J.B.S. Haldane - Communists, Birthday and Life
J.B.S. Haldane's Personal Details
J.B.S
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | November 5, 1892 |
| Died on | December 1, 1964 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Communists, Eton College, Scientists, Biologists, Geneticists |
| Ideologies | Communists |
| Spouses | Helen Spurway (m. 1945), Charlotte Haldane (m. 1926–1945) |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Oxford, United Kingdom |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | John Scott Haldane |
| Mother | Louisa Kathleen Haldane |
| Sun Sign | Scorpio |
| Born in | Oxford, United Kingdom |
| Famous as | Geneticist |
| Died at Age | 72 |
// Famous Geneticists
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
George Wells Beadle
George Wells Beadle was an American geneticist who won the 1958 Nobel Prize in Medicine. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Mendel was an Austrian scientist and monk credited with being the father of modern genetics for his pioneering work in the study of heredity. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, & timeline.
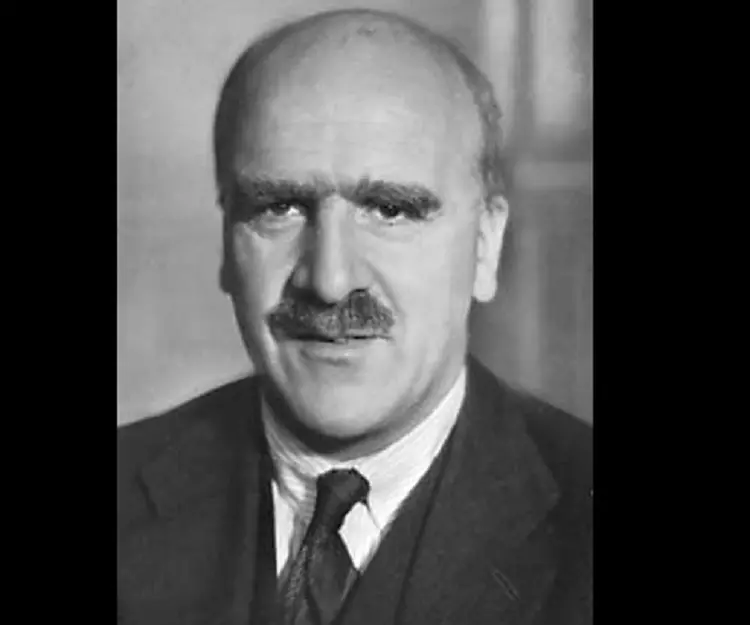
J.B.S. Haldane's photo
Who is J.B.S. Haldane?
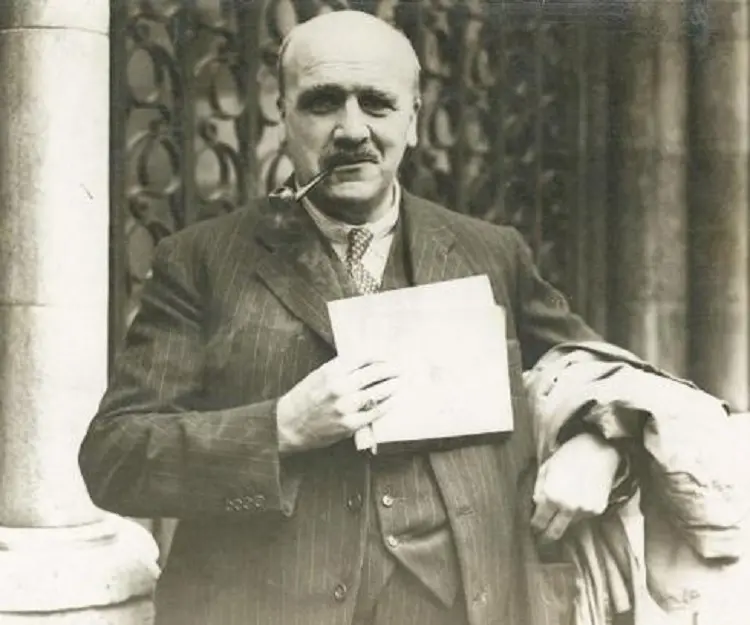
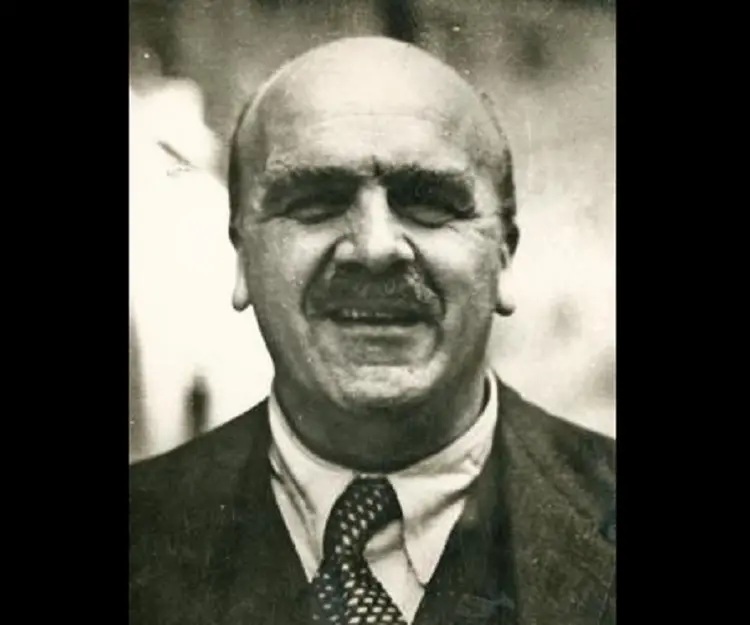
J.B.S. Haldane was a British-born Indian scientist and geneticist who made remarkable contribution in the field of population genetics and evolution. Born to renowned physiologist John Scott Haldane, he began assisting his father at the age of eight. His college education was interrupted because of World War I, during which he served in the British army. After the war he became a fellow of New College and later taught at the Universities of Cambridge, California and London. He followed the Marxist philosophy and joined the British Communist Party. Later in his career, he shifted to India and led the government Genetics and Biometry Laboratory in Orissa. Apart from his extensive research in biology and genetics, he made important contributions to enzyme kinetics in biochemistry. He also developed a treatment for tetanus. He would often subject himself to self-experimentations in order to acquire new data. His amazing intelligence and sharp memory allowed him to concentrate on two completely different subjects at the same time. Apart from technical publications, he wrote numerous articles for newspapers and popular magazines globally. Some of his major works include ‘Daedalus’ (1924), ‘The Causes of Evolution’ (1932), ‘The Marxist Philosophy and the Sciences’ (1938), and ‘The Biochemistry of Genetics’ (1954).
// Famous Eton College
Karl Marx
Karl Marx was a Prussian-German philosopher, revolutionary, historian and socialist whose communist ideologies and works laid the foundation for ‘Marxism’. Explore this biography to learn more about his childhood, life achievements, works & timeline.
Antony Armstrong-Jones, 1st Earl of Snowdon
Antony Armstrong-Jones was a British photographer and film-maker. Check out this biography formore information on his childhood, family, personal life, etc.
Bear Grylls
Bear Grylls is an adventurer popularly known for his bizarre survival tactics in reality television series Man vs. Wild. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, profile, career and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
J.B.S. Haldane was born on 5 November 1892, in Oxford, England. He belonged to an upper-class, secular family of scholars. His father, John Scott Haldane, was a physiologist who researched on human respiration, and his mother’s name was Louisa Kathleen Trotter. His younger sister, Naomi Mitchison, grew up to be a writer.
He spent his childhood in North Oxford. He began to read at the age of three and showed a keen interest in science. From the age of eight, he started working with his father in their home laboratory.
In 1897, he commenced his formal education at Oxford Preparatory School. Two years later, his family shifted to a Victorian house with a private laboratory, at the outskirts of Oxford.
In 1905, he joined Eton College where senior students repeatedly misbehaved with him. Since the college management failed to curb this menace, he developed a strong disliking for the English education system.
He later joined New College, University of Oxford and graduated with distinction in 1914 with a degree in mathematics, classics and philosophy. At the age 20, his first research paper, co-authored with his father, was published.
Career
During World War I, his education was sporadic. He fought in the British Army as second lieutenant in the Royal Highland Regiment. For his bravery, he was promoted to the position of temporary lieutenant and later, temporary captain.
His life was in constant danger when he fought in France and Iraq. In 1920, he resigned from his military duty. This was made possible by his uncle, Lord Haldane, who was Minister for War at that time.
In 1919, he received a Fellowship in Physiology at New College, Oxford University, where he researched in both physiology and genetics. In 1923, he moved to Cambridge University, where he accepted the Dunn readership in Biochemistry under Professor F. G. Hopkins, at Trinity College, and taught there until 1932.
At Cambridge, he worked on enzymes and genetics, particularly the mathematical aspect of genetics. From 1927 to 1937, he was also Head of Genetical Research at the John Innes Horticultural Institution.
From 1930 to 1932, he was the Fullerian Professor of Physiology at the Royal Institution. In 1933, he became Professor of Genetics at University College, London. Four years later in 1937, he became the first Weldon Professor of Biometry at University College, London.
In 1956, he migrated to India and joined the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in Kolkata as Head of the biometry department; a post he held till 1961. He eventually took Indian citizenship and coverted to Hinduism. He blamed the Suez Crisis for leaving the UK.
Political differences with the then Director of ISI, P. C. Mahalanobis, led him to resign in 1961. Thereafter, he moved to Bhubaneswar, Odisha, to a newly established biometry unit.
During his lifetime, he authored 24 books, hundreds of popular articles, and 400 papers.
Major Works
Together with his sister, Naomi Mitchison, he demonstrated the genetic linkage in mammals in 1915. He researched on the chemical properties of haemoglobin, examined the various aspects of kidney functions and the mechanism of excretion.
He applied Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's study of genetics to his own mathematics-based research on population growth. He pioneered the thought of duplication of humans, and coined the term ‘clone’.
In 1923, he predicted the exhaustion of coal for power generation in Britain and proposed a network of hydrogen-generating windmills; the first of its kind in renewable energy.
Some of his major publications are ‘Daedalus’ (1924), ‘Enzymes’ (1930), and ‘The Causes of Evolution’ (1932). Apart from technical publications, he also wrote about science for beginners. Some of his essays were published in the collection ‘Possible Worlds’ (1927).
Awards & Achievements
Haldane was named a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1932.
He was awarded the Legion of Honor by the French Government in 1937.
In 1952, he received the Darwin Medal from the Royal Society.
In 1956, he received the Huxley Memorial Medal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain.
In 1961, he received the Feltrinelli Prize from Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei.
Personal Life & Legacy
J.B.S. Haldane hailed from a family of scholars and prominent personalities. His uncle, Viscount Haldane, was a scholar and prominent politician in Prime Minister’s cabinet. His great uncle, Burdon Sanderson, was the first Waynflete Professor of Physiology at Oxford University.
He married twice. In 1926, he married Charlotte Burghes, a writer and journalist. Following their separation in 1942, the couple divorced in 1945. He later married Dr. Helen Spurway, a biologist.
During World War I, he was a socialist. In the 1930s, inspired by the work of Lenin, he became a Marxist. He joined the British Communist Party in 1942. Although he left the party later, he continued to support Marxism all through his life.
He died of cancer on 1 December 1964, at Bhubaneswar, at the age of 72. While in the hospital, he wrote a witty poem titled ‘Cancer's a Funny Thing’ scorning the fatal disease. He donated his body for study at the Rangaraya Medical College, Kakinada.
Trivia
J.B.S. Haldane would often endure dangerous self-experimentations to acquire new data. For example, he drank dilute hydrochloric acid and enclosed himself in an airtight room containing 7% carbon dioxide to assess the consequence of acidification of the blood. Some of his other self-experimentations resulted in a crushed backbone and punctured eardrums.
// Famous Biologists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug was an American biologist known as the “Father of the Green Revolution”. This biography of Norman Borlaug provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
J.B.S. Haldane's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Darwin–Wallace Medal | |
J.B.S. Haldane biography timelines
- // 5th Nov 1892J.B.S. Haldane was born on 5 November 1892, in Oxford, England. He belonged to an upper-class, secular family of scholars. His father, John Scott Haldane, was a physiologist who researched on human respiration, and his mother’s name was Louisa Kathleen Trotter. His younger sister, Naomi Mitchison, grew up to be a writer.
- // 1897In 1897, he commenced his formal education at Oxford Preparatory School. Two years later, his family shifted to a Victorian house with a private laboratory, at the outskirts of Oxford.
- // 1905In 1905, he joined Eton College where senior students repeatedly misbehaved with him. Since the college management failed to curb this menace, he developed a strong disliking for the English education system.
- // 1914He later joined New College, University of Oxford and graduated with distinction in 1914 with a degree in mathematics, classics and philosophy. At the age 20, his first research paper, co-authored with his father, was published.
- // 1915Together with his sister, Naomi Mitchison, he demonstrated the genetic linkage in mammals in 1915. He researched on the chemical properties of haemoglobin, examined the various aspects of kidney functions and the mechanism of excretion.
- // 1920His life was in constant danger when he fought in France and Iraq. In 1920, he resigned from his military duty. This was made possible by his uncle, Lord Haldane, who was Minister for War at that time.
- // 1923In 1923, he predicted the exhaustion of coal for power generation in Britain and proposed a network of hydrogen-generating windmills; the first of its kind in renewable energy.
- // 1927 To 1937At Cambridge, he worked on enzymes and genetics, particularly the mathematical aspect of genetics. From 1927 to 1937, he was also Head of Genetical Research at the John Innes Horticultural Institution.
- // 1932Haldane was named a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1932.
- // 1937He was awarded the Legion of Honor by the French Government in 1937.
- // 1942During World War I, he was a socialist. In the 1930s, inspired by the work of Lenin, he became a Marxist. He joined the British Communist Party in 1942. Although he left the party later, he continued to support Marxism all through his life.
- // 1952In 1952, he received the Darwin Medal from the Royal Society.
- // 1956 To 1961In 1956, he migrated to India and joined the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in Kolkata as Head of the biometry department; a post he held till 1961. He eventually took Indian citizenship and coverted to Hinduism. He blamed the Suez Crisis for leaving the UK.
- // 1956In 1956, he received the Huxley Memorial Medal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain.
- // 1961Political differences with the then Director of ISI, P. C. Mahalanobis, led him to resign in 1961. Thereafter, he moved to Bhubaneswar, Odisha, to a newly established biometry unit.
- // 1961In 1961, he received the Feltrinelli Prize from Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei.
- // 1st Dec 1964He died of cancer on 1 December 1964, at Bhubaneswar, at the age of 72. While in the hospital, he wrote a witty poem titled ‘Cancer's a Funny Thing’ scorning the fatal disease. He donated his body for study at the Rangaraya Medical College, Kakinada.
// Famous Communists
Simone de Beauvoir
Simone de Beauvoir was an eminent French writer, intellectual, activist, and philosopher. This biography profiles her childhood, life, thoughts, achievements and timeline.
Karl Marx
Karl Marx was a Prussian-German philosopher, revolutionary, historian and socialist whose communist ideologies and works laid the foundation for ‘Marxism’. Explore this biography to learn more about his childhood, life achievements, works & timeline.
Pablo Neruda
Pablo Neruda was a Chilean poet, politician and Nobel laureate. Go through this biography to learn more about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Pol Pot
Pol Pot was the Cambodian revolutionary who led the Khmer Rouge. This biography provides a glimpse of his childhood, career, profile and timeline.
Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Khrushchev was a former Soviet premier. This biography gives detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements and timeline.
Josip Broz Tito
Josip Broz Tito was the powerful revolutionary leader of Yugoslav Partisans. Check this biography to know more about his childhood, life, profile and timeline.
J.B.S. Haldane's FAQ
What is J.B.S. Haldane birthday?
J.B.S. Haldane was born at 1892-11-05
When was J.B.S. Haldane died?
J.B.S. Haldane was died at 1964-12-01
Which age was J.B.S. Haldane died?
J.B.S. Haldane was died at age 72
Where is J.B.S. Haldane's birth place?
J.B.S. Haldane was born in Oxford, United Kingdom
What is J.B.S. Haldane nationalities?
J.B.S. Haldane's nationalities is British
What is J.B.S. Haldane ideologies?
J.B.S. Haldane's ideologies is Communists
Who is J.B.S. Haldane spouses?
J.B.S. Haldane's spouses is Helen Spurway (m. 1945), Charlotte Haldane (m. 1926–1945)
What was J.B.S. Haldane universities?
J.B.S. Haldane studied at Eton College
What was J.B.S. Haldane notable alumnis?
J.B.S. Haldane's notable alumnis is Eton College
Who is J.B.S. Haldane's father?
J.B.S. Haldane's father is John Scott Haldane
Who is J.B.S. Haldane's mother?
J.B.S. Haldane's mother is Louisa Kathleen Haldane
What is J.B.S. Haldane's sun sign?
J.B.S. Haldane is Scorpio
How famous is J.B.S. Haldane?
J.B.S. Haldane is famouse as Geneticist