Wilhelm Ostwald - Chemists, Career and Facts
Wilhelm Ostwald's Personal Details
Wilhelm Ostwald was a famous scientist who is credited with discovery of Ostwald Process for manufacture of nitric acid
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | September 2, 1853 |
| Died on | April 4, 1932 |
| Nationality | German |
| Famous | Atheists, Scientists, Chemists, Physical Chemists |
| Childrens | Wolfgang Ostwald |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Riga |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Riga |
| Famous as | Chemist |
| Died at Age | 78 |
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
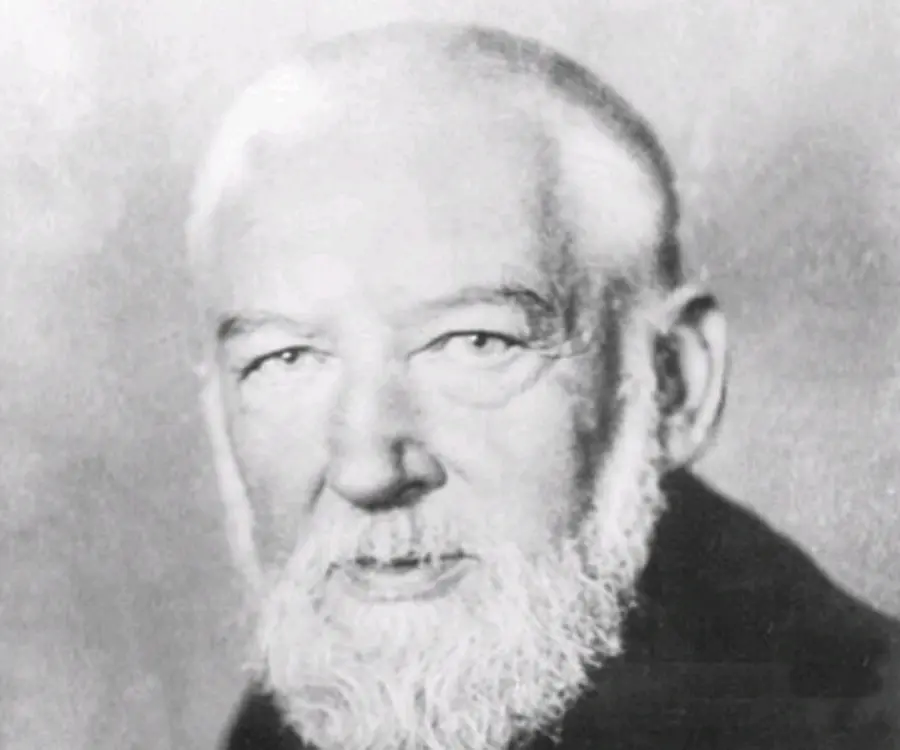
Wilhelm Ostwald's photo
Who is Wilhelm Ostwald?
Wilhelm Ostwald was a renowned chemist of Baltic German origins and is regarded as the father of modern day physical chemistry. In college he was impressed by the work of his mentor Carl Schmidt and decided to pursue general chemistry at a time when most of his peers focussed on organic chemistry. He started out by studying law of mass action and acid-base reaction. Throughout his career he was appointed in numerous academic positions and it was during his tenure at the ‘Riga Polytechnicum’ that he started working on the theory of electrolytic dissociation. His move to the University of Leipzig was a major milestone in his career as it was in Leipzig he made some of his most important contribution. He proposed the law of dilution which was a benchmark discovery in the study of dissociation theory. The theory was termed as ‘Ostwald’s law of dilution’. Mole, which is a standard unit of measurement, was introduced by Ostwald. But probably the discovery for which he is most renowned is the Ostwald Process for manufacture of Nitric acid. The process was pivotal for large scale production of nitrogenous fertilizers. In his later years, Wilhelm studied colour theory and was active in implementation of educational and social reforms. Read on to know more about his life and works.
// Famous Physical Chemists
Willard Libby
Willard Frank Libby was an American physical chemist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize’ in Chemistry in 1960. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, research, achievements and timeline.
Ilya Prigogine
Ilya Prigogine was a Russian-born Belgian physical chemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1977. This biography of Ilya Prigogine provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Fritz Haber
Fritz Haber was a German chemist who won the 1918 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the synthesis of ammonia from its elements. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Born to professional cooper Gottfried Ostwald and his wife Elisabeth Leuckel, on September 2, 1853, Wilhelm Ostwald was their second child. Wilhelm had two more brothers and the family stayed in Riga, the capital city of Latvia.
He completed his early studies from Riga and then attended the ‘University of Dorpat’ for his higher studies. After obtaining his bachelor’s degree in 1875, he successfully completed his master’s degree, the following year.
Ostwald then pursued his Ph. D. in chemistry and worked on his dissertation under the Russian chemist Carl Schmidt, receiving a doctoral degree in the year 1878.
Career
During 1875-1878, he studied the physical chemistry as he felt the area was neglected by the scientific community in Germany who were then focussed mostly on organic chemistry. He dedicated himself to study of the law of mass action of water and chemical affinity occurring in an acid-base reaction.
Wilhelm then accepted a teaching position in 1881 at the technical university ‘Riga Polytechnicum’.
During his tenure at Riga, he embarked on deducing scientific evidence to verify the dissociation theory, propounded by Svante Arrhenius, an eminent chemist from Sweden, in 1884. The same year his first book catering to general chemistry, entitled ‘Lehrbuch der Allegemeinen Chemie’ was written.
A pioneer of physical chemistry, in 1887, he founded a scientific journal for ‘Zeitschrift für physikalische Chemie’ (Journal of Physical Chemistry). He served as the editor of the journal for nearly twenty five years. The same year he moved to the ‘University of Leipzig’, as the head of the department of physical chemistry.
Continuing his work in electrolytic dissociation theory he succeeded in establishing the mathematical proof, which describes the relationship between degree of dissociation, concentration of acid and the equilibrium constant which is unique to each acid. The postulate was named Ostwald’s Law of Dilution, in 1888.
The book ‘Outline of general chemistry’ (‘Grundriss der Allgemeinen Chemie’) was first published in 1889 and became one of the most important textbooks in general chemistry. He also founded the series ‘Classics of exact sciences’ (Klassiker der exakten Wissenschaften) in the same year and more than 250 books have been printed under the series till date.
His third textbook of general chemistry titled ‘Handbook and manual for physiochemical measurements’ (Hand-und Hilfsbuch zur Ausfuhrung physikalisch-chemischer Messungen) was printed in 1893. The following year ‘German Electrochemical Society’ was established at the ‘Leipzig University’, where Wilhelm presided over the department of physical chemistry.
The term ‘Mole’, which is used as a standard unit of measurement of chemical substances, was first propounded by Ostwald in the year 1900.
Initially a non-believer of the atomic theory he later accepted it when Jean Perrin conducted studies on the Brownian motion. His views on ‘energetics’ as opposed to the ‘particulate nature of matter’ is explored in the journal ‘Annalen der naturophilosophie’, which he founded in 1902.
The process of manufacturing nitric acid was invented by this eminent chemist, in 1902. The ‘Bosch Haber Process’ for nitrogen fixation along with the ‘Ostwald Process’ revolutionized the manufacture of fertilizers and explosives, as they enabled mass-production.
In 1906, he would retire from his post at the university after serving for nearly two decades. The same year he was nominated to the scientific committee, which deals with evaluation of atomic weights, ‘International Committee on Atomic Weights’. His membership was terminated, after the WWI, as Ostwald was unable to communicate with the committee.
Towards the latter part of his career, he was devoted to the ‘colour theory’ and shapes. In this regard, between 1904-16, he penned many scientific papers which included ‘Malerbriefe’ (‘Letters to a Painter’) and ‘Die Farbenfibel’ (‘The Color Primer’).
He also contributed to social and educational reforms, and a crusader of the ‘Monism’ school of philosophy. The ‘Monistic Alliance’ named Wilhelm their President in the year 1911.
He was also an active participant of the ‘Ido movement’ and was a champion of eugenics, euthanasia, and ‘Social Darwinism’.
Major Works
Ostwald was responsible for numerous path-breaking discoveries in the field of chemistry but his work on chemical equilibria undoubtedly remains his most important contribution. He studied the basic principles regulating the equilibrium in a chemical reaction and derived the formulas for calculating rate of reactions which holds good till date.
Awards & Achievements
The erudite scientist who coined the term ‘Mole’ was honoured with t eh Nobel Prize for Chemistry in the year 1909 for his work on equilibrium of chemical reaction.
Personal Life & Legacy
Suffering from illness of the prostate and bladder, this eminent scientist breathed his last on April 4, 1932 and was interred in Leipzig. Later on his remains were moved to the Great Cemetery in the city of Riga.
// Famous Atheists
Morgan Freeman
Morgan Freeman is an Academy Award winning actor known for his work in movies like ‘Street Smart’, ‘Driving Miss Daisy’ and ‘Million Dollar Baby’. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Robert Smith
Robert Smith is an English musician and the lead singer of the British rock band, ‘The Cure.’ This biography of Robert Smith gives detailed information on his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Jack Black
Jack Black is a renowned American actor-producer and voice artist. Explore this biography to learn more about his profile, childhood, career and timeline
Wilhelm Ostwald's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Chemistry | |
Wilhelm Ostwald biography timelines
- // 2nd Sep 1853Born to professional cooper Gottfried Ostwald and his wife Elisabeth Leuckel, on September 2, 1853, Wilhelm Ostwald was their second child. Wilhelm had two more brothers and the family stayed in Riga, the capital city of Latvia.
- // 1875He completed his early studies from Riga and then attended the ‘University of Dorpat’ for his higher studies. After obtaining his bachelor’s degree in 1875, he successfully completed his master’s degree, the following year.
- // 1875 To 1878During 1875-1878, he studied the physical chemistry as he felt the area was neglected by the scientific community in Germany who were then focussed mostly on organic chemistry. He dedicated himself to study of the law of mass action of water and chemical affinity occurring in an acid-base reaction.
- // 1878Ostwald then pursued his Ph. D. in chemistry and worked on his dissertation under the Russian chemist Carl Schmidt, receiving a doctoral degree in the year 1878.
- // 1881Wilhelm then accepted a teaching position in 1881 at the technical university ‘Riga Polytechnicum’.
- // 1884During his tenure at Riga, he embarked on deducing scientific evidence to verify the dissociation theory, propounded by Svante Arrhenius, an eminent chemist from Sweden, in 1884. The same year his first book catering to general chemistry, entitled ‘Lehrbuch der Allegemeinen Chemie’ was written.
- // 1887A pioneer of physical chemistry, in 1887, he founded a scientific journal for ‘Zeitschrift für physikalische Chemie’ (Journal of Physical Chemistry). He served as the editor of the journal for nearly twenty five years. The same year he moved to the ‘University of Leipzig’, as the head of the department of physical chemistry.
- // 1888Continuing his work in electrolytic dissociation theory he succeeded in establishing the mathematical proof, which describes the relationship between degree of dissociation, concentration of acid and the equilibrium constant which is unique to each acid. The postulate was named Ostwald’s Law of Dilution, in 1888.
- // 1889The book ‘Outline of general chemistry’ (‘Grundriss der Allgemeinen Chemie’) was first published in 1889 and became one of the most important textbooks in general chemistry. He also founded the series ‘Classics of exact sciences’ (Klassiker der exakten Wissenschaften) in the same year and more than 250 books have been printed under the series till date.
- // 1893His third textbook of general chemistry titled ‘Handbook and manual for physiochemical measurements’ (Hand-und Hilfsbuch zur Ausfuhrung physikalisch-chemischer Messungen) was printed in 1893. The following year ‘German Electrochemical Society’ was established at the ‘Leipzig University’, where Wilhelm presided over the department of physical chemistry.
- // 1900The term ‘Mole’, which is used as a standard unit of measurement of chemical substances, was first propounded by Ostwald in the year 1900.
- // 1902Initially a non-believer of the atomic theory he later accepted it when Jean Perrin conducted studies on the Brownian motion. His views on ‘energetics’ as opposed to the ‘particulate nature of matter’ is explored in the journal ‘Annalen der naturophilosophie’, which he founded in 1902.
- // 1902The process of manufacturing nitric acid was invented by this eminent chemist, in 1902. The ‘Bosch Haber Process’ for nitrogen fixation along with the ‘Ostwald Process’ revolutionized the manufacture of fertilizers and explosives, as they enabled mass-production.
- // 1904 To 1916Towards the latter part of his career, he was devoted to the ‘colour theory’ and shapes. In this regard, between 1904-16, he penned many scientific papers which included ‘Malerbriefe’ (‘Letters to a Painter’) and ‘Die Farbenfibel’ (‘The Color Primer’).
- // 1906In 1906, he would retire from his post at the university after serving for nearly two decades. The same year he was nominated to the scientific committee, which deals with evaluation of atomic weights, ‘International Committee on Atomic Weights’. His membership was terminated, after the WWI, as Ostwald was unable to communicate with the committee.
- // 1909The erudite scientist who coined the term ‘Mole’ was honoured with t eh Nobel Prize for Chemistry in the year 1909 for his work on equilibrium of chemical reaction.
- // 1911He also contributed to social and educational reforms, and a crusader of the ‘Monism’ school of philosophy. The ‘Monistic Alliance’ named Wilhelm their President in the year 1911.
- // 4th Apr 1932Suffering from illness of the prostate and bladder, this eminent scientist breathed his last on April 4, 1932 and was interred in Leipzig. Later on his remains were moved to the Great Cemetery in the city of Riga.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Gabe Newell
Gabe Newell is an American computer programmer and businessman, best known as the co-founder of ‘Valve Corporation.’ This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Grigori Perelman
Grigori Perelman is a Russian mathematician who is best known for his contributions to Riemannian geometry and geometric topology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Eduardo Saverin
Eduardo Luiz Saverin is a Brazilian internet entrepreneur and investor. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements, and timeline
Wilhelm Ostwald's FAQ
What is Wilhelm Ostwald birthday?
Wilhelm Ostwald was born at 1853-09-02
When was Wilhelm Ostwald died?
Wilhelm Ostwald was died at 1932-04-04
Where was Wilhelm Ostwald died?
Wilhelm Ostwald was died in Leipzig
Which age was Wilhelm Ostwald died?
Wilhelm Ostwald was died at age 78
Where is Wilhelm Ostwald's birth place?
Wilhelm Ostwald was born in Riga
What is Wilhelm Ostwald nationalities?
Wilhelm Ostwald's nationalities is German
Who is Wilhelm Ostwald childrens?
Wilhelm Ostwald's childrens is Wolfgang Ostwald
What was Wilhelm Ostwald universities?
Wilhelm Ostwald studied at University of Tartu
What is Wilhelm Ostwald's sun sign?
Wilhelm Ostwald is Virgo
How famous is Wilhelm Ostwald?
Wilhelm Ostwald is famouse as Chemist