Pierre-Simon Laplace - Mathematicians, Timeline and Childhood
Pierre-Simon Laplace's Personal Details
Pierre-Simon Laplace was a French mathematician and astronomer
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | March 23, 1749 |
| Died on | March 5, 1827 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Mathematicians, Astronomers |
| Spouses | Marie-Charlotte de Courty de Romanges |
| Known as | Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Beaumont-en-Auge |
| Religion | Catholicism |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Aries |
| Born in | Beaumont-en-Auge |
| Famous as | Scientist |
| Died at Age | 77 |
// Famous Mathematicians
Grigori Perelman
Grigori Perelman is a Russian mathematician who is best known for his contributions to Riemannian geometry and geometric topology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Terence Tao
Terence Tao is an Australian- American mathematician who has contributed enormously to the field of mathematics. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life and achievements.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton was an English scientist and mathematician, who discovered gravitation and Newtonian Mechanics. Read this biography to find more on his life.
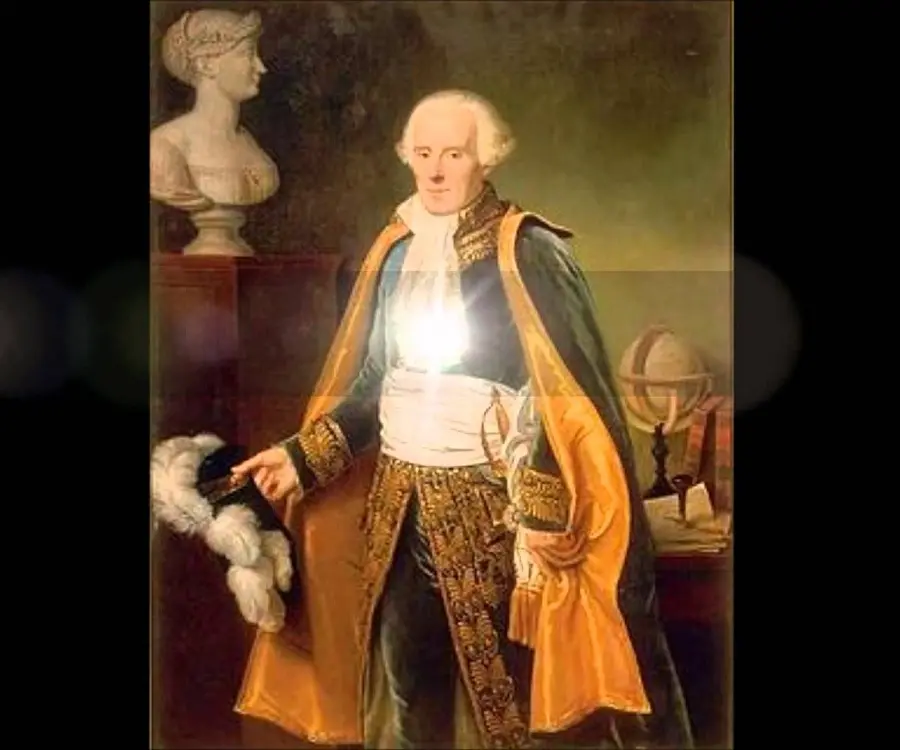
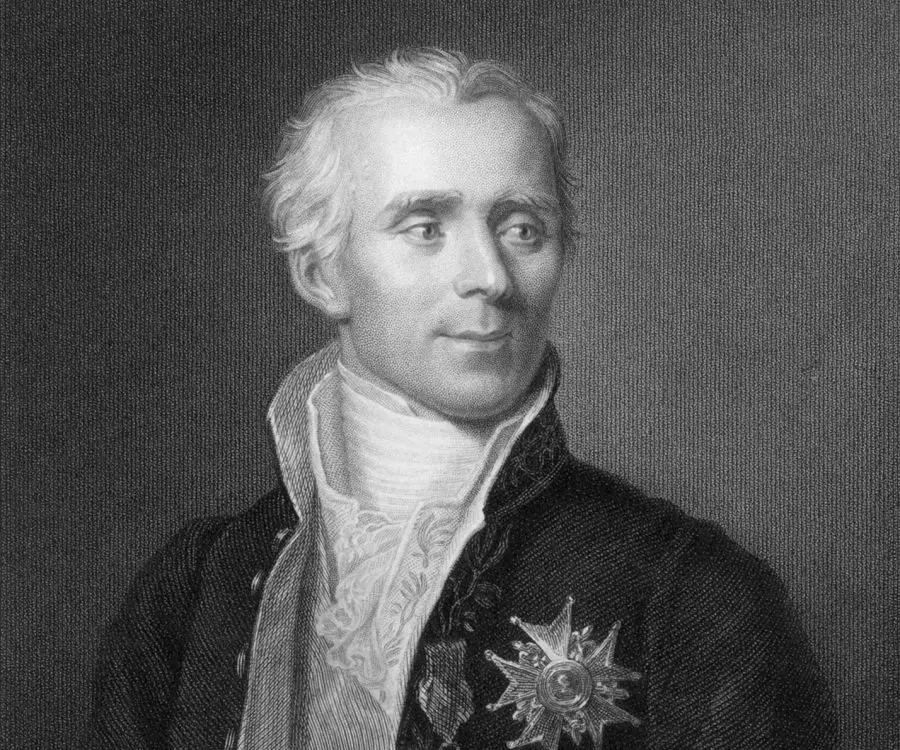
Pierre-Simon Laplace's photo
Who is Pierre-Simon Laplace?
Pierre-Simon Laplace was a French mathematician and astronomer who carried out remarkable studies regarding the stability of the solar system and is famously known as the ‘French Newton’. He also did pioneering work in mathematics regarding the theory of probability and statistics which influenced a whole new generation of mathematicians. Born in a poor family, his education was financed by neighbors and he was sent to study theology at the age of 16. But, he soon developed a keen interest in mathematics and was subsequently drawn to physics and astronomy. He served as a professor of mathematics for seven years and also published several scientific papers alongside. Laplace successfully accounted for all the observed deviations of the planets from their theoretical orbits by applying Sir Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation to the solar system, and he developed a conceptual view of evolutionary change in the structure of the solar system. He also demonstrated the usefulness of probability for interpreting scientific data and applied his own definition of probability to justify the fundamental mathematical manipulations. He restated and developed the nebular hypothesis of the origin of the solar system and also postulated the existence of black holes along with the notion of gravitational collapse
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
Pierre-Simon Laplace was born on March 23, 1749, in Beaumont-en-Auge, a village in Normandy, France, to Pierre de Laplace, owner of small farms of Maarquis, and his wife, Marie-Anne Sochon.
Despite his family’s poor financial condition, Laplace was able to receive a good education courtesy his wealthy neighbors. His father wanted him to be ordained in the Roman Catholic Church and thus sent him to Caen University to study theology at the age of 16. But, Laplace developed a keen interest in mathematics.
At the age of 19, he dropped out of college and moved to Paris where he worked as a professor of mathematics at the École Militaire from 1769 to 1776. During this time, he published several papers regarding integral calculus, mechanics and physical astronomy, which gained him much acclaim all over France.
Career
In 1771, his early published work focused on differential equations and finite differences. Subsequently, he started to think about the mathematical and philosophical concepts of probability and statistics.
In 1774, his paper titled ‘Mémoire sur la probabilité des causes par les événements’ was published. Two years later, he published another paper which further elaborated his statistical thinking and also began his systematic work on celestial mechanics and the stability of the solar system.
During 1784–87, he worked on the subject of attraction between spheroids which laid the mathematical foundation for the scientific study of heat, magnetism, and electricity.
In 1796, he published ‘Exposition du système du monde (The System of the World)’, which included his ‘nebular hypothesis’.
Between 1799 and 1825, he published five volumes of ‘Traité de mécanique céleste (Celestial Mechanics)’, which summarized the results obtained by his mathematical development and application of the law of gravitation.
In 1812, he published his comprehensive research in mathematics titled ‘Théorie analytique des probabilités (Analytic Theory of Probability)’. Another major work on the theory of probability, titled ‘Essai philosophique sur les probabilités (A Philosophical Essay on Probability)’ was published in 1814.
He theorized the existence of black holes, suggesting that there could be massive stars whose gravity is so great that not even light could escape from its surface. He also stated the fact that the speed of sound in air depends on the heat capacity ratio.
His other discoveries in pure and applied mathematics include Laplace's method for approximating integrals, solution of the linear partial differential equation of the second order, and general proof of the Lagrange reversion theorem.
Major Works
Pierre-Simon Laplace is highly regarded for his influential five-volume treatise ‘Traité de mécanique céleste’ (Celestial mechanics; 1799-1825), which developed a strong mathematical understanding of the motion of the heavenly bodies. He established that the small perturbations observed in the orbital motion of the planets will always remain small, constant and self-correcting.
He formulated Laplace's equation, and pioneered the Laplace transform which appears in many branches of mathematical physics. The Laplacian differential operator, widely used in mathematics, is also named after him.
Awards & Achievements
In 1806, Laplace was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
In 1822, he was appointed a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
Personal Life & Legacy
In March 1788, he married Marie-Charlotte de Courty de Romanges, a girl from Besançon who was twenty years younger to him. The couple had a son, Charles-Émile, and a daughter, Sophie-Suzanne.
Pierre-Simon Laplace died on March 5, 1827, in Paris, France, at the age of 77. After he died, his physician, François Magendie, removed Laplace’s brain which was later displayed in a roving anatomical museum in Britain.
// Famous Astronomers
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton was an English scientist and mathematician, who discovered gravitation and Newtonian Mechanics. Read this biography to find more on his life.
Henrietta Swan Leavitt
Henrietta Swan Leavitt was an American astronomer. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, discoveries, achievements, etc.
Pierre-Simon Laplace biography timelines
- // 23rd Mar 1749Pierre-Simon Laplace was born on March 23, 1749, in Beaumont-en-Auge, a village in Normandy, France, to Pierre de Laplace, owner of small farms of Maarquis, and his wife, Marie-Anne Sochon.
- // 1769 To 1776At the age of 19, he dropped out of college and moved to Paris where he worked as a professor of mathematics at the École Militaire from 1769 to 1776. During this time, he published several papers regarding integral calculus, mechanics and physical astronomy, which gained him much acclaim all over France.
- // 1771In 1771, his early published work focused on differential equations and finite differences. Subsequently, he started to think about the mathematical and philosophical concepts of probability and statistics.
- // 1774In 1774, his paper titled ‘Mémoire sur la probabilité des causes par les événements’ was published. Two years later, he published another paper which further elaborated his statistical thinking and also began his systematic work on celestial mechanics and the stability of the solar system.
- // 1784During 1784–87, he worked on the subject of attraction between spheroids which laid the mathematical foundation for the scientific study of heat, magnetism, and electricity.
- // Mar 1788In March 1788, he married Marie-Charlotte de Courty de Romanges, a girl from Besançon who was twenty years younger to him. The couple had a son, Charles-Émile, and a daughter, Sophie-Suzanne.
- // 1796In 1796, he published ‘Exposition du système du monde (The System of the World)’, which included his ‘nebular hypothesis’.
- // 1799 To 1825Between 1799 and 1825, he published five volumes of ‘Traité de mécanique céleste (Celestial Mechanics)’, which summarized the results obtained by his mathematical development and application of the law of gravitation.
- // 1799 To 1825Pierre-Simon Laplace is highly regarded for his influential five-volume treatise ‘Traité de mécanique céleste’ (Celestial mechanics; 1799-1825), which developed a strong mathematical understanding of the motion of the heavenly bodies. He established that the small perturbations observed in the orbital motion of the planets will always remain small, constant and self-correcting.
- // 1806In 1806, Laplace was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
- // 1812 To 1814In 1812, he published his comprehensive research in mathematics titled ‘Théorie analytique des probabilités (Analytic Theory of Probability)’. Another major work on the theory of probability, titled ‘Essai philosophique sur les probabilités (A Philosophical Essay on Probability)’ was published in 1814.
- // 1822In 1822, he was appointed a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
- // 5th Mar 1827Pierre-Simon Laplace died on March 5, 1827, in Paris, France, at the age of 77. After he died, his physician, François Magendie, removed Laplace’s brain which was later displayed in a roving anatomical museum in Britain.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Alex Lange
Alex Lange is a French-South African model, who is quite popular on Instagram. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Tina Kunakey
Tina Kunakey Di Vita is a model and wife of the French actor Vincent Cassel. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jeanne Calment
Jeanne Calment was a French supercentenarian who had the longest confirmed lifespan in human history. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, death, etc.
Pierre-Simon Laplace's FAQ
What is Pierre-Simon Laplace birthday?
Pierre-Simon Laplace was born at 1749-03-23
When was Pierre-Simon Laplace died?
Pierre-Simon Laplace was died at 1827-03-05
Where was Pierre-Simon Laplace died?
Pierre-Simon Laplace was died in Paris
Which age was Pierre-Simon Laplace died?
Pierre-Simon Laplace was died at age 77
Where is Pierre-Simon Laplace's birth place?
Pierre-Simon Laplace was born in Beaumont-en-Auge
What is Pierre-Simon Laplace nationalities?
Pierre-Simon Laplace's nationalities is French
Who is Pierre-Simon Laplace spouses?
Pierre-Simon Laplace's spouses is Marie-Charlotte de Courty de Romanges
What was Pierre-Simon Laplace universities?
Pierre-Simon Laplace studied at University of Caen Lower Normandy
What is Pierre-Simon Laplace's religion?
Pierre-Simon Laplace's religion is Catholicism
What is Pierre-Simon Laplace's sun sign?
Pierre-Simon Laplace is Aries
How famous is Pierre-Simon Laplace?
Pierre-Simon Laplace is famouse as Scientist















