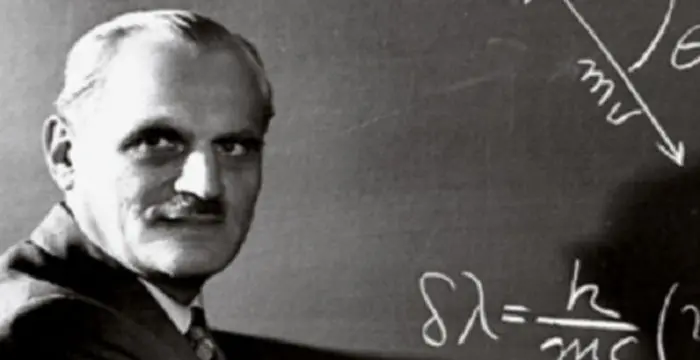
Arthur Compton - Nobel Prize Laureate in Physics, Family and Life
Arthur Compton's Personal Details
Arthur Compton was a renowned American physicist who discovered the Compton Effect
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | September 10, 1892 |
| Died on | March 15, 1962 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Princeton University, Scientists, Physicists, Nobel Prize Laureate in Physics |
| Spouses | Betty Charity McCloskey |
| Siblings | Karl Taylor Compton, Wilson Martindale Compton |
| Known as | Arthur Holly Compton |
| Childrens | Arthur Allen Compton, John Joseph Compton |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Discoveries / Inventions |
|
| Birth Place | Wooster, Ohio, USA |
| Religion | Baptist |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Elias Compton |
| Mother | Otelia Catherine |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Wooster, Ohio, USA |
| Famous as | Nobel Prize Laureate in Physics |
| Died at Age | 69 |
Arthur Compton's photo
Who is Arthur Compton?
Arthur Holly Compton was a renowned American physicist who first rose to fame with his famous revolutionary discovery of the Compton Effect for which he also won the Nobel Prize in Physics. This discovery confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle. Thomson was initially interested in astronomy before he shifted his focus to the study of quantum physics. He started his research in Cavendish Laboratory of Cambridge University and this research led to the discovery of Compton Effect. Later on, during the Second World War, Compton became head of the Manhattan Project’s Metallurgical Laboratory. Manhattan Project developed the first nuclear weapons of the world and Compton played a key role in it. He also served as Chancellor of Washington University in St. Louis. Under his leadership, the University made remarkable academic progress; the university formally desegregated its undergraduate divisions, named its first female full professor, and enrolled a record number of students. After he retired as Chancellor, he continued to work as Distinguished Service Professor of Natural Philosophy till 1961. For his contribution to the science, Compton received many awards and honors in his lifetime.
// Famous Physicists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, best known for his development of alternating current electrical systems. This biography of Nikola Tesla provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Arthur Compton was born on September 10, 1892, in Wooster, Ohio, to Elias and Otelia. He was born into a family of academics. His father was a dean of the University of Wooster, while both his brothers, Karl and Wilton attended the Princeton University and earned PhDs from the University.
In his early years, Compton was more interested in astronomy; he photographed the Halley’s Comet in 1910.
In 1913, he earned his Bachelor’s Degree in Science from the Wooster University. A year after his graduation, Compton earned his Master of Arts degree from Princeton University. He completed his PhD in Physics in 1916.
Career
Arthur began his career in 1916–1917, as a physics instructor at the University of Minnesota. For the following two years he worked on the development of sodium lamps as a research engineer of the Westinghouse Lamp Company. During the First World War, Compton developed aircraft instrumentation for the Signal Corps.
In 1919, Compton was awarded one of the first two National Research Council Fellowships that allowed students to study abroad. He decided to go to Cambridge University’s Cavendish Laboratory, where he worked with George Paget Thomson, and studied X-ray scattering and Gamma Ray Absorption.
In 1920, he returned to the United States and was appointed as the Head of the Department of Physics at Washington University, St. Louis.
In 1922, he discovered the ‘Compton Effect’, which confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle.
In 1923, Compton’s paper explaining X-Ray shifts was published in the Physical Review. The same year, he moved to the Chicago University as a Physics Professor.
In 1926, he worked for General Electric. He was a consultant for the Lamp department, here. In the same year, he came up with his first book called ‘X-Rays and Electrons’.
During 1930–1940 Arthur Compton became interested in the Earth’s cosmic rays. He led a world-wide study of the geographic variations in the intensity of cosmic rays.
Compton was appointed as the chairman of the NASC (National Academic Sciences Committee) in 1941. The committee studied the military potential of atomic energy. The committee’s work led to the development of the popular Manhattan Project.
In 1942, he became head of the Manhattan Project's Metallurgical Laboratory. He was tasked with responsibility for producing nuclear reactors to convert uranium into plutonium, finding ways to separate the plutonium from the uranium and to design an atomic bomb.
After the Second World War ended Compton resigned from his post of the Physics professor at the University of Chicago and became Chancellor of the Washington University in 1946.
Compton resigned from the post of Chancellor of Washington University in 1954. However, he continued to work as Distinguished Service Professor of Natural Philosophy till 1961. .
Major Works
The most remarkable work of Arthur Compton was the discovery of the Compton Effect in 1922. This discovery confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle.
In 1942, he played a key role in Manhattan Project which led to the development of first nuclear weapons in the world.
Awards & Achievements
Compton shared the 1927 Nobel Prize in Physics with C.T.R. Wilson. He won the prize for his discovery of Compton Effect which confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle.
In 1930, he won the Matteucci Gold Medal for his discovery of the Compton Effect.
In 1940, he was awarded the Hughes Medal of Royal Society and Benjamin Franklin Medal. He was awarded these medals for his huge contribution in the field of science.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married Betty Charity in 1916. Charity was his classmate in Wooster University. The couple had two sons: Arthur Alan and John Joseph Compton.
He died on March 15 1962, at the age of 69, in Berkely, California. He died due to cerebral haemorrhage and was buried in the Wooster Cemetery, Ohio.
Moon’s ‘Compton Crater’ has been named after Arthur Compton and his brother Karl Compton.
The Compton Gamma Ray Observatory of NASA is also named in the honour of Arthur Compton.
Trivia
After completing his PhD, Arthur Holly Compton wanted to pursue a career in religion.
The Compton brothers —Arthur, Karl and Wilson —became the first group of three brothers to earn PhDs from Princeton.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Arthur Compton's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize for Physics (1927) | |
| 0 | Matteucci Medal (1930) | |
| 0 | Franklin Medal (1940) | |
| 0 | Hughes Medal (1940) | |
Arthur Compton biography timelines
- // 10th Sep 1892Arthur Compton was born on September 10, 1892, in Wooster, Ohio, to Elias and Otelia. He was born into a family of academics. His father was a dean of the University of Wooster, while both his brothers, Karl and Wilton attended the Princeton University and earned PhDs from the University.
- // 1910In his early years, Compton was more interested in astronomy; he photographed the Halley’s Comet in 1910.
- // 1913 To 1916In 1913, he earned his Bachelor’s Degree in Science from the Wooster University. A year after his graduation, Compton earned his Master of Arts degree from Princeton University. He completed his PhD in Physics in 1916.
- // 1916 To 1917Arthur began his career in 1916–1917, as a physics instructor at the University of Minnesota. For the following two years he worked on the development of sodium lamps as a research engineer of the Westinghouse Lamp Company. During the First World War, Compton developed aircraft instrumentation for the Signal Corps.
- // 1916He married Betty Charity in 1916. Charity was his classmate in Wooster University. The couple had two sons: Arthur Alan and John Joseph Compton.
- // 1919In 1919, Compton was awarded one of the first two National Research Council Fellowships that allowed students to study abroad. He decided to go to Cambridge University’s Cavendish Laboratory, where he worked with George Paget Thomson, and studied X-ray scattering and Gamma Ray Absorption.
- // 1920In 1920, he returned to the United States and was appointed as the Head of the Department of Physics at Washington University, St. Louis.
- // 1922In 1922, he discovered the ‘Compton Effect’, which confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle.
- // 1922The most remarkable work of Arthur Compton was the discovery of the Compton Effect in 1922. This discovery confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle.
- // 1923In 1923, Compton’s paper explaining X-Ray shifts was published in the Physical Review. The same year, he moved to the Chicago University as a Physics Professor.
- // 1926In 1926, he worked for General Electric. He was a consultant for the Lamp department, here. In the same year, he came up with his first book called ‘X-Rays and Electrons’.
- // 1927Compton shared the 1927 Nobel Prize in Physics with C.T.R. Wilson. He won the prize for his discovery of Compton Effect which confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle.
- // 1930 To 1940During 1930–1940 Arthur Compton became interested in the Earth’s cosmic rays. He led a world-wide study of the geographic variations in the intensity of cosmic rays.
- // 1930In 1930, he won the Matteucci Gold Medal for his discovery of the Compton Effect.
- // 1940In 1940, he was awarded the Hughes Medal of Royal Society and Benjamin Franklin Medal. He was awarded these medals for his huge contribution in the field of science.
- // 1941Compton was appointed as the chairman of the NASC (National Academic Sciences Committee) in 1941. The committee studied the military potential of atomic energy. The committee’s work led to the development of the popular Manhattan Project.
- // 1942In 1942, he became head of the Manhattan Project's Metallurgical Laboratory. He was tasked with responsibility for producing nuclear reactors to convert uranium into plutonium, finding ways to separate the plutonium from the uranium and to design an atomic bomb.
- // 1942In 1942, he played a key role in Manhattan Project which led to the development of first nuclear weapons in the world.
- // 1946After the Second World War ended Compton resigned from his post of the Physics professor at the University of Chicago and became Chancellor of the Washington University in 1946.
- // 1954 To 1961Compton resigned from the post of Chancellor of Washington University in 1954. However, he continued to work as Distinguished Service Professor of Natural Philosophy till 1961. .
- // 15th Mar 1962He died on March 15 1962, at the age of 69, in Berkely, California. He died due to cerebral haemorrhage and was buried in the Wooster Cemetery, Ohio.
// Famous Princeton University
Wentworth Miller
Wentworth Miller is an American actor and screenwriter who achieved recognition for his role in the TV series ‘Prison Break’.
Pete Hegseth
Pete Hegseth is a FOX News Channel contributor from America. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Terence Tao
Terence Tao is an Australian- American mathematician who has contributed enormously to the field of mathematics. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life and achievements.
Michael Porter
Michael Porter is an economist, researcher, author, advisor, speaker and teacher. This biography profiles his childhood, career, academic contribution, works, life, achievements and timeline.
Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman was a Nobel Prize winning American physicist who proposed the theory of quantum electrodynamics. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Brooke Shields
Brooke Shields is an American actress and model. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Arthur Compton's FAQ
What is Arthur Compton birthday?
Arthur Compton was born at 1892-09-10
When was Arthur Compton died?
Arthur Compton was died at 1962-03-15
Where was Arthur Compton died?
Arthur Compton was died in Berkeley, California, USA
Which age was Arthur Compton died?
Arthur Compton was died at age 69
Where is Arthur Compton's birth place?
Arthur Compton was born in Wooster, Ohio, USA
What is Arthur Compton nationalities?
Arthur Compton's nationalities is American
Who is Arthur Compton spouses?
Arthur Compton's spouses is Betty Charity McCloskey
Who is Arthur Compton siblings?
Arthur Compton's siblings is Karl Taylor Compton, Wilson Martindale Compton
Who is Arthur Compton childrens?
Arthur Compton's childrens is Arthur Allen Compton, John Joseph Compton
What was Arthur Compton universities?
Arthur Compton studied at Princeton University, University of Cambridge, The College of Wooster, Princeton University
What was Arthur Compton notable alumnis?
Arthur Compton's notable alumnis is Princeton University
What is Arthur Compton's inventions/discoveries?
Compton Effect was invented (or discovered) by Arthur Compton
What is Arthur Compton's religion?
Arthur Compton's religion is Baptist
Who is Arthur Compton's father?
Arthur Compton's father is Elias Compton
Who is Arthur Compton's mother?
Arthur Compton's mother is Otelia Catherine
What is Arthur Compton's sun sign?
Arthur Compton is Virgo
How famous is Arthur Compton?
Arthur Compton is famouse as Nobel Prize Laureate in Physics











