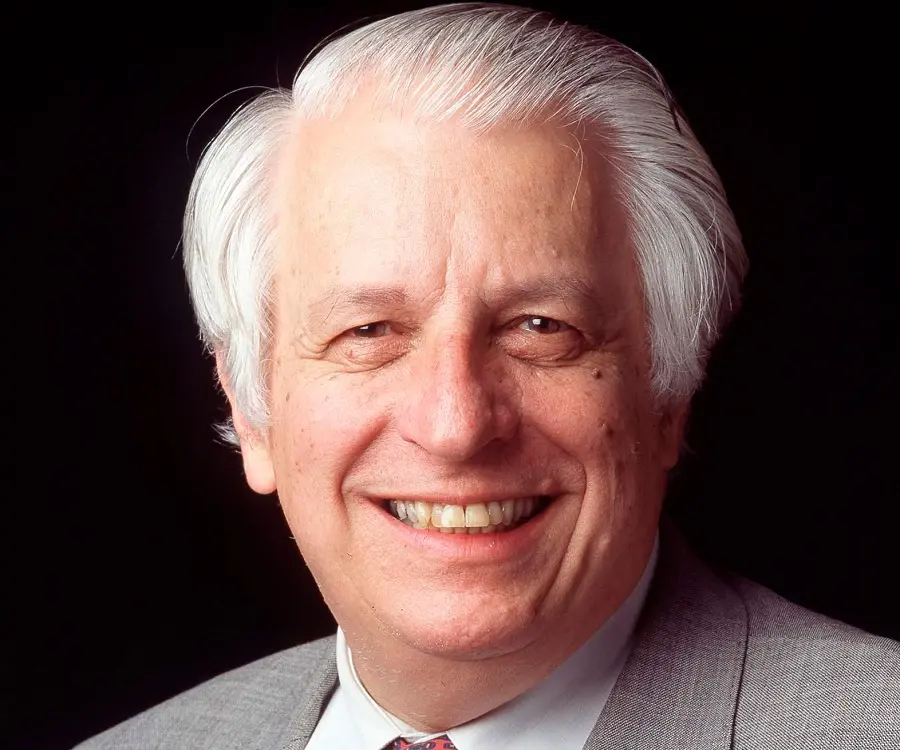
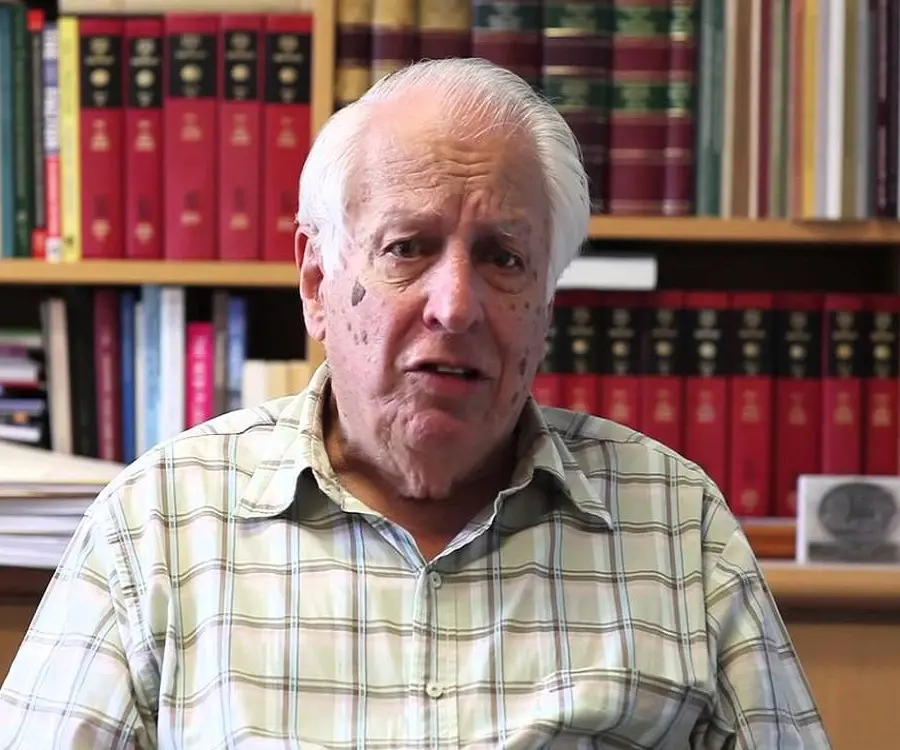
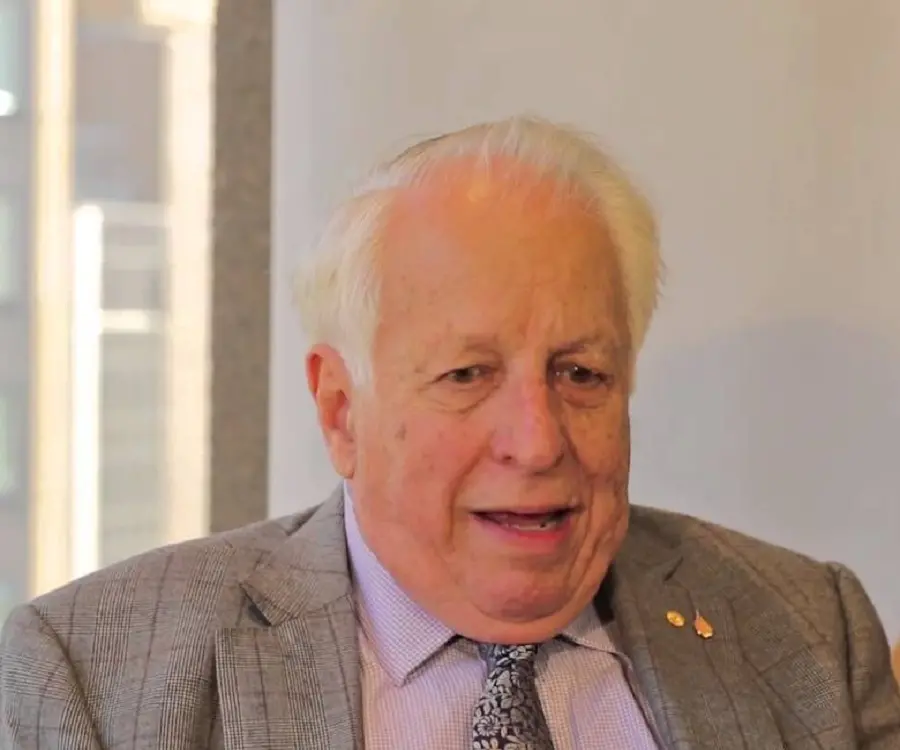
Gustav Nossal - Immunologists, Life Achievements and Life
Gustav Nossal's Personal Details
Gustav Nossal is a distinguished Australian researcher and scientist
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | June 4, 1931 |
| Nationality | Australian |
| Famous | University Of Melbourne, Scientists, Biologists, Immunologists |
| Spouses | Lyn |
| Known as | Sir Gustav Victor Joseph Nossal |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Bad Ischl, Austria |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Gemini |
| Born in | Bad Ischl, Austria |
| Famous as | Immunologist |
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Gustav Nossal's photo
Who is Gustav Nossal?
Gustav Nossal is one of Australia’s most celebrated scientists and research biologists. A pioneering researcher, his accomplishments in the field of antibody formation and immunological tolerance are world-renowned. Born in Austria with a Jewish ancestry but baptized as a Roman Catholic, he moved to Australia with his family when he was barely eight years old. Since young, Nossal aimed to become a doctor and researcher. He studied accordingly and gained a degree in medicine and science from the University of Sydney. Thereafter, he moved to Melbourne where he worked under his mentor and guide Sir Macfarlane Burnet and soon took up the latter’s position as Director of Walter and Eliza Hall of Institute of Medical Research, which he served for 31 years from 1965 to 1996. It was during this time that he made the revolutionary discovery of ‘one cell one antibody’ rule. Over the years, Nossal made noteworthy contribution in the field of medical science and research and has been felicitated with numerous prestigious honors and awards.
// Famous Immunologists
Georges J. F. Kohler
Georges J. F. Kohler was a German immunologist who received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1984. Check this biography to get details about his life, profile and timeline.
Cesar Milstein
Cesar Milstein was an Argentinian biochemist who received the Nobel Prize for his discovery of monoclonal antibody. Explore this biography to get details about his life, career and scientific discoveries.
Susumu Tonegawa
Susumu Tonegawa is a Japanese molecular biologist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1987. This biography of Susumu Tonegawa provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Gustav Nossal was born as Gustav Victor Joseph Nossal on June 4, 1931 in Bad Ischl, Austria.
Since his paternal lineage was Jewish, the Nossal family was at a risk during Nazi Germany’s annexation of Austria, despite young Nossal being baptized as Roman Catholic. To evade danger, the family shifted base to Australia in 1939
Completing his preliminary education, he enrolled at the St Aloysius' College. Interestingly, in spite of not knowing English, he graduated from the same as the dux of the College in 1947.
Following year, he attained admission at the Sydney Medical School, from where he graduated with first-class honors, earning a BSc in Medicine in 1953 and a Bachelor in Surgery in 1955.
Career
Completing his studies, he took up a job in Sydney at the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital but did not continue in the same for long and in 1957, he moved to Melbourne, where he started working with Macfarlane Burnet in medical science at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research. In 1960, he earned his PhD degree from University of Melbourne.
Meanwhile for two years, from 1959 to 1961, he served as the Assistant Professor of Genetics at the Stanford University before returning to Australia to work with Burnet.
Following Burnet’s retirement in 1965, he took up the latter position and served as the Director of Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, which he continued until 1996. However, this wasn’t the only profile that he was holding. He concurrently served as the professor of biology at the University of Melbourne.
For a year each in 1968 and later in 1976, he served at the Pasteur Institute in Paris and later as a Special Consultant to the World Health Organization.
During his term as the Director of Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, he not just helped in the expansion and diversification of the institute’s research work but also built on the work started off by his mentor, thus laying the foundation of modern immunology.
Throughout his life, he researched on the various segments of immunology or nature’s defences. His main work comprised of finding out how the body manufactures the precious antibody molecules that helps an individual to be free from infection.
The magnum opus of his research work was the discovery of the ‘one cell-one antibody’ rule. According to this rule, each B lymphocyte developed in bone marrow secretes a specific antibody in response to an encounter with a specific foreign antigen.
His discoveries in fundamental immunology and related fields are mostly summarized in his 530 scientific articles and five books which he has published over the course of his career. These include ‘Antibodies and Immunity’ in 1968, ‘Antigens, Lymphoid Cells and the Immune Response’ in 1971, ‘Medical Science and Human Goals’ in 1975, ‘Nature's Defences’ in 1978, and ‘Reshaping Life: Key Issues in Genetic Engineering’ in 1984.
He served as the President of the International Union of Immunological Societies from 1986 to 1989 and of the Australian Academy of Science from 1994 to 1998. Meanwhile, from 1989 to 1998, he served as the member of the Prime Minister’s Science, Engineering and Innovation Council (PMSEIC) and Chairman of the Victorian Health Promotion Foundation from 1987 to 1996.
From 1993 to 2002, he chaired the committee in charge of supervising the World Health Organization’s Global Program for Vaccines and Immunization. Additionally, he also chaired the Strategic Advisory Council of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Children’s Vaccine Program from 1998 to 2003.
For two years, from 1998 to 2000, he served as the Deputy Chairman of the Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation and serves as the Chairman of the Advisory Committee of the Global Foundation. Furthermore, he is a member of the Patrons Council of the Epilepsy Foundation of Victoria and of the Advisory Board of the Health Impact Fund.
Awards & Achievements
For his extensive contribution in the field of medical research and science, in 1970, he was appointed as a Commander of the Order of the British Empire.
Seven years later in 1977, he was knighted for his revolutionary discovery in the field of immunology.
In 1982, he was conferred with the ANZAAS medal.
For his service in the field of research, medicine and science, he was bestowed with the prestigious honor of Companion of the Order of Australia in 1989.
In 1990, he was conferred with the highly-esteemed Albert Einstein World Award of Science.
In the year 1996, he won the Koch Gold Medal. The award is usually given to scientists and researchers who make major advances in the field of biomedical sciences, especially in microbiology and immunology.
In 1997, he was identified and listed as one of the 100 Australians who were Australia's Living National Treasures. Three years later, he was named Australian of the Year.
For his study of antibody formation and immunological tolerance, he was presented with the Centenary Medal in 2001. Following year, his portrait was featured on an Australian postage stamp.
In 2006, he was inducted as honorary member of the Monash University Golden Key Society. Four year later, he was awarded the Inaugural Monash Medal as an Outstanding Australian for his accomplishment in the field of medical science and research. In 2012, he received the Lifetime Achievement Award by Monash University Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences
Personal Life & Legacy
It was while he was working at the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital at Sydney that he married his wife, Lyn.
Over the years, other than being involved in research work and scientific discovery, he has been heavily involved in charitable work and is the patron of a number of organizations.
Several institutions of research and study have been named in his honor including The Nossal Institute for Global Health at the University of Melbourne and The Nossal High School located at the Berwick campus of Monash University
Trivia
This Austria-Born Australian researcher and scientist came up with the revolutionary discovery of ‘one-cell one antibody’ rule in the field of immunology.
// Famous University Of Melbourne
Nicole Kidman
Nicole Kidman is one of the most talented actors that the Hollywood film industry can boast of. Browse through this biography to get detailed information regarding her life, childhood, profile & timeline
Peter Singer
Peter Singer is an Australian moral philosopher who has challenged traditional notions of applied ethics throughout his philosophical and literary career. Check out this biography to get detailed information on his life.
Julia Gillard
Julia Gillard is a former Prime Minister of Australia and the first woman to hold the position. To know more about her childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Gustav Nossal's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Australian Living National Treasures (1997) | |
| 0 | Australian of the Year (2000) | |
| 0 | Companion of the Order of Australia (1989) | |
| 0 | Albert Einstein World Award of Science (1990) | |
| 0 | Koch Gold Medal (1996) | |
Gustav Nossal biography timelines
- // 4th Jun 1931Gustav Nossal was born as Gustav Victor Joseph Nossal on June 4, 1931 in Bad Ischl, Austria.
- // 1939Since his paternal lineage was Jewish, the Nossal family was at a risk during Nazi Germany’s annexation of Austria, despite young Nossal being baptized as Roman Catholic. To evade danger, the family shifted base to Australia in 1939
- // 1947Completing his preliminary education, he enrolled at the St Aloysius' College. Interestingly, in spite of not knowing English, he graduated from the same as the dux of the College in 1947.
- // 1955Following year, he attained admission at the Sydney Medical School, from where he graduated with first-class honors, earning a BSc in Medicine in 1953 and a Bachelor in Surgery in 1955.
- // 1957Completing his studies, he took up a job in Sydney at the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital but did not continue in the same for long and in 1957, he moved to Melbourne, where he started working with Macfarlane Burnet in medical science at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research. In 1960, he earned his PhD degree from University of Melbourne.
- // 1959 To 1961Meanwhile for two years, from 1959 to 1961, he served as the Assistant Professor of Genetics at the Stanford University before returning to Australia to work with Burnet.
- // 1965 To 1996Following Burnet’s retirement in 1965, he took up the latter position and served as the Director of Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, which he continued until 1996. However, this wasn’t the only profile that he was holding. He concurrently served as the professor of biology at the University of Melbourne.
- // 1970For his extensive contribution in the field of medical research and science, in 1970, he was appointed as a Commander of the Order of the British Empire.
- // 1977Seven years later in 1977, he was knighted for his revolutionary discovery in the field of immunology.
- // 1982In 1982, he was conferred with the ANZAAS medal.
- // 1989For his service in the field of research, medicine and science, he was bestowed with the prestigious honor of Companion of the Order of Australia in 1989.
- // 1990In 1990, he was conferred with the highly-esteemed Albert Einstein World Award of Science.
- // 1996In the year 1996, he won the Koch Gold Medal. The award is usually given to scientists and researchers who make major advances in the field of biomedical sciences, especially in microbiology and immunology.
- // 1997In 1997, he was identified and listed as one of the 100 Australians who were Australia's Living National Treasures. Three years later, he was named Australian of the Year.
- // 1998 To 2000For two years, from 1998 to 2000, he served as the Deputy Chairman of the Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation and serves as the Chairman of the Advisory Committee of the Global Foundation. Furthermore, he is a member of the Patrons Council of the Epilepsy Foundation of Victoria and of the Advisory Board of the Health Impact Fund.
- // 2001For his study of antibody formation and immunological tolerance, he was presented with the Centenary Medal in 2001. Following year, his portrait was featured on an Australian postage stamp.
- // 2006In 2006, he was inducted as honorary member of the Monash University Golden Key Society. Four year later, he was awarded the Inaugural Monash Medal as an Outstanding Australian for his accomplishment in the field of medical science and research. In 2012, he received the Lifetime Achievement Award by Monash University Faculty of Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Richard Dawkins
Richard Dawkins is an English ethologist and evolutionary biologist. This biography of Richard Dawkins provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Carl Linnaeus
Carolus Linnaeus was a renowned Swedish biologist popularly known as the ‘Father of Modern Taxonomy’ who founded the binomial nomenclature. Read on to know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline
Alexander Fleming
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish biologist and pharmacologist who discovered enzyme lysozyme and antibiotic penicillin. This biography of Alexander Fleming profiles his childhood, life, research, discoveries, achievements and timeline.
Gustav Nossal's FAQ
What is Gustav Nossal birthday?
Gustav Nossal was born at 1931-06-04
Where is Gustav Nossal's birth place?
Gustav Nossal was born in Bad Ischl, Austria
What is Gustav Nossal nationalities?
Gustav Nossal's nationalities is Australian
Who is Gustav Nossal spouses?
Gustav Nossal's spouses is Lyn
What was Gustav Nossal universities?
Gustav Nossal studied at University Of Melbourne
What was Gustav Nossal notable alumnis?
Gustav Nossal's notable alumnis is University Of Melbourne
What is Gustav Nossal's inventions/discoveries?
One-Cell One Antibody Rule was invented (or discovered) by Gustav Nossal
What is Gustav Nossal's sun sign?
Gustav Nossal is Gemini
How famous is Gustav Nossal?
Gustav Nossal is famouse as Immunologist