Antoine Lavoisier - Chemists, Career and Family
Antoine Lavoisier's Personal Details
Antoine Lavoisier was a famous French chemist, known for his extraordinary research on oxygen and combustion
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | August 26, 1743 |
| Died on | May 8, 1794 |
| Nationality | French |
| Famous | Scientists, Chemists |
| Hobbies | Meteorological observation, Botany, French politics, Chemistry |
| Spouses | Marie-Anne Paulze Lavoisier |
| Known as | Antoine Laurent Lavoisier |
| Cause of death |
|
| Birth Place | Paris |
| Religion | Catholicism |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Virgo |
| Born in | Paris |
| Famous as | Chemist |
| Died at Age | 50 |
// Famous Chemists
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Walter Kohn
Nobel Laureate Walter Kohn was an Austrian-born American theoretical chemist and physicist. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jabir Ibn Hayyan
Jabir Ibn Hayyan was a medieval era polymath. Check out this biography to know about his life, works and achievements.
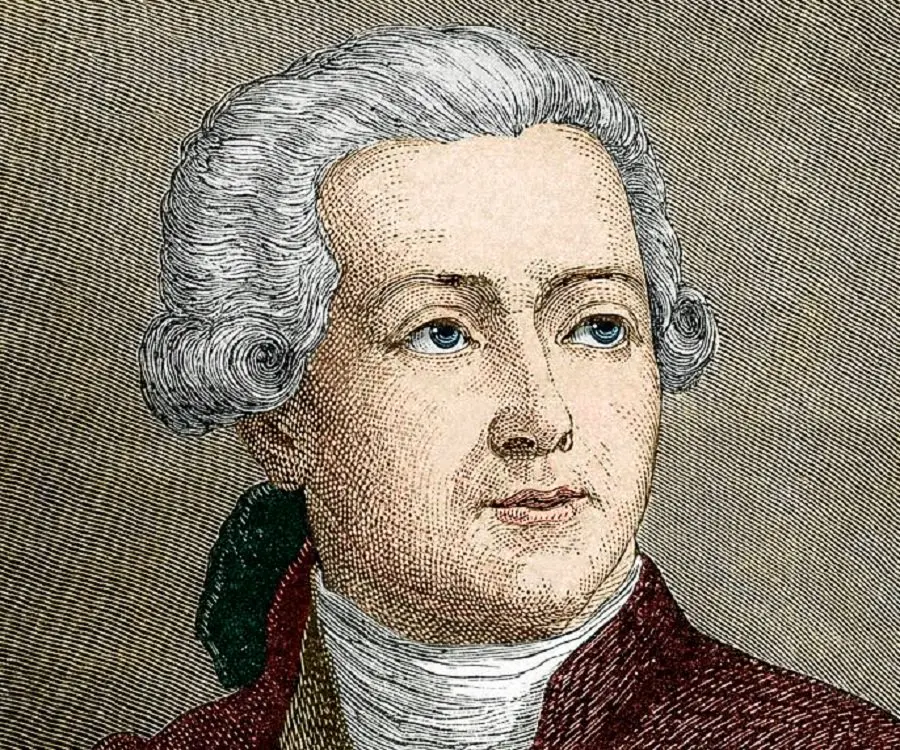
Antoine Lavoisier's photo
Who is Antoine Lavoisier?
Antoine Lavoisier was an 18th century French chemist, who was known for having recognized one of the most important chemical elements, oxygen. Not just that, he also identified the significance of this gas in the process of combustion. He developed an interest in science while still in school, and though he was a qualified lawyer, he ended up working as a scientist instead. This genius' contribution to the field of chemistry, in particular, is extremely indispensable, and forms the basis of several present day scientific theories. He stated that during the process of combustion, not only is a substantial quantity of air used, but there is also a visible gain in the mass of the substance. He improved upon the works of scientists like Joseph Black and Joseph Priestley, especially contributing to the experiments conducted by the latter. His work was so remarkable that the French government decided to hire him as a supervisor for the ammunition department, working specifically on the production of gunpowder. However, despite all his efforts, during the 'Reign of Terror' in France, twenty-eight Frenchmen, including Lavoisier, were convicted of crimes against the nation by the political leader Maximilien de Robespierre. Though the wrongly accused scientist was executed early in his life, he is idolized by scientists across the globe for having revolutionized the field of chemistry
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Childhood & Early Life
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier was born to well-to-do parents, in Paris, France, on 26 August 1743.
The child pursued his primary schooling from the 'Collège des Quatre-Nations', graduating in 1761. In school, he developed an interest in subjects like botany, chemistry, mathematics and astronomy. His philosophy teacher, Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, influenced his love for meteorological observation.
By 1764, Antoine graduated from the school of law and became a qualified lawyer, though his actual interests lay in scientific studies.
Career
Lavoisier's passion for science grew mainly because of the works of scholars like Étienne Condillac and Pierre Macquer. During 1763 to 1767, the young man was trained in geology by Jean-Étienne Guettard, who the former assisted in a survey of the Alsace-Lorraine territory.
The year 1764 was in particular quite fruitful for Antoine, since he published his first ever scientific paper, dealing with the properties of the sulfate mineral, 'gypsum'. This paper, which was read to the 'French Academy of Sciences', marked the beginning of his career as a scientist.
In 1768, the 'French Academy of Sciences' employed Lavoisier as one of its members, in the capacity of which he began making France's earliest geological map.
It was in 1772 that Lavoisier found out the effects of combustion of phosphorus. He realized that the process required a lot of air and the consequence was a gain in mass.
Later, he conducted the same experiment on sulphur, and arrived at the same inferences. This research proved to be one of the most pioneering chemical theory ever deduced, which remains applicable in the field of science, to this day.
From 1773-74, the talented chemist conducted extensive research on the works of other scientists, including that of Joseph Black from Scotland. Antoine's publication named 'Opuscules physiques et chimiques' ('Physical and Chemical Essays'), was an important example of such research.
Black specialized in alkalis of all kinds, stating the dissimilarities between mild and caustic forms. In this regard, Black had experimented on chalk and quicklime, drawing his conclusion that mild alkalis are comprised of what he termed as "fixed air". This "fixed air" was different from the air we breathe and is now known as carbon dioxide.
It was Lavoisier who surmised that the same "fixed air" was emitted when metals were burnt along with charcoal in a limited reserve of oxygen, a process known as calcination.
The French chemist also inferred in 1774 that any substance can alter its state, liquid, gaseous or solid, during a chemical reaction. During this process however, one does not see any difference in the mass of the substance.
The same year, he met Joseph Priestly, an English scientist, who urged Antoine to carry on further experimentation on the gas released while burning mercury.
Lavoisier's research was so significant and impressive that along with three other scientists, he was given the responsibility of improving the quality of gunpowder used by the French army, in the year 1775.
During 1777-87, it was the brilliant French scientist who identified oxygen, named it so, and determined the fact that sulphur was actually an element, contrary to the established belief of the day. He also discovered hydrogen gas, and stated that there was a possibility that a substance having the properties of silicon, existed.
Antoine was one of the four scientists who set down rules for naming chemical substances in a systematic way, in 1787. The other chemists were Antoine François de Fourcroy, L. B. Guyton de Morveau, and Claude-Louis Berthollet.
Major Works
Lavoisier is best known, even today, for his invaluable identification of oxygen, and his theory determining the role that the gas plays in the process of combustion of any substance.
Awards & Achievements
In 1766, this remarkable scientist was the recipient of a gold medal, presented by the French emperor. The chemist had written a well-appreciated essay that suggested solutions to the difficulties of providing light to the roads in a city.
Personal Life & Legacy
In 1771, the young scientist married a girl fifteen years younger to him, Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze. An intelligent young girl, she became Antoine's assistant, helping him not just with his experiments, but also with his publications.
With the advent of the 'French Revolution', Antoine soon lost his government job, and was forced to halt his scientific research. Since he was an influential member of the tax collecting establishment, 'Ferme Générale', the new French leader, Maximilien de Robespierre, labelled him a renegade.
In 1794, he was indicted for various crimes, including being a quisling of foreign scientists like Joseph Louis Lagrange, and was executed on May 8, along with twenty-seven other accused.
It was only after more than a year that the body of the famous scientist was exhumed, and his possessions were given to his wife, Marie-Anne. By then, the French government had established the fact that the scientist had been wrongly executed.
Several streets, schools and buildings have been named after this accomplished scientist.
His theories have been declared by establishments like 'Société Chimique de France', 'American Chemical Society', and the 'French Academy of Sciences' as one of greatest contributions to the field of science.
Trivia
After 1894, a statue of this great French scientist was unveiled in Paris, which was later found to have been modelled on his colleague, Marquis de Condorcet. Paucity of funds hampered its reconstruction, and after its destruction during the World War II, it has never been rebuilt.
// Famous Virgo Celebrities peoples
Temple Grandin
Temple Grandin is a well-known American writer, autistic activist and animal expert. This biography profiles her childhood, life, achievements, career and timeline
Alex Holtti
Check out all that you wanted to know about Alex Holtti, the famous Danish Viner & YouTuber; his birthday, his family and personal life, his girlfriends, fun trivia facts and more.
Benjamin Atkinson
Benjamin Atkinson is the son of the world-renowned British actor and comedian, Rowan Atkinson. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family, personal life, including his age, birthday, etc.
Antoine Lavoisier biography timelines
- // 26th Aug 1743Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier was born to well-to-do parents, in Paris, France, on 26 August 1743.
- // 1761The child pursued his primary schooling from the 'Collège des Quatre-Nations', graduating in 1761. In school, he developed an interest in subjects like botany, chemistry, mathematics and astronomy. His philosophy teacher, Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, influenced his love for meteorological observation.
- // 1763 To 1767Lavoisier's passion for science grew mainly because of the works of scholars like Étienne Condillac and Pierre Macquer. During 1763 to 1767, the young man was trained in geology by Jean-Étienne Guettard, who the former assisted in a survey of the Alsace-Lorraine territory.
- // 1764By 1764, Antoine graduated from the school of law and became a qualified lawyer, though his actual interests lay in scientific studies.
- // 1764The year 1764 was in particular quite fruitful for Antoine, since he published his first ever scientific paper, dealing with the properties of the sulfate mineral, 'gypsum'. This paper, which was read to the 'French Academy of Sciences', marked the beginning of his career as a scientist.
- // 1766In 1766, this remarkable scientist was the recipient of a gold medal, presented by the French emperor. The chemist had written a well-appreciated essay that suggested solutions to the difficulties of providing light to the roads in a city.
- // 1768In 1768, the 'French Academy of Sciences' employed Lavoisier as one of its members, in the capacity of which he began making France's earliest geological map.
- // 1771In 1771, the young scientist married a girl fifteen years younger to him, Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze. An intelligent young girl, she became Antoine's assistant, helping him not just with his experiments, but also with his publications.
- // 1772It was in 1772 that Lavoisier found out the effects of combustion of phosphorus. He realized that the process required a lot of air and the consequence was a gain in mass.
- // 1773 To 1774From 1773-74, the talented chemist conducted extensive research on the works of other scientists, including that of Joseph Black from Scotland. Antoine's publication named 'Opuscules physiques et chimiques' ('Physical and Chemical Essays'), was an important example of such research.
- // 1774The French chemist also inferred in 1774 that any substance can alter its state, liquid, gaseous or solid, during a chemical reaction. During this process however, one does not see any difference in the mass of the substance.
- // 1775Lavoisier's research was so significant and impressive that along with three other scientists, he was given the responsibility of improving the quality of gunpowder used by the French army, in the year 1775.
- // 1777 To 1787During 1777-87, it was the brilliant French scientist who identified oxygen, named it so, and determined the fact that sulphur was actually an element, contrary to the established belief of the day. He also discovered hydrogen gas, and stated that there was a possibility that a substance having the properties of silicon, existed.
- // 1787Antoine was one of the four scientists who set down rules for naming chemical substances in a systematic way, in 1787. The other chemists were Antoine François de Fourcroy, L. B. Guyton de Morveau, and Claude-Louis Berthollet.
- // 1794In 1794, he was indicted for various crimes, including being a quisling of foreign scientists like Joseph Louis Lagrange, and was executed on May 8, along with twenty-seven other accused.
// Famous French peoples
Simone Signoret
Simone Signoret was a French actress who became the first French person to win an Academy Award. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to her life.
Jade Weber
Scroll down this bio to find out everything about French model Jade Weber. Be it fun facts, birthday, trivia or details of her personal and family life, you’ll find everything here.
Micheline Roquebrune
Micheline Roquebrune is a petite Moroccan-French painter best known as the third wife the legendary Scottish actor Sir Sean Connery. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Alex Lange
Alex Lange is a French-South African model, who is quite popular on Instagram. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Tina Kunakey
Tina Kunakey Di Vita is a model and wife of the French actor Vincent Cassel. Check out this biography to know about her birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about her.
Jeanne Calment
Jeanne Calment was a French supercentenarian who had the longest confirmed lifespan in human history. Check out this biography to know about her childhood, family, personal life, death, etc.
Antoine Lavoisier's FAQ
What is Antoine Lavoisier birthday?
Antoine Lavoisier was born at 1743-08-26
When was Antoine Lavoisier died?
Antoine Lavoisier was died at 1794-05-08
Where was Antoine Lavoisier died?
Antoine Lavoisier was died in Place de la Concorde
Which age was Antoine Lavoisier died?
Antoine Lavoisier was died at age 50
Where is Antoine Lavoisier's birth place?
Antoine Lavoisier was born in Paris
What is Antoine Lavoisier nationalities?
Antoine Lavoisier's nationalities is French
What is Antoine Lavoisier hobbies?
Antoine Lavoisier's hobbies is Meteorological observation, Botany, French politics, Chemistry
Who is Antoine Lavoisier spouses?
Antoine Lavoisier's spouses is Marie-Anne Paulze Lavoisier
What is Antoine Lavoisier's cause of dead?
Antoine Lavoisier dead because of Execution
What is Antoine Lavoisier's religion?
Antoine Lavoisier's religion is Catholicism
What is Antoine Lavoisier's sun sign?
Antoine Lavoisier is Virgo
How famous is Antoine Lavoisier?
Antoine Lavoisier is famouse as Chemist