopher.
He had three brothers, Karl August Friedrich Staudinger, Wilhelm Staudinger and Hans Wilhelm Staudinger and one sister Luise Federn.
He attended the Gymnasium in Worms and completed his matriculation in 1899.
Thereafter he enrolled at the ‘University of Halle’ and after a short while transferred to technical university at Darmstadt following his father’s new teaching job at Darmstadt.
He then furthered his studies in Munich and Halle, ultimately earning Ph.D. from the ‘University of Halle’ in 1903, submitting his thesis on the malonic esters of unsaturated compounds.
Career
After completing his Ph.D. he joined the ‘University of Strasbourg’ where he worked under Professor Johannes Thiele, a noted German chemist, and made his first discovery, the ketenes. The Ketenes were studied by Staudinger as a class, the first study of its kind by anyone. These are highly reactive organic compounds that are defined by form R′R″C=C=O, which later proved to be synthetically significant intermediary in producing antibiotics like amoxicillin and penicillin.
His research followed by his discovery of ketenes became the subject of his ‘Habilitation’, the highest academic qualification bestowed on a scholar, which he received in 1907. The same year in November he was inducted by the ‘Institute of Chemistry’ of the ‘Technical University of Karlsruhe’ as an Assistant Professor of Organic Chemistry. During his tenure at the university he became successful in isolating several useful organic compounds.
He started investigations on polymers while conducting his research on the synthesis of isoprene, monomer of natural rubber, in 1910 for the German chemical company ‘BASF’. Through his groundbreaking research work he published a paper in 1920 where he suggested that polymers like rubber, starch, proteins and cellulose are long-chain molecules that are formed out of chemical interaction of molecular units.
This idea was contrary to the prevailing concept suggested by leading chemists of those times like Heinrich Wieland and Emil Fischer, who believed that these high-molecular weight compounds were a result of physical aggregation of small molecules into colloids.
In 1912 he joined the faculty at the ‘Swiss Federal Institute of Technology’ located at Zürich, Switzerland and served the institute for fourteen years till 1926.
In 1919 he researched with his colleague Meyer and discovered that the anion azide reacts with triphenylphosphine, a common organophosphorus compound commonly used as a reducing agent, to generate phosphazide. This chemical reaction was named after him as the ‘Staudinger reaction’ or the ‘Staudinger reduction’.
In 1922 he as well as J. Fritschi suggested that polymers are giant molecular structures, which are adhered together through covalent bonds. He also demonstrated that different procedures could be applied to obtain synthesis of the chainlike molecules, which he termed as macromolecules, and suggested that these high molar masses could retain their identity even after being subjected to chemical alterations.
The ‘University of Freiburg’ located at Freiburg in Breisgau, southwest Germany, inducted him as lecturer of chemistry in 1926.
In 1940 he took up additional responsibility as the Principal of the ‘Research Institute for Macromolecular Chemistry’. The same year he established the first ever journal on polymer chemistry.
In 1951 he was selected as Head of the ‘State Research Institute for Macromolecular Chemistry’, a position he served till April 1956.
He was a prolific writer and wrote several books over the years. Some of his published books are ‘Die Ketene’ (Ketenes), 1912; ‘Die hochmolekularen organischen Verbindungen, Kautschak und Cellulose’ (The high-molecular organic compounds, rubber and cellulose), 1932; ‘Makromolekulare Chemie und Biologie’ (Macromolecular chemistry and biology), 1947; and ‘Arbeitserinnerungen’ (Working Memoirs), 1961.
Apart from books, many scientific papers were published by him on his works on ketenes, macromolecular compounds, autoxidation, insecticides, oxalyl chloride and aliphatic diazo-compounds among others. Of these around 120 papers were on cellulose with a total of about 500 scientific papers on macromolecular compounds.
He was a member and honorary member of many Chemical Societies including Tokyo’s ‘Society of Macromolecular Chemistry’.
He was conferred with honorary doctorates from several universities including ‘University of Strasbourg’, ‘University of Torino’, ‘University of Mainz’, ‘Technische Hochschule Karlsruhe’ and ‘University of Salamanca’.
Major Works
His path-breaking illustration of the nature of high molar masses that he termed as macromolecules led to a new field of chemistry - polymer chemistry. The potentiality of the field that he viewed long back proved to be of immense use with his pioneering research work leading the world to a new era of textiles, myriad plastics and other polymeric materials. While the consumers are benefited with more affordable products, the engineers are able to develop lighter and more durable structures.
His research on polymers also helped in the development of molecular biology that deals with understanding the structure of proteins as well as other high molar masses of living things.
Awards & Achievements
He received the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1953.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married Magda Woit, a Latvian plant physiologist, in 1927. She remained his co-worker for years and her contributions were acknowledged by Staudinger while accepting the Nobel Prize. Magda was also a co-author of many of his publications.
He passed away on September 8, 1965, at the age of 84 years in Freiburg, West Germany.
Trivia
In recognition to his remarkable contributions in chemistry, the ‘Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker’ and the ‘American Chemical Society’ labelled his work in 1999 as ‘International Historic Chemical Landmark’.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Hermann Staudinger's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Chemistry | |
| 0 | 1953 | |
Hermann Staudinger biography timelines
- // 23rd Mar 1881He was born on March 23, 1881, in Worms, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany to Dr. Franz Gottfried Christian Karl Georg Staudinger and his wife Auguste Staudinger. His father was a neo-Kantian philosopher.
- // 1899He attended the Gymnasium in Worms and completed his matriculation in 1899.
- // 1903He then furthered his studies in Munich and Halle, ultimately earning Ph.D. from the ‘University of Halle’ in 1903, submitting his thesis on the malonic esters of unsaturated compounds.
- // 1907His research followed by his discovery of ketenes became the subject of his ‘Habilitation’, the highest academic qualification bestowed on a scholar, which he received in 1907. The same year in November he was inducted by the ‘Institute of Chemistry’ of the ‘Technical University of Karlsruhe’ as an Assistant Professor of Organic Chemistry. During his tenure at the university he became successful in isolating several useful organic compounds.
- // 1910 To 1920He started investigations on polymers while conducting his research on the synthesis of isoprene, monomer of natural rubber, in 1910 for the German chemical company ‘BASF’. Through his groundbreaking research work he published a paper in 1920 where he suggested that polymers like rubber, starch, proteins and cellulose are long-chain molecules that are formed out of chemical interaction of molecular units.
- // 1912 To 1926In 1912 he joined the faculty at the ‘Swiss Federal Institute of Technology’ located at Zürich, Switzerland and served the institute for fourteen years till 1926.
- // 1919In 1919 he researched with his colleague Meyer and discovered that the anion azide reacts with triphenylphosphine, a common organophosphorus compound commonly used as a reducing agent, to generate phosphazide. This chemical reaction was named after him as the ‘Staudinger reaction’ or the ‘Staudinger reduction’.
- // 1922In 1922 he as well as J. Fritschi suggested that polymers are giant molecular structures, which are adhered together through covalent bonds. He also demonstrated that different procedures could be applied to obtain synthesis of the chainlike molecules, which he termed as macromolecules, and suggested that these high molar masses could retain their identity even after being subjected to chemical alterations.
- // 1926The ‘University of Freiburg’ located at Freiburg in Breisgau, southwest Germany, inducted him as lecturer of chemistry in 1926.
- // 1927He married Magda Woit, a Latvian plant physiologist, in 1927. She remained his co-worker for years and her contributions were acknowledged by Staudinger while accepting the Nobel Prize. Magda was also a co-author of many of his publications.
- // 1940In 1940 he took up additional responsibility as the Principal of the ‘Research Institute for Macromolecular Chemistry’. The same year he established the first ever journal on polymer chemistry.
- // 1951 To Apr 1956In 1951 he was selected as Head of the ‘State Research Institute for Macromolecular Chemistry’, a position he served till April 1956.
- // 1953He received the ‘Nobel Prize in Chemistry’ in 1953.
- // 8th Sep 1965He passed away on September 8, 1965, at the age of 84 years in Freiburg, West Germany.
- // 1999In recognition to his remarkable contributions in chemistry, the ‘Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker’ and the ‘American Chemical Society’ labelled his work in 1999 as ‘International Historic Chemical Landmark’.
// Famous Aries Celebrities peoples
Skai Jackson
Skai Jackson is an American child actress with huge fan following. Find more about her family & personal life, relationships, facts and more.
Shemar Moore
Shemar Moore is a model turned actor best known for his role in the television series ‘The Young and the Restless’. This biography of Shemar Moore provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Vasily Zaytsev
Vasily Zatysev was a Russian sniper who served during the World War II. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Ivey Meeks
Ivey Meeks is an American YouTube star and model. Let’s have a look at her family and personal life including age, date of birth, net worth, boyfriends and fun facts.
Tobi Lerone
Check out all that you wanted to know about Tobi Lerone, the famous YouTube Personality and gamer; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Hermann Staudinger's FAQ
What is Hermann Staudinger birthday?
Hermann Staudinger was born at 1881-03-23
When was Hermann Staudinger died?
Hermann Staudinger was died at 1965-09-08
Where was Hermann Staudinger died?
Hermann Staudinger was died in Freiburg, West Germany
Which age was Hermann Staudinger died?
Hermann Staudinger was died at age 84
Where is Hermann Staudinger's birth place?
Hermann Staudinger was born in Worms, Grand Duchy of Hesse, German Empire
What is Hermann Staudinger nationalities?
Hermann Staudinger's nationalities is German
Who is Hermann Staudinger spouses?
Hermann Staudinger's spouses is Magda Woit
Who is Hermann Staudinger siblings?
Hermann Staudinger's siblings is Hans Wilhelm Staudinger, Karl August Friedrich Staudinger, Luise Federn, Wilhelm Staudinger
What was Hermann Staudinger universities?
Hermann Staudinger studied at University of Halle
Who is Hermann Staudinger's father?
Hermann Staudinger's father is Dr. Franz Gottfried Christian Karl Georg Staudinger
Who is Hermann Staudinger's mother?
Hermann Staudinger's mother is Auguste Staudinger
What is Hermann Staudinger's sun sign?
Hermann Staudinger is Aries
How famous is Hermann Staudinger?
Hermann Staudinger is famouse as Chemist