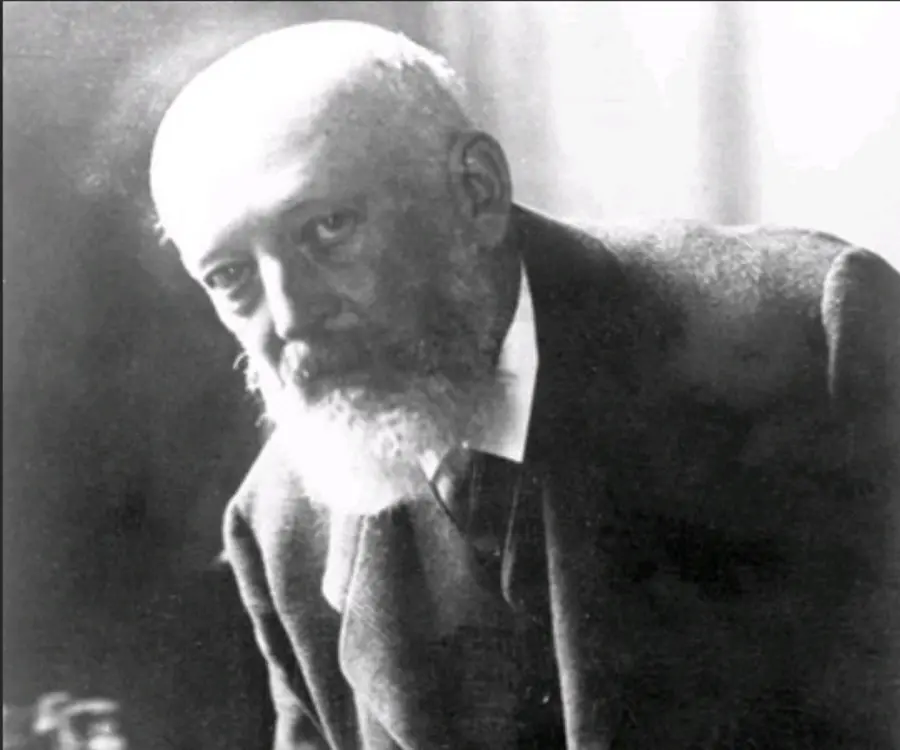
Adolf von Baeyer - Organic Chemists, Life Achievements and Childhood
Adolf von Baeyer's Personal Details
Adolf von Baeyer was a well-known German chemist who synthesized indigo
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | October 31, 1835 |
| Died on | August 20, 1917 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Scientists, Chemists, Organic Chemists |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Berlin |
| Religion | Judaism |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Scorpio |
| Born in | Berlin |
| Famous as | Chemist |
| Died at Age | 81 |
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
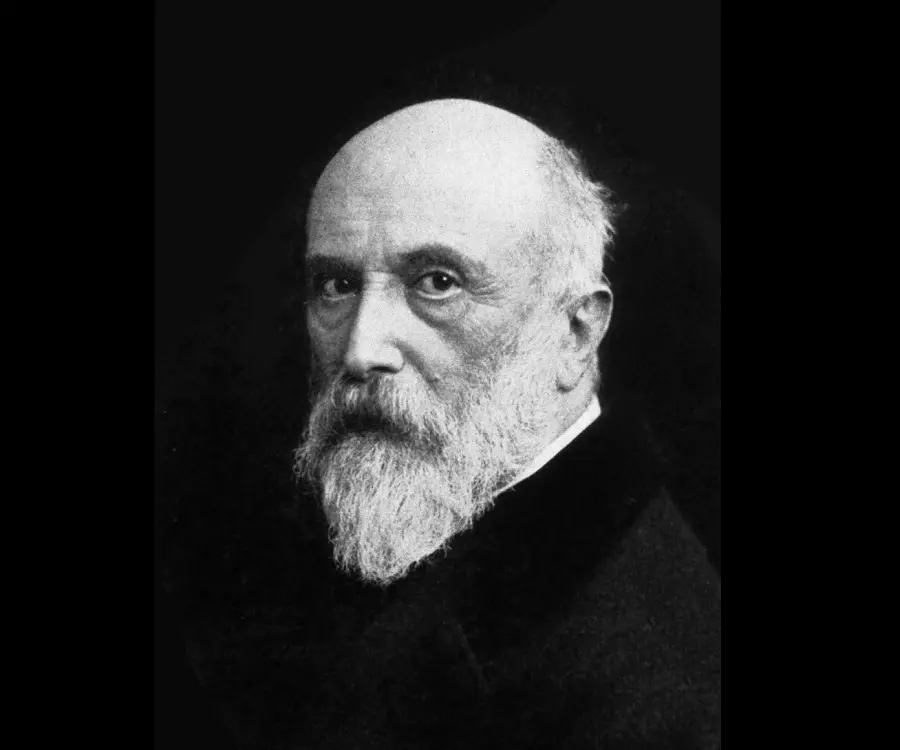
Adolf von Baeyer's photo
Who is Adolf von Baeyer?
Adolf von Baeyer, born as Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf Baeyer, was a well-known German chemist best-known for synthesizing indigo, the blue color natural dye used in the textile industry. Coming from an enlightened family he carried out unique experiments when he was still a child and soon developed a keen interest in chemistry. He discovered a double salt of copper at the age of twelve and barbituric acid while doing his post doctorate. When he was around thirty years old he started his experiments on indigo and worked at it for eighteen long years before he could find a suitable formula for its laboratory production. On the basis of his work, scientists later found the appropriate formula for the industrial production of the dye. However, Baeyer’s achievement did not stop at that. He is also famous for synthesizing phenolphthalein and fluorescein. He was also proponent of strain theory of carbon ring. Known as ‘Baeyer Strain Theory’ it later became one of the pillars of biochemistry. However, Baeyer was more than just an inventor; he was equally popular as an academician and had trained many students who later made names for themselves.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Childhood & Early Years
Adolf von Baeyer was born on October 31, 1835, in Berlin. His father, Johann Jakob Baeyer, a lieutenant-general under the Prussian army, was the creator of the European system of geodetic measurement. His mother, Eugenie, was the daughter of famous German author Julius Eduard Hitzig. Adolf von Baeyer was the eldest of his parents’ five children.
Even as a child Adolf was highly inquisitive. At the age of eight, he planted date seeds in a series of pots and fed them successively with milk, wine and ink. However, his experiments at the age of twelve were more successful; he found a new double salt of copper.
Adolf had his secondary education at Friedrich-Wilhelms Gymnasium. In 1853, he joined Berlin University with mathematics and physics as his subjects. Soon he realized that his real interest lay in chemistry. Consequently in 1856, he joined Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen’s laboratory in Heidelberg.
There he worked under German organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé on methyl chloride. The result of this work was published in 1857. Thereafter, he joined Kekulé's private laboratory in Heidelberg and began to work with him on ingenious structure theory.
Adolf von Baeyer received his PhD in 1858 on his work on cacodyl compounds. Although the work was done in Heidelberg at Kekulé’s laboratory, he received his degree from Berlin University.
After receiving his PhD, Baeyer rejoined Kekulé, who was then a professor at the University of Ghent. Here Baeyer worked on uric acid, which led to the discovery of barbituric acid. Barbiturate, a component of sleeping pills, is produced from this acid. The thesis made him eligible for teaching post.
Career
Adolf von Baeyer began his academic career as a lecturer (privatdozent) in organic chemistry at the Berlin Gewerbe-Akademie (Trade Academy) in 1860. Although he received a small remuneration he took up the job because the Academy provided him with a spacious laboratory. It is here that Baeyer started his research on indigo.
Until then, the blue pigment could be obtained only from indigo plant grown in India. Consequently the price was too high and the supply was limited. For the chemists, it was a challenge to reproduce the pigment synthetically and make it available at an affordable price.
Although he started his experimentation in 1865, while he was still working at Trade Academy, it took many years to complete. The complex nature of indigo made it a very hard and time consuming task.
Meanwhile in 1866, Baeyer was appointed to the post of the assistant professor in chemistry at the University of Berlin. In the same year, he reduced oxindole to indole using zinc dust. In 1869, he proposed the Baeyer–Emmerling indole synthesis method.
In 1871, Baeyer joined the University of Strasbourg as a full professor and along with working on indigo he kept on experimenting with various products. His theory of carbon-dioxide assimilation in formaldehyde was formed during his tenure here. He also discovered the synthesis of phenolphthalein and obtained synthetic fluorescein during this period.
Four years later in 1875, he shifted to the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich as professor of chemistry and remained there until his death in 1917. Here he had the opportunity to build up an excellent chemical laboratory and continue with his work on indigo at full force.
In 1882, Bayer published the ‘Baeyer–Drewson indigo syntheses’. It turned out to be an easy route for producing indigo at laboratory scale. However, it was not until the following year that Baeyer could fully determine the structure of indigo.
Apart from working on indigo, Baeyer worked on many other products such as acetylene and polyacetylene. The famous ‘Baeyer strain theory’ of the carbon rings was derived from these experiments. Later, he received the coveted Nobel Prize in chemistry for developing this theory.
In addition, he and his team studied constitution of benzene and also investigated into cyclic terpene. He also worked on cyclic ketone and published the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation theory in 1899. His work on organic peroxides and oxonium compounds also aroused interest among the chemists.
From 1900, von Baeyer started working on triphenylmethane. From this work, a new notion about the chemical composition of pigments began to be developed. Moreover, his works helped to understand the relationship between the optical properties of organic substances and their interior atomic structure to a large extent.
He continued working at the University of Munich almost till his end. During that period, he was considered to be one of the best known teachers in the field of organic chemistry. All through his career, he had nurtured at least fifty talented students, who later became well-known academicians.
Major Works
Synthesizing of indigo, which took almost eighteen years to complete, was one of Baeyer’s most important works. Although his formula was meant only for laboratory production of the pigment his work paved the way for further experimentation and by 1897, indigo began to be produced commercially.
Synthesis of phenolphthalein, a chemical compound used mainly as an indicator in acid based tritrations, is another of his major works done in 1871. To get the product, he condensed phthalic anhydride with two equivalents of phenol under acidic conditions.
Synthesized fluorescein, which is mainly used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications, is another of his important work. In 1871, he prepared it from phthalic anhydride and resorcinol in the presence of zinc chloride via the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Awards & Achievements
In 1905, Adolf von Baeyer received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "in recognition of his services in the advancement of organic chemistry and the chemical industry, through his work on organic dyes and hydroaromatic compounds".
Earlier in 1881, Baeyer was awarded the Davy Medal by the Royal Society of London for his work with indigo.
In 1884, he was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Personal Life & Legacy
Adolf Baeyer married Adelheid (Lida) Bendemann in 1868. They had three children; one daughter, who later married one of Adolf’s students Oskar Piloty and two sons, Hans and Otto. While Hans was a professor of medicine at the University of Munich, Otto was a professor of physics at the University of Berlin.
Baeyer was raised to hereditary nobility on his fiftieth birthday in 1885 and since then he began to be known as Adolf von Baeyer.
Baeyer was active till his end. He died from a seizure on August 20, 1917 at his country home in Starnberger See.
// Famous Organic Chemists
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist who is best known for his discovery of the periodic law. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Aleksandr Borodin
Aleksandr Borodin was a prodigal Russian music composer and scientist. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements and timeline.
Hermann Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer was a Nobel Prize winning chemist from Germany who is known for inventing the ‘Fischer Projection’ method. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Adolf von Baeyer's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Chemistry | |
Adolf von Baeyer biography timelines
- // 31st Oct 1835Adolf von Baeyer was born on October 31, 1835, in Berlin. His father, Johann Jakob Baeyer, a lieutenant-general under the Prussian army, was the creator of the European system of geodetic measurement. His mother, Eugenie, was the daughter of famous German author Julius Eduard Hitzig. Adolf von Baeyer was the eldest of his parents’ five children.
- // 1853 To 1856Adolf had his secondary education at Friedrich-Wilhelms Gymnasium. In 1853, he joined Berlin University with mathematics and physics as his subjects. Soon he realized that his real interest lay in chemistry. Consequently in 1856, he joined Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen’s laboratory in Heidelberg.
- // 1857There he worked under German organic chemist Friedrich August Kekulé on methyl chloride. The result of this work was published in 1857. Thereafter, he joined Kekulé's private laboratory in Heidelberg and began to work with him on ingenious structure theory.
- // 1858Adolf von Baeyer received his PhD in 1858 on his work on cacodyl compounds. Although the work was done in Heidelberg at Kekulé’s laboratory, he received his degree from Berlin University.
- // 1860Adolf von Baeyer began his academic career as a lecturer (privatdozent) in organic chemistry at the Berlin Gewerbe-Akademie (Trade Academy) in 1860. Although he received a small remuneration he took up the job because the Academy provided him with a spacious laboratory. It is here that Baeyer started his research on indigo.
- // 1865Although he started his experimentation in 1865, while he was still working at Trade Academy, it took many years to complete. The complex nature of indigo made it a very hard and time consuming task.
- // 1866 To 1869Meanwhile in 1866, Baeyer was appointed to the post of the assistant professor in chemistry at the University of Berlin. In the same year, he reduced oxindole to indole using zinc dust. In 1869, he proposed the Baeyer–Emmerling indole synthesis method.
- // 1868Adolf Baeyer married Adelheid (Lida) Bendemann in 1868. They had three children; one daughter, who later married one of Adolf’s students Oskar Piloty and two sons, Hans and Otto. While Hans was a professor of medicine at the University of Munich, Otto was a professor of physics at the University of Berlin.
- // 1871In 1871, Baeyer joined the University of Strasbourg as a full professor and along with working on indigo he kept on experimenting with various products. His theory of carbon-dioxide assimilation in formaldehyde was formed during his tenure here. He also discovered the synthesis of phenolphthalein and obtained synthetic fluorescein during this period.
- // 1871Synthesis of phenolphthalein, a chemical compound used mainly as an indicator in acid based tritrations, is another of his major works done in 1871. To get the product, he condensed phthalic anhydride with two equivalents of phenol under acidic conditions.
- // 1871Synthesized fluorescein, which is mainly used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications, is another of his important work. In 1871, he prepared it from phthalic anhydride and resorcinol in the presence of zinc chloride via the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
- // 1875 To 1917Four years later in 1875, he shifted to the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich as professor of chemistry and remained there until his death in 1917. Here he had the opportunity to build up an excellent chemical laboratory and continue with his work on indigo at full force.
- // 1881Earlier in 1881, Baeyer was awarded the Davy Medal by the Royal Society of London for his work with indigo.
- // 1882In 1882, Bayer published the ‘Baeyer–Drewson indigo syntheses’. It turned out to be an easy route for producing indigo at laboratory scale. However, it was not until the following year that Baeyer could fully determine the structure of indigo.
- // 1884In 1884, he was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
- // 1885Baeyer was raised to hereditary nobility on his fiftieth birthday in 1885 and since then he began to be known as Adolf von Baeyer.
- // 1897Synthesizing of indigo, which took almost eighteen years to complete, was one of Baeyer’s most important works. Although his formula was meant only for laboratory production of the pigment his work paved the way for further experimentation and by 1897, indigo began to be produced commercially.
- // 1899In addition, he and his team studied constitution of benzene and also investigated into cyclic terpene. He also worked on cyclic ketone and published the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation theory in 1899. His work on organic peroxides and oxonium compounds also aroused interest among the chemists.
- // 1900From 1900, von Baeyer started working on triphenylmethane. From this work, a new notion about the chemical composition of pigments began to be developed. Moreover, his works helped to understand the relationship between the optical properties of organic substances and their interior atomic structure to a large extent.
- // 1905In 1905, Adolf von Baeyer received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "in recognition of his services in the advancement of organic chemistry and the chemical industry, through his work on organic dyes and hydroaromatic compounds".
- // 20th Aug 1917Baeyer was active till his end. He died from a seizure on August 20, 1917 at his country home in Starnberger See.
// Famous German peoples
Jordan Carver
Jordan Carver is a famous German model. Let’s take a close look at her personal life, including her age, career, net worth, achievements and some fun facts.
Jürgen Klopp
Jürgen Klopp is a German football manager, and a former professional football player. Check out this biography to know more about his childhood, family, personal life, etc.
Irma Grese
Irma Grese was a notorious German Nazi concentration camp guard during the Second World War. This biography profiles her childhood, life, horrifying acts, death and other facts.
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Jawed Karim
Jawed Karim is a German-American internet entrepreneur, technologist and co-founder of the video-sharing website, YouTube. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, personal life, achievements, age, etc.
Charles Bukowski
Charles Bukowski was a German-born American novelist, short story writer and poet. With this biography, learn in details about his childhood, life, works, career and timeline
Adolf von Baeyer's FAQ
What is Adolf von Baeyer birthday?
Adolf von Baeyer was born at 1835-10-31
When was Adolf von Baeyer died?
Adolf von Baeyer was died at 1917-08-20
Where was Adolf von Baeyer died?
Adolf von Baeyer was died in Starnberg
Which age was Adolf von Baeyer died?
Adolf von Baeyer was died at age 81
Where is Adolf von Baeyer's birth place?
Adolf von Baeyer was born in Berlin
What is Adolf von Baeyer nationalities?
Adolf von Baeyer's nationalities is German
What was Adolf von Baeyer universities?
Adolf von Baeyer studied at Humboldt University of Berlin, Heidelberg University
What is Adolf von Baeyer's religion?
Adolf von Baeyer's religion is Judaism
What is Adolf von Baeyer's sun sign?
Adolf von Baeyer is Scorpio
How famous is Adolf von Baeyer?
Adolf von Baeyer is famouse as Chemist