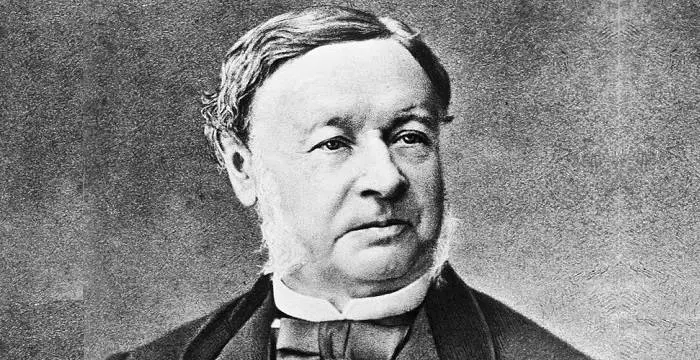André Lwoff - Microbiologists, Life Achievements and Family
André Lwoff's Personal Details
André Michel Lwoff was a French microbiologist, geneticist and protozoologist, who received the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | May 8, 1902 |
| Died on | September 30, 1994 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Biologists, Microbiologists |
| Spouses | Marguerite Bourdaleix |
| Known as | André Michel Lwoff |
| Birth Place | Ainay-le-Château, Allier, Auvergne, France |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Solomon Lwoff |
| Mother | Marie |
| Sun Sign | Taurus |
| Born in | Ainay-le-Château, Allier, Auvergne, France |
| Famous as | Microbiologist |
| Died at Age | 92 |
// Famous Microbiologists
Ferdinand Cohn
Ferdinand Cohn was a German biologist who is considered as the father of bacteriology and microbiology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist who developed the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. This biography of Louis Pasteur provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Carlo Urbani
Italian epidemiologist Carlo Urbani was the first person who identified SARS as a highly contagious disease. Find out more about his life in this biography.
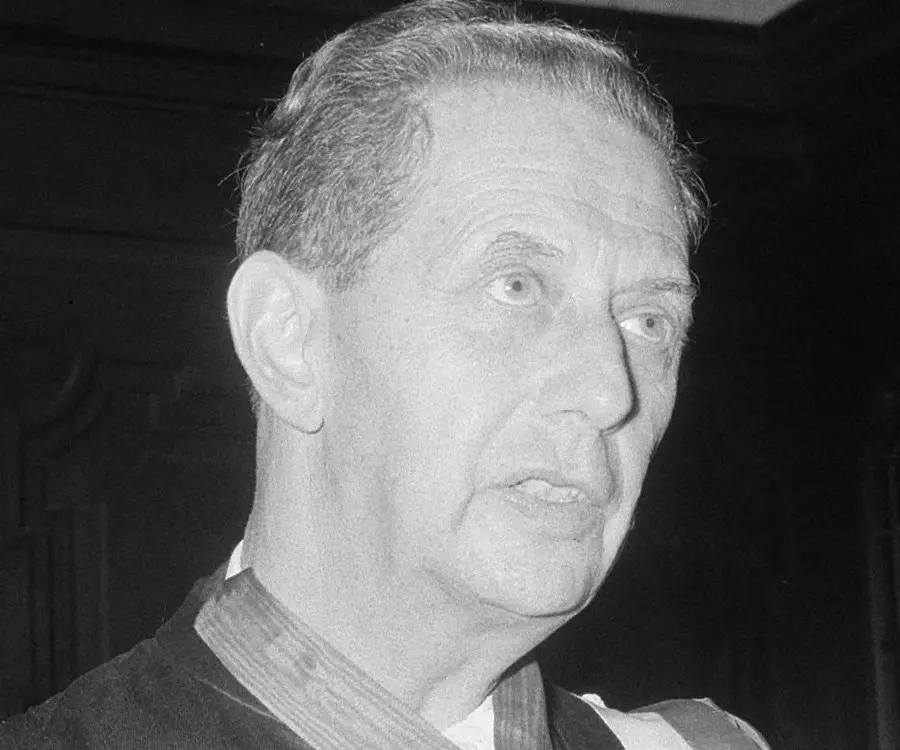
André Lwoff's photo
Who is André Lwoff?
André Michel Lwoff was a French microbiologist, geneticist and protozoologist, who received the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965 along with two French biologists François Jacob and Jacques Monod for his contributions in the discoveries regarding genetic control of enzyme and synthesis of virus. Together with Jacob and Monod he contributed in comprehending the lysogeny or the lysogenic cycle mechanism where bacteriophage, a bacterial virus, causes infection to bacteria which is then transferred to succeeding generations of bacteria entirely by way of cell division of its host. He showed that the infection is passed on in a non-infective form, which is called a prophage. He also showed that the prophage under some conditions engender an infective form that results in lysis or breaking down of the membrane of the bacterial cell and the viruses thus released due to such disintegration can infect other hosts of bacteria. He had done significant research on poliovirus, microbiota and bacteriophages at the renowned ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France where he served as departmental head. He received several honours and awards including the ‘Leeuwenhoek Medal’ from the ‘Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences’ in 1960 and the ‘Grand Prix Charles-Leopold Mayer’ from the French ‘Académie des Sciences’ in 1964. His written works include ‘Problems of Morphogenesis in Ciliates’ (1950) and ‘Biological Order’ (1962).
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
He was born on May 8, 1902, in Ainay-le-Château, Allier, in Auvergne, France, to Solomon Lwoff and his wife Marie. His father was a psychiatrist and his mother an artist.
He attended the ‘University of Paris’ from where he completed his graduation with a Science degree and thereafter in 1921, he joined the ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France at 19. He met great French biologist Edouard Chatton at the institute who became his mentor and with time the two scientists remained associated for around seventeen years till the death of the latter in 1947.
Edouard Chatton helped him join the laboratory of Félix Mesnil in the ‘Pasteur Institute’. He first examined the parasitic ciliates and their development cycle and studied morphogenesis. He further investigated issues related to nutrition of protozoan. In 1927 he earned his M.D.
Career
He partnered with his wife (a French microbiologist and virologist), Marguerite Lwoff, née Bourdaleix, all through his career, although Marguerite could not garner much recognition for her contributions as her husband did. She was best known for her investigations on metabolism. Her research work began with a group of protozoans called ciliates and continued with other significant investigations including Apostomatida.
The Lwoff couple were given a laboratory at the ‘Pasteur Institute’ where the duo investigated on Haemophilus metabolism and eventually they discovered the function of cozymase.
In 1932 he earned his Ph.D and upon obtaining a grant from the ‘Rockefeller Foundation’, he relocated for a year to the ‘Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Medical Research’ in the city of Heidelberg in south-west Germany. He joined the laboratory of German physician and biochemist Otto Meyerhof and researched on haematin, a developmental factor of flagellates, the particularity of protohaematin and related subjects.
He obtained another grant from the ‘Rockefeller Foundation’ and went to the ‘University of Cambridge’ with his wife in 1937 and spent seven months there in the lab of David Keilin.
He was inducted as Head of Department at the ‘Pasteur Institute’ in 1938. He carried on significant research work while serving at the institute.
By the time Lwoff began his investigation related to the problem of lysogenic bacteria, many such research works were being conducted on the developmental aspects of flagellates and ciliates.
While examining isolated bacteria, he concluded that bacteriophages are not secreted by lysogenic bacteria. He found that the generation of bacteriophages leads to fatality of the bacterium. He also suggested that external factors must be inducing such generation.
He started research on poliovirus from 1954. He conducted investigations to study how temperature sensitivity of viral development is associated with neurovirulence and such study made him consider the viral infection problem. Gradually it became apparent that non-specific aspects play a significant role in the growth of primary infection. He then further investigated on the mechanics of particular deterrents of viral growth.
He became the Corresponding Member of the ‘Botanical Society of America’ in 1956.
In 1958 he became the ‘Foreign Member of the Royal Society’ (ForMemRS), London as also the Honorary Foreign Member of the ‘American Academy of Arts and Sciences’.
He served the ‘Sorbonne’ from 1959 to 1968 as Professor of Microbiology.
He remained one of the driving forces in the establishment of the ‘European Organization of Molecular Biology’ that was officially formed in July 1964.
For his services during the ‘Second World War’ he received the ‘Medal of the Resistance’ in 1964 and was made the commander of the ‘Légion d'Honneur’ in 1966.
He retired from the ‘Pasteur Institute’ in 1968 and thereafter served the ‘Cancer Research Institute’ at Villejuif, near Paris, as the Director till 1972.
He was an Honorary Member of the ‘Harvey Society’ (1954), the ‘New York Academy of Sciences’ (1955), the ‘American Society of Biological Chemists’ (1961) and the ‘Society for General Microbiology’ (1962).
He also remained member of several national and international societies and committees like the ‘International Committee for the Organization of Medical Sciences’, the ‘Société de Pathologie exotique’ and the ‘Société Zoologique de France’.
He served as President of the ‘Société des Microbiologistes de langue française’ and the ‘International Association of Microbiological Societies’.
He was conferred honorary degrees by several prestigious universities, which include a D.Sc. from the ‘University of Oxford’ as also from the ‘University of Chicago’, both in 1959; a Doctor of Laws from the ‘University of Glasgow’ in 1963; and an M.D. from the ‘Université catholique de Louvain’ in 1966.
Awards & Achievements
In 1965 he was jointly awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ along with two other French biologists, François Jacob and Jacques Monod
Personal Life & Legacy
On December 5, 1925 he married French microbiologist and virologist Marguerite Bourdaleix. The couple worked closely at the ‘‘Pasteur Institute’ and remained close colleagues while working on the parasitical ciliates at the ‘Roscoff Marine Biological Station’ along with French biologist Édouard Chatton.
He was a humanist and strongly opposed capital punishment.
Lwoff was fond of music, painting and sculpture.
On September 30, 1994, he passed away in Paris at 92 years of age. He was the last surviving member of the trio who jointly received the ‘Nobel Prize’ in 1965.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
André Lwoff's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | ForMemRS (1958) | |
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Medicine (1965) | |
| 0 | Leeuwenhoek Medal (1960) | |
André Lwoff biography timelines
- // 8th May 1902He was born on May 8, 1902, in Ainay-le-Château, Allier, in Auvergne, France, to Solomon Lwoff and his wife Marie. His father was a psychiatrist and his mother an artist.
- // 1921 To 1947He attended the ‘University of Paris’ from where he completed his graduation with a Science degree and thereafter in 1921, he joined the ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France at 19. He met great French biologist Edouard Chatton at the institute who became his mentor and with time the two scientists remained associated for around seventeen years till the death of the latter in 1947.
- // 5th Dec 1925On December 5, 1925 he married French microbiologist and virologist Marguerite Bourdaleix. The couple worked closely at the ‘‘Pasteur Institute’ and remained close colleagues while working on the parasitical ciliates at the ‘Roscoff Marine Biological Station’ along with French biologist Édouard Chatton.
- // 1927Edouard Chatton helped him join the laboratory of Félix Mesnil in the ‘Pasteur Institute’. He first examined the parasitic ciliates and their development cycle and studied morphogenesis. He further investigated issues related to nutrition of protozoan. In 1927 he earned his M.D.
- // 1932In 1932 he earned his Ph.D and upon obtaining a grant from the ‘Rockefeller Foundation’, he relocated for a year to the ‘Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Medical Research’ in the city of Heidelberg in south-west Germany. He joined the laboratory of German physician and biochemist Otto Meyerhof and researched on haematin, a developmental factor of flagellates, the particularity of protohaematin and related subjects.
- // 1937He obtained another grant from the ‘Rockefeller Foundation’ and went to the ‘University of Cambridge’ with his wife in 1937 and spent seven months there in the lab of David Keilin.
- // 1938He was inducted as Head of Department at the ‘Pasteur Institute’ in 1938. He carried on significant research work while serving at the institute.
- // 1954He started research on poliovirus from 1954. He conducted investigations to study how temperature sensitivity of viral development is associated with neurovirulence and such study made him consider the viral infection problem. Gradually it became apparent that non-specific aspects play a significant role in the growth of primary infection. He then further investigated on the mechanics of particular deterrents of viral growth.
- // 1956He became the Corresponding Member of the ‘Botanical Society of America’ in 1956.
- // 1958In 1958 he became the ‘Foreign Member of the Royal Society’ (ForMemRS), London as also the Honorary Foreign Member of the ‘American Academy of Arts and Sciences’.
- // 1959 To 1968He served the ‘Sorbonne’ from 1959 to 1968 as Professor of Microbiology.
- // 1964 To 1966For his services during the ‘Second World War’ he received the ‘Medal of the Resistance’ in 1964 and was made the commander of the ‘Légion d'Honneur’ in 1966.
- // Jul 1964He remained one of the driving forces in the establishment of the ‘European Organization of Molecular Biology’ that was officially formed in July 1964.
- // 1965In 1965 he was jointly awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ along with two other French biologists, François Jacob and Jacques Monod
- // 30th Sep 1965 To 30th Sep 1994On September 30, 1994, he passed away in Paris at 92 years of age. He was the last surviving member of the trio who jointly received the ‘Nobel Prize’ in 1965.
- // 1968 To 1972He retired from the ‘Pasteur Institute’ in 1968 and thereafter served the ‘Cancer Research Institute’ at Villejuif, near Paris, as the Director till 1972.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Alex Lange
Alex Lange is a French-South African model, who is quite popular on Instagram. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Tina Kunakey
Tina Kunakey Di Vita is a model and wife of the French actor Vincent Cassel. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jeanne Calment
Jeanne Calment was a French supercentenarian who had the longest confirmed lifespan in human history. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, death, etc.
André Lwoff's FAQ
What is André Lwoff birthday?
André Lwoff was born at 1902-05-08
When was André Lwoff died?
André Lwoff was died at 1994-09-30
Where was André Lwoff died?
André Lwoff was died in Paris, France
Which age was André Lwoff died?
André Lwoff was died at age 92
Where is André Lwoff's birth place?
André Lwoff was born in Ainay-le-Château, Allier, Auvergne, France
What is André Lwoff nationalities?
André Lwoff's nationalities is French
Who is André Lwoff spouses?
André Lwoff's spouses is Marguerite Bourdaleix
Who is André Lwoff's father?
André Lwoff's father is Solomon Lwoff
Who is André Lwoff's mother?
André Lwoff's mother is Marie
What is André Lwoff's sun sign?
André Lwoff is Taurus
How famous is André Lwoff?
André Lwoff is famouse as Microbiologist