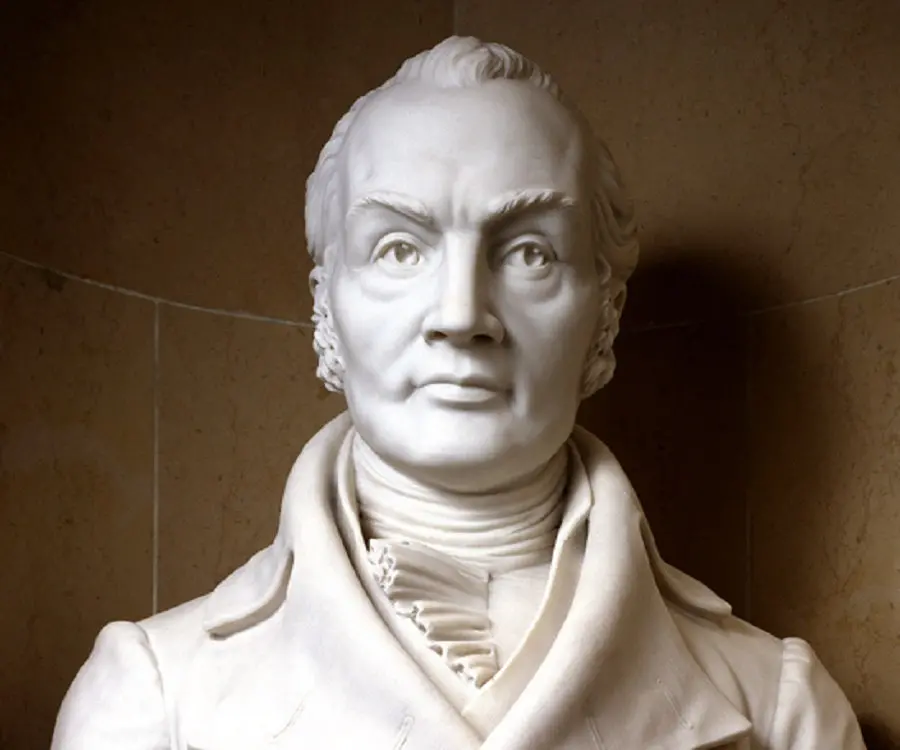
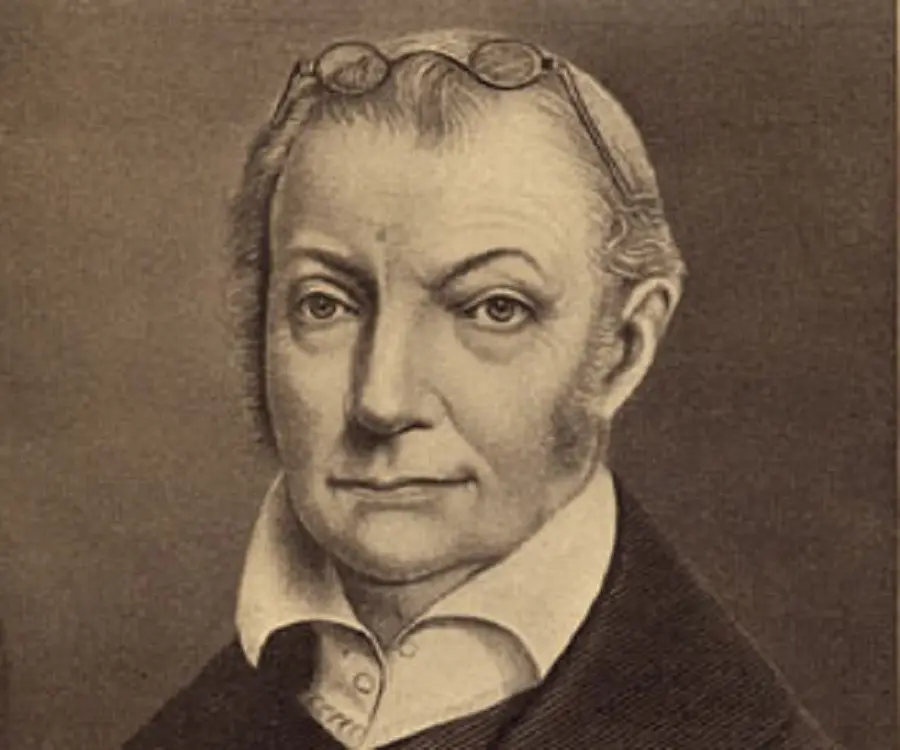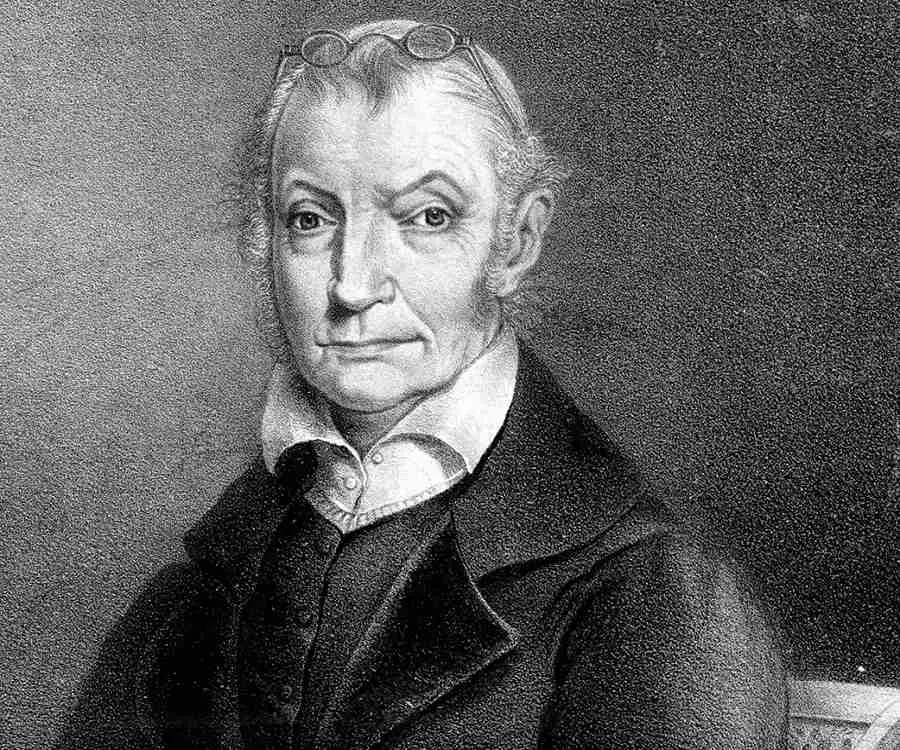Aaron Burr - 3rd Vice President of United States, Birthday and Childhood
Aaron Burr's Personal Details
Aaron Burr was the 3rd Vice President of United States
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | February 6, 1756 |
| Died on | September 14, 1836 |
| Nationality | American |
| Famous | Republicans, Leaders, Political Leaders, 3rd Vice President of United States |
| Ideologies | Republicans |
| City/State | New Jersey |
| Spouses | Eliza Bowen Jumel, Theodosia Bartow Prevost |
| Childrens | Sarah, Theodosia Bartow Burr |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Newark |
| Political Ideology | Democratic-Republican |
| Religion | Presbyterianism |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Rev. Aaron Burr |
| Mother | Esther Edwards |
| Sun Sign | Aquarius |
| Born in | Newark |
| Famous as | 3rd Vice President of United States |
| Died at Age | 80 |
Aaron Burr's photo
Who is Aaron Burr?
Aaron Burr was an American politician and a successful lawyer who served as the third Vice President of the United States. He was born in the middle of the eighteenth century into a well-known family, whose origin could be traced back to Pilgrim Fathers. Starting his career as an ordinary soldier during the American Revolution, he quickly rose through the ranks and ultimately became the third Vice President of the United States of America. Meanwhile, he had been elected twice to the New York State Assembly and once to the United States Senate. For a brief period, he was also the New York State Attorney General. His political career came to an end when in the last year of his Vice Presidency he fatally wounded Alexander Hamilton in a duel. To recoup his fortune, he fled to the west, where he unsuccessfully tried to establish a new regime. The failed attempt led to his arrest. Although he was acquitted due to lack of evidence, it practically ended his chances of political return. After a short trip to Europe, where he tried to drum up support, he returned to the U.S.A and started practicing law, leading a life of financial constraints and deteriorating health.
// Famous Republicans
Simon Bolivar
Simón Bolívar was a Venezuelan military leader who was instrumental in independence of several Latin American countries from the Spanish rule. This biography profiles his childhood, life, achievements and timeline.
Nizar Qabbani
Nizar Qabbani was a poet, and is one among the most honoured men in the Arab Literary world. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, career, profile and timeline.
William Ruto
William Ruto is a politician who hails from Kenya and is the first Deputy President of the Republic of Kenya. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, Profile, career and timeline
Childhood & Early Life
Aaron Burr Jr. was born on February 6, 1756 in Newark, New Jersey. His father, Reverend Aaron Burr Sr., was a Presbyterian minister and second president of the College of New Jersey. His mother, Esther Burr (née Edwards), was the daughter of a noted Calvinist theologian. He had an elder sister named Sarah.
Aaron’s father died in 1757, barely a year after his birth and his mother passed away in 1758. Initially the siblings lived with their maternal grandparents; but they too died within a year.
Thereafter, from 1758 to 1759, they were put under the care of noted physician William Shippen. In 1759, their maternal uncle Timothy Edwards came of age; he then assumed their guardianship.
As a child Aaron Burr was bright, charming, handsome, and witty. He was also intellectually gifted but at the same time unmanageably naughty. Even at this early age, he began to show a determination to succeed.
In 1769, at the age of 13, Burr entered the College of New Jersey to the sophomore class. Here, he became member of both the American Whig Society and Cliosophic Society. Concurrently, he also excelled academically.
In 1772, after graduating from there summa cum laud, Burr decided to study theology. He was then 16 years old. After two years of rigorous training he changed his mind and enrolled at the Litchfield law school at Connecticut.
In 1775 as the news came that the local militia had clashed with the British troops at Lexington and Concord, he abandoned his studies to join the Continental Army. He was then 19 years old.
Career
In September 1775, Aaron Burr joined Colonel Benedict Arnold’s troops and became a member of his expedition to Quebec, involving a difficult trek of three hundred miles. During the long march, he had to withstand cold, hunger and fatigue; yet his enthusiasm and determination never waned, which attracted the colonel’s attention.
By now, General Richard Montgomery had taken Montreal. On reaching Quebec, Arnold sent Burr to Montreal to escort Montgomery back to Quebec. Impressed, Montgomery promoted him to the post of captain and also made him an aid-de-camp.
As the Battle of Quebec began on December 31, 1775, he showed great valor and courage. Although the war resulted in the defeat for the Americans, he was noticed by his superiors.
In early 1776, he was inducted as a staff of General Washington at Manhattan. However, he soon antagonized Washington and within two weeks, was transferred to General Israel Putnam’s troop.
While retreating with the troop from lower Manhattan to Harlem, Burr was able to save a full brigade from being captured by the British. However, Washington neglected to commend his action; which generally resulted in quick promotion.
After resigning from the army, he once more entered the law school and was admitted to the bar at Albany in 1782. However, he had not all together severed connection with the army, and had undertaken several intelligence missions at the request of George Washington during this period.
In 1783, he moved to New York City and began practicing law, which soon began to flourish. Subsequently, he started taking interest in politics and in 1784 and 1785 was elected to the state assembly.
In 1789, he became the Attorney General of New York State and in 1791Commissioner of Revolutionary War Claims. By then, he had been successful in building a coalition against Gen. Philip Schuyler, the sitting Senator from New York and also the father-in-law of Alexander Hamilton, then Secretary of Treasury.
Thus when in 1791, the election for the seat took place, he won it easily. The incident marked the start of a bitter rivalry between him and Hamilton. Nonetheless, he served as the Senator, but lost the next election, held in 1797, to Schuyler.
Burr attributed his defeat to Hamilton’s effort to undermine his chances and so the rivalry continued. Meanwhile, in 1796, he had run for the Presidential seat, but had lost. Therefore, he spent the next two years as a member of the New York State Assembly.
In 1800, he once again entered the Presidential race on Republican ticket with Thomas Jefferson. Because of his extensive campaign, the Republicans won the election; but Burr and Jefferson got equal numbers of electoral votes.
Later, at the tie breaker by the Federalist controlled House of Representatives, he lost to Jefferson by 36 votes and became the Vice President, while Jefferson became the President. Here too, Hamilton played a decisive role in his defeat.
As Vice President of the USA and President of the Senate, Burr earned praise for his sense of justice even from his critics. During this period, he began some traditions for the office of the Vice President, which continued for a long time.
However, Jefferson never trusted him fully and so he not only kept him out of party matters, but also refused to give him ticket for the 1804 Presidential election. Therefore Burr decided to run for the post of Governor of the New York State.
Hamilton soon started a smear campaign against him, largely as a result of which, Burr lost the election to Morgan Lewis. Burr called for public apology from Hamilton for the smear campaign and when the other man refused to comply, he challenged him in a personal combat under the code duello.
The duel took place on July 11, 1804 in outside Weehawken, New Jersey, where duels had been declared illegal, but did not attract death penalty. Burr’s bullet mortally wounded Hamilton, who was then evacuated to Manhattan and died the next day. Burr, who came off unscathed, fled to South Carolina.
Subsequently, he returned to Washington to complete his term as Vice President, but avoided both New Jersey and New York, where multiple cases were lodged against him. Eventually, all cases were dropped against him because although Hamilton was shot in New Jersey he died in New York.
In 1805, after his term as the Vice President expired, he travelled to the Western Frontier, where he joined General James Wilkinson with the aim of establishing an independent government in that area. Their plan was to invade Mexico and at the same time, foment a secessionist movement in the West.
However Wilkinson soon began to have second thoughts and informed Jefferson of the plan. The President declared Burr a traitor and issued an order of arrest. Burr tried to flee to Spanish Florida; but he was arrested on February 19, 1807.
Subsequently, he was brought to trial before the United States Circuit Court at Richmond, Virginia in August 1807. The Jefferson administration put all their political force against him. Yet Burr was acquitted on September 1 because there was no evidence against him.
However, the incident put a death knell on his political ambition and so Burr left for Europe, where he stayed from 1808 to 1812. Here he tried to enlist the help of Napoleon, but was rebuffed.
Ultimately, Burr returned to the USA, and to keep off the creditors, he for some time had to use his mother’s maiden name Edwards. Later, he resumed his law practice and spent the last years of his life in relative peace.
Personal Life & Legacy
On July 2, 1782, Aaron Burr married Theodosia Bartow Prevost, an American Patriot, whom he had met as a young soldier in 1777. At that time, she was married to Jacques Marcus Prevost, a British Army officer of Swiss origin and had five children with him.
Although she was ten years senior to him, they gradually fell in love and by 1780, were openly lovers. Later as Prevost died and Burr received his bar license, the two got married and shifted to New York. Their daughter, also named Theodosia, was their only child to survive infancy.
The marriage ended when Theodosia died of stomach cancer in 1794. However, by then he had also fathered two illegitimate children, Louisa Charlotte Burr and John Pierre Burr by Mary Emmons, an East Indian woman who was a servant in the household.
In 1834, Burr suffered a series of strokes, which made him physically dependent on others. He lived in that condition until his death on September 14, 1836. Interestingly, the divorce proceeding, initiated by Jumel, was finalized on that very day.
// Famous Political Leaders
Edi Rama
Edi Rama is the current Prime Minister of Albania. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan
Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan is the current President of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Check out this biography to know about his birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Leo Varadkar
Cam Leo Varadkar is the current Taoiseach—the Prime Minister—of the Republic of Ireland. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and other facts about his life.
Aaron Burr biography timelines
- // 6th Feb 1756Aaron Burr Jr. was born on February 6, 1756 in Newark, New Jersey. His father, Reverend Aaron Burr Sr., was a Presbyterian minister and second president of the College of New Jersey. His mother, Esther Burr (née Edwards), was the daughter of a noted Calvinist theologian. He had an elder sister named Sarah.
- // 1757 To 1758Aaron’s father died in 1757, barely a year after his birth and his mother passed away in 1758. Initially the siblings lived with their maternal grandparents; but they too died within a year.
- // 1758 To 1759Thereafter, from 1758 to 1759, they were put under the care of noted physician William Shippen. In 1759, their maternal uncle Timothy Edwards came of age; he then assumed their guardianship.
- // 1769In 1769, at the age of 13, Burr entered the College of New Jersey to the sophomore class. Here, he became member of both the American Whig Society and Cliosophic Society. Concurrently, he also excelled academically.
- // 1772In 1772, after graduating from there summa cum laud, Burr decided to study theology. He was then 16 years old. After two years of rigorous training he changed his mind and enrolled at the Litchfield law school at Connecticut.
- // 1775In 1775 as the news came that the local militia had clashed with the British troops at Lexington and Concord, he abandoned his studies to join the Continental Army. He was then 19 years old.
- // 1775In September 1775, Aaron Burr joined Colonel Benedict Arnold’s troops and became a member of his expedition to Quebec, involving a difficult trek of three hundred miles. During the long march, he had to withstand cold, hunger and fatigue; yet his enthusiasm and determination never waned, which attracted the colonel’s attention.
- // 31st Dec 1775As the Battle of Quebec began on December 31, 1775, he showed great valor and courage. Although the war resulted in the defeat for the Americans, he was noticed by his superiors.
- // 1776In early 1776, he was inducted as a staff of General Washington at Manhattan. However, he soon antagonized Washington and within two weeks, was transferred to General Israel Putnam’s troop.
- // 1780Although she was ten years senior to him, they gradually fell in love and by 1780, were openly lovers. Later as Prevost died and Burr received his bar license, the two got married and shifted to New York. Their daughter, also named Theodosia, was their only child to survive infancy.
- // 1782After resigning from the army, he once more entered the law school and was admitted to the bar at Albany in 1782. However, he had not all together severed connection with the army, and had undertaken several intelligence missions at the request of George Washington during this period.
- // 2nd Jul 1782On July 2, 1782, Aaron Burr married Theodosia Bartow Prevost, an American Patriot, whom he had met as a young soldier in 1777. At that time, she was married to Jacques Marcus Prevost, a British Army officer of Swiss origin and had five children with him.
- // 1783In 1783, he moved to New York City and began practicing law, which soon began to flourish. Subsequently, he started taking interest in politics and in 1784 and 1785 was elected to the state assembly.
- // 1789In 1789, he became the Attorney General of New York State and in 1791Commissioner of Revolutionary War Claims. By then, he had been successful in building a coalition against Gen. Philip Schuyler, the sitting Senator from New York and also the father-in-law of Alexander Hamilton, then Secretary of Treasury.
- // 1791Thus when in 1791, the election for the seat took place, he won it easily. The incident marked the start of a bitter rivalry between him and Hamilton. Nonetheless, he served as the Senator, but lost the next election, held in 1797, to Schuyler.
- // 1800In 1800, he once again entered the Presidential race on Republican ticket with Thomas Jefferson. Because of his extensive campaign, the Republicans won the election; but Burr and Jefferson got equal numbers of electoral votes.
- // 11th Jul 1804The duel took place on July 11, 1804 in outside Weehawken, New Jersey, where duels had been declared illegal, but did not attract death penalty. Burr’s bullet mortally wounded Hamilton, who was then evacuated to Manhattan and died the next day. Burr, who came off unscathed, fled to South Carolina.
- // 1805In 1805, after his term as the Vice President expired, he travelled to the Western Frontier, where he joined General James Wilkinson with the aim of establishing an independent government in that area. Their plan was to invade Mexico and at the same time, foment a secessionist movement in the West.
- // 1807Subsequently, he was brought to trial before the United States Circuit Court at Richmond, Virginia in August 1807. The Jefferson administration put all their political force against him. Yet Burr was acquitted on September 1 because there was no evidence against him.
- // 19th Feb 1807However Wilkinson soon began to have second thoughts and informed Jefferson of the plan. The President declared Burr a traitor and issued an order of arrest. Burr tried to flee to Spanish Florida; but he was arrested on February 19, 1807.
- // 1834 To 14th Sep 1836In 1834, Burr suffered a series of strokes, which made him physically dependent on others. He lived in that condition until his death on September 14, 1836. Interestingly, the divorce proceeding, initiated by Jumel, was finalized on that very day.
// Famous Leaders
Edi Rama
Edi Rama is the current Prime Minister of Albania. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Tecumseh
Tecumseh was a Native American leader of the Shawnee clan. This biography profiles his childhood, life and timeline.
Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan
Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan is the current President of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Check out this biography to know about his birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Anwar Sadat
Anwar Sadat was the third President of Egypt and has been awarded the Nobel Prize for his peace initiatives. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on the following biography.
Leo Varadkar
Cam Leo Varadkar is the current Taoiseach—the Prime Minister—of the Republic of Ireland. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and other facts about his life.
Swami Vivekananda
Swami Vivekananda was the chief disciple of Sri Ramakrishna, and was responsible for awakening India spiritually. Check this biography to know in detail about his life, profile and timeline.
Aaron Burr's FAQ
What is Aaron Burr birthday?
Aaron Burr was born at 1756-02-06
When was Aaron Burr died?
Aaron Burr was died at 1836-09-14
Where was Aaron Burr died?
Aaron Burr was died in Staten Island
Which age was Aaron Burr died?
Aaron Burr was died at age 80
Where is Aaron Burr's birth place?
Aaron Burr was born in Newark
What is Aaron Burr nationalities?
Aaron Burr's nationalities is American
What is Aaron Burr ideologies?
Aaron Burr's ideologies is Republicans
Who is Aaron Burr spouses?
Aaron Burr's spouses is Eliza Bowen Jumel, Theodosia Bartow Prevost
Who is Aaron Burr childrens?
Aaron Burr's childrens is Sarah, Theodosia Bartow Burr
What was Aaron Burr universities?
Aaron Burr studied at College of New Jersey
What is Aaron Burr's political ideology?
Aaron Burr's political ideology is Democratic-Republican
What is Aaron Burr's religion?
Aaron Burr's religion is Presbyterianism
Who is Aaron Burr's father?
Aaron Burr's father is Rev. Aaron Burr
Who is Aaron Burr's mother?
Aaron Burr's mother is Esther Edwards
What is Aaron Burr's sun sign?
Aaron Burr is Aquarius
How famous is Aaron Burr?
Aaron Burr is famouse as 3rd Vice President of United States