Jacques Monod - Biologists, Timeline and Life
Jacques Monod's Personal Details
Jacques Lucien Monod was a French biologist who received the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | February 9, 1910 |
| Died on | May 31, 1976 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Biologists |
| Spouses | Odette Bruhl |
| Known as | Jacques Lucien Monod |
| Birth Place | 1910 |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Lucien Monod |
| Mother | Charlotte (Sharlie) MacGregor Todd |
| Sun Sign | Aquarius |
| Born in | 1910 |
| Famous as | Biologist |
| Died at Age | 66 |
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
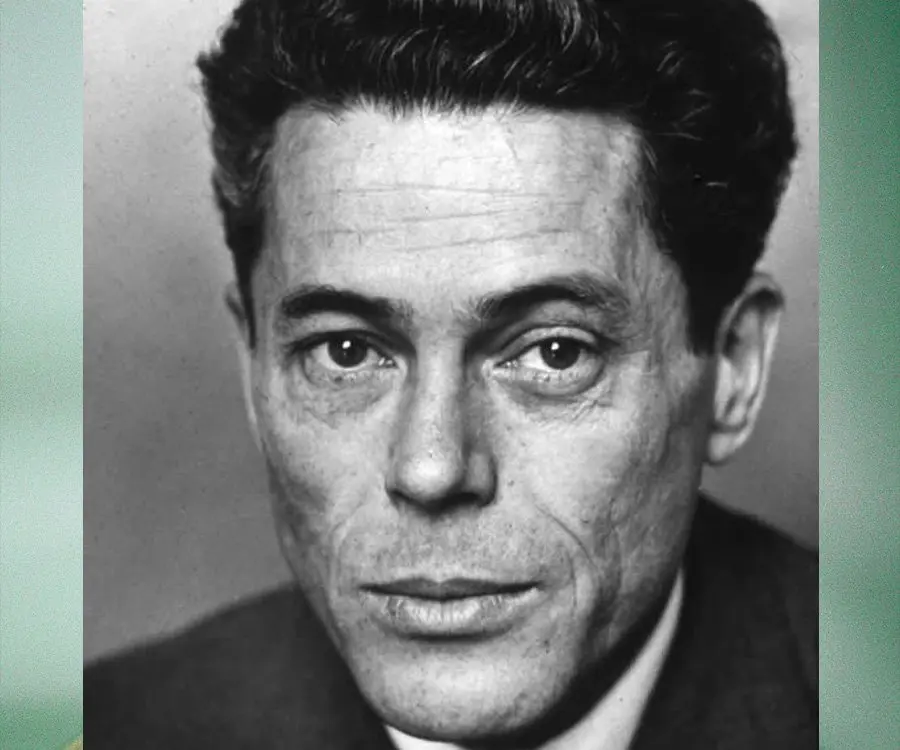
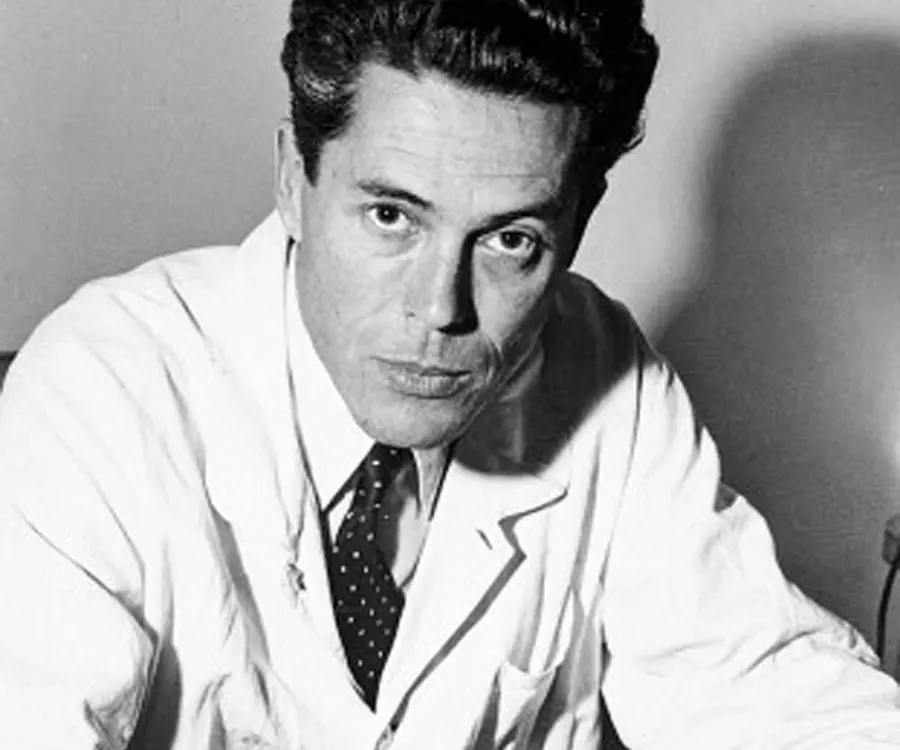
Jacques Monod's photo
Who is Jacques Monod?
Jacques Lucien Monod was a French biologist who received the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965 along with another French biologist François Jacob and French microbiologist Andre Lwoff for their discoveries regarding genetic regulation of enzyme and synthesis of virus. Monod and François Jacob suggested the presence of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), that acts as a courier and convey genetic information from the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the carrier of genetic instructions, to the ribosome, which is the protein synthesizer of cell. The most notable and significant finding of Monod that he worked together with Jacob was perceiving of a specific class of genes that regulate the activities of other genes by affecting the synthesis of mRNA. They developed the Jacob-Monod operon model that helps in elucidating the way genes are regulated. The duo also showed the effects of balance and imbalance between regulator genes and structural genes in a normal cell. He received several honours and distinctions that include ‘Montyon Physiology Prize’ and the ‘Charles Léopold Mayer Prize’ from the ‘Acadèmie des Sciences’, Paris in 1955 and 1962 respectively; and the ‘Louis Rapkine Medal’ in London in 1958. The military decorations conferred on him include Chevalier de la Légion d’Honneur and Croix de Guerre in 1945. In 1968 he became an elected ‘Foreign Member of the Royal Society’ (ForMemRS).
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
He was born on February 9, 1910, in Paris, to Lucien Monod and his wife Charlotte (Sharlie) MacGregor Todd. His father, a French Huguenot, was a painter and his mother was an American from Milwaukee.
He was intellectually and artistically inspired by his father, who was an avid reader of Darwin and probably this infused an interest in little Jacob in the field of biology.
In his childhood he used to involve himself in several activities including rock climbing, searching for fossils, sailing yachts and dissecting cats.
He completed his secondary education from the lycée de Cannes and thereafter in October 1928 he enrolled at the ‘Faculte des Sciences’ at the ‘University of Paris’ (‘Sorbonne’) to study natural sciences.
In 1931 he earned his Science Degree and began to pursue a Ph.D. He received a fellowship to work at the ‘University of Strasbourg’ with French biologist Edouard Chatton.
He was inducted as assistant professor of zoology at the ‘Faculte des Sciences’ and from 1932 to 1934 he remained engrossed in investigating the evolution of life.
He earned a Rockefeller fellowship in 1936 to study genetics at the ‘California Institute of Technology’ (Caltech) and Professor of Genetics Boris Ephrussi took him to the institute. At Caltech he worked on Drosophila genetics for a year in the lab of American geneticist, biologist and embryologist Thomas Hunt Morgan.
Though his tenure in Caltech was not that rewarding he impressed the local residents with his musical talent and was also offered a job in the local orchestra. However he returned to Paris giving up his musical career options in order to complete his Ph.D.
In his doctoral work he examined bacterial growth on sugar mixtures and detailed the sequential application of two or more sugars. The term diauxie was coined by him to mean the repeated observations of two specific bacterial growth phases developed in two sugars. He earned his Ph.D. in Natural sciences in1941.
Career
Monod was a political activist and played an active role in the ‘French Resistance’ during the ‘Second World War’. In course of time he became the chief of staff of operations for the ‘French Forces of the Interior’. In pursuit of Allied landings, he made arrangements for mail interceptions, bombing railroads and also dropping of weapons through parachute.
Post liberation he was inducted in the renowned ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France as Laboratory Director in the department of Andre Lwoff. In 1954 he became the Director of the ‘Cell Biochemistry Department’.
During 1958 Monod, Jacob and American biochemist Arthur Beck Pardee were involved in an experiment which became famous as the ‘PaJaMo’. This experiment and later research revealed that commencement of protein synthesis from a gene can take place almost immediately as it enters an E.coli cell. Earlier theories regarding interpretation of genetic data into proteins were focused on ribosomes.
In 1959, he became a Professor of the Chemistry of Metabolism at the ‘University of Paris’ (‘Sorbonne’), where he was once a student.
In 1961 Monod and Jacob worked on the mechanics responsible for genetic data transfer and the controlling pathways that exist in bacterial cell that control the activities and synthesis of macromolecules. These experiments led to a new theory of an existence of another species of RNA, which is the messenger RNA (mRNA).
Monod and Jacob earned reputation for their research on E.coli Lac operon that encodes protein required for the transfer and breakdown of sugar lactose. They showed a model that elucidated the way levels of some of the cell proteins are controlled. Their model suggests that protein development is restricted when a DNA- binding protein or a RNA-binding protein i.e., a repressor, encoded by a regulatory gene, binds to a segment of DNA i.e., an operator.
Their findings convey that the regulator genes are the controlling genes that regulate the activities of the structural genes. They further suggested that the balance between regulator genes and structural genes in a normal cell permits it to adjust in different conditions while an imbalance can result in development of new enzymes that can be either beneficial or cause harm to the cell.
In 1967 he was appointed a Professor at the ‘Collège de France’.
He advocated the view that life on earth is the result of an unusual chemical accident, a unique event that took place, which would never be repeated. His views on the evolution of life interpreted as the result of natural processes by "pure chance" was expressed in his book ‘Chance and Necessity: Essay on the Natural Philosophy of Modern Biology’.
He became the Director of the ‘Pasteur Institute’ in 1971.
Awards & Achievements
He was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965 together with François Jacob and Andre Lwoff.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1938 Monod married Odette Bruhl, an archaeologist who later became the curator of the ‘Guimet Museum’.
In 1939 their twin sons, Philippe and Olivier were born. Though Monod never influenced his children to pursue science, one of his sons became a geologist while the other became a physicist.
Apart from being a biologist he was a gifted musician and his favourite pastimes included music and sailing.
On May 31, 1976, he passed away after suffering from leukaemia. His last words were "Je cherche a comprendre" i.e., “I am trying to understand”. He was interred in Cannes’ ‘Cimetière du Grand Jas’ on the French Riviera.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jacques Monod's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1965) | |
| 0 | Legion of Honour ForMemRS (1968) | |
Jacques Monod biography timelines
- // 9th Feb 1910He was born on February 9, 1910, in Paris, to Lucien Monod and his wife Charlotte (Sharlie) MacGregor Todd. His father, a French Huguenot, was a painter and his mother was an American from Milwaukee.
- // Oct 1928He completed his secondary education from the lycée de Cannes and thereafter in October 1928 he enrolled at the ‘Faculte des Sciences’ at the ‘University of Paris’ (‘Sorbonne’) to study natural sciences.
- // 1931In 1931 he earned his Science Degree and began to pursue a Ph.D. He received a fellowship to work at the ‘University of Strasbourg’ with French biologist Edouard Chatton.
- // 1932 To 1934He was inducted as assistant professor of zoology at the ‘Faculte des Sciences’ and from 1932 to 1934 he remained engrossed in investigating the evolution of life.
- // 1936He earned a Rockefeller fellowship in 1936 to study genetics at the ‘California Institute of Technology’ (Caltech) and Professor of Genetics Boris Ephrussi took him to the institute. At Caltech he worked on Drosophila genetics for a year in the lab of American geneticist, biologist and embryologist Thomas Hunt Morgan.
- // 1938In 1938 Monod married Odette Bruhl, an archaeologist who later became the curator of the ‘Guimet Museum’.
- // 1939In 1939 their twin sons, Philippe and Olivier were born. Though Monod never influenced his children to pursue science, one of his sons became a geologist while the other became a physicist.
- // 1941In his doctoral work he examined bacterial growth on sugar mixtures and detailed the sequential application of two or more sugars. The term diauxie was coined by him to mean the repeated observations of two specific bacterial growth phases developed in two sugars. He earned his Ph.D. in Natural sciences in1941.
- // 1954Post liberation he was inducted in the renowned ‘Pasteur Institute’ of France as Laboratory Director in the department of Andre Lwoff. In 1954 he became the Director of the ‘Cell Biochemistry Department’.
- // 1958During 1958 Monod, Jacob and American biochemist Arthur Beck Pardee were involved in an experiment which became famous as the ‘PaJaMo’. This experiment and later research revealed that commencement of protein synthesis from a gene can take place almost immediately as it enters an E.coli cell. Earlier theories regarding interpretation of genetic data into proteins were focused on ribosomes.
- // 1959In 1959, he became a Professor of the Chemistry of Metabolism at the ‘University of Paris’ (‘Sorbonne’), where he was once a student.
- // 1961In 1961 Monod and Jacob worked on the mechanics responsible for genetic data transfer and the controlling pathways that exist in bacterial cell that control the activities and synthesis of macromolecules. These experiments led to a new theory of an existence of another species of RNA, which is the messenger RNA (mRNA).
- // 1965He was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine’ in 1965 together with François Jacob and Andre Lwoff.
- // 1967In 1967 he was appointed a Professor at the ‘Collège de France’.
- // 1970He advocated the view that life on earth is the result of an unusual chemical accident, a unique event that took place, which would never be repeated. His views on the evolution of life interpreted as the result of natural processes by "pure chance" was expressed in his book ‘Chance and Necessity: Essay on the Natural Philosophy of Modern Biology’.
- // 1971He became the Director of the ‘Pasteur Institute’ in 1971.
- // 31st May 1976On May 31, 1976, he passed away after suffering from leukaemia. His last words were "Je cherche a comprendre" i.e., “I am trying to understand”. He was interred in Cannes’ ‘Cimetière du Grand Jas’ on the French Riviera.
// Famous Aquarius Celebrities peoples
Jessii Vee
Check out all that you wanted to know about Jessii Vee, the famous Canadian Vlogger & YouTube Personality; her birthday, her family and personal life, her boyfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Luara Fonseca
Luara Fonseca, known on the web as “luaraff,” is a musical.ly star. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Shane Blanchard
Shane Blanchard is an American TV actor. Let’s take a look at his family and personal life including age, birthday, net worth, family life and some fun facts.
Nora Fatehi
Nora Fatehi is a dancer, model, and actress of Indo–Arabic descent. This biography profiles her childhood, family, personal life, etc.
Soni Nicole Bringas
Soni Nicole Bringas is an American dancer and actress. Let’s have a look at her family and personal life including age. Date of birth, boyfriends, net worth, and fun facts.
Davis Cleveland
Davis Cleveland is an American actor. Let’s have a look at his family & personal life including age, net worth, and fun facts.
Jacques Monod's FAQ
What is Jacques Monod birthday?
Jacques Monod was born at 1910-02-09
When was Jacques Monod died?
Jacques Monod was died at 1976-05-31
Where was Jacques Monod died?
Jacques Monod was died in Cannes, France
Which age was Jacques Monod died?
Jacques Monod was died at age 66
Where is Jacques Monod's birth place?
Jacques Monod was born in 1910
What is Jacques Monod nationalities?
Jacques Monod's nationalities is French
Who is Jacques Monod spouses?
Jacques Monod's spouses is Odette Bruhl
Who is Jacques Monod's father?
Jacques Monod's father is Lucien Monod
Who is Jacques Monod's mother?
Jacques Monod's mother is Charlotte (Sharlie) MacGregor Todd
What is Jacques Monod's sun sign?
Jacques Monod is Aquarius
How famous is Jacques Monod?
Jacques Monod is famouse as Biologist