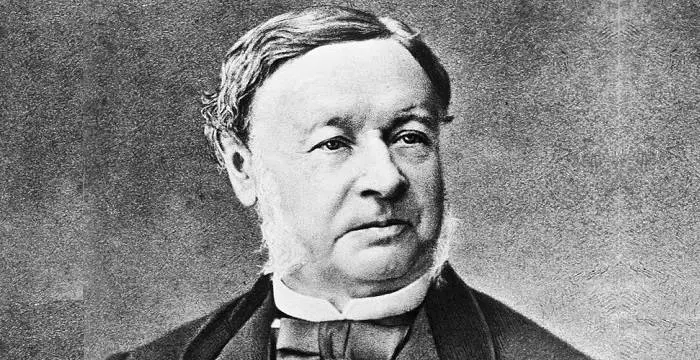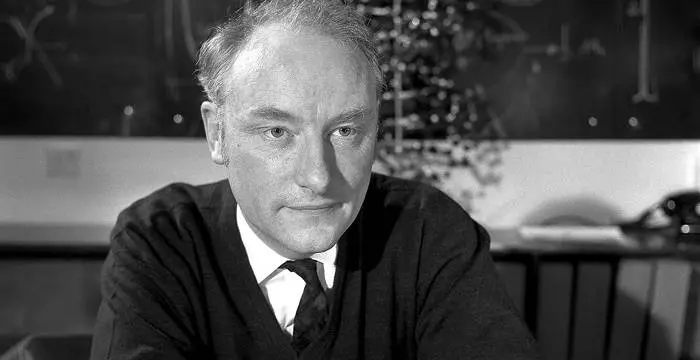Andrew Huxley - Physiologists, Facts and Childhood
Andrew Huxley's Personal Details
Sir Andrew Fielding Huxley was a British physiologist, biophysicist, mathematician and a mechanical wizard
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | November 22, 1917 |
| Died on | May 30, 2012 |
| Nationality | British |
| Famous | Trinity College, Cambridge, Scientists, Biophysicists, Physiologists, Physiologists |
| Spouses | Richenda Gammell |
| Known as | Sir Andrew Fielding Huxley |
| Childrens | Camilla, Clare, Eleanor, Henrietta, Janet, Stewart |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Birth Place | Hampstead, London, England |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Leonard Huxley |
| Mother | Rosalind Bruce |
| Sun Sign | Scorpio |
| Born in | Hampstead, London, England |
| Famous as | Physiologist & Biophysicist |
| Died at Age | 94 |
// Famous Physiologists
Alan Lloyd Hodgkin
Sir Alan Lloyd Hodgkin was an English biophysicist and a physiologist who received the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1963. This biography profiles his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
John James Rickard Macleod
John James Rickard Macleod was a Scottish biochemist and physiologist who is credited for the discovery of insulin. With this biography, explore in detail about his life, career, scientific research and timeline.
Emil Adolf von Behring
Emil Behring was a famous German physiologist who won the Nobel Prize for discovering an antitoxin for diphtheria. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
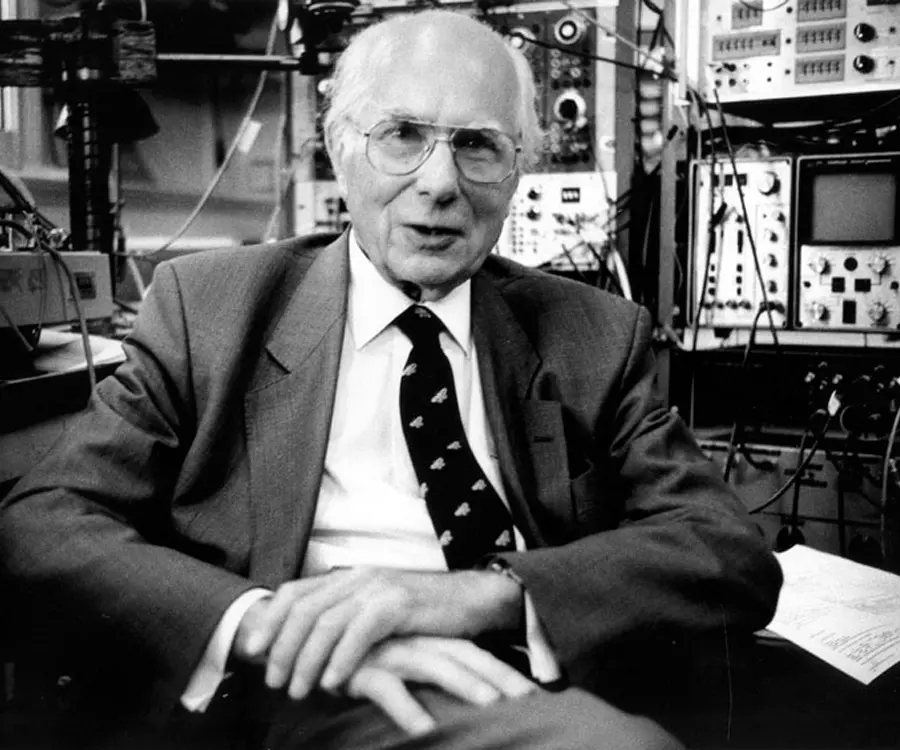
Andrew Huxley's photo
Who is Andrew Huxley?
Sir Andrew Fielding Huxley was a British physiologist, biophysicist, mathematician and mechanical wizard. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for showing how nerve cells produce electrical impulses to control the sensations of human body and all its activities. He shared this prize with Sir Alan Hodgkin who was a British scientist and his former teacher, and Sir John Eccles, an Australian biophysicist. The experiments carried out by Huxley and Hodgkin helped to explain the effect of anesthesia on the human body and the identification of many genetic diseases. Their work also helped in the design of prosthetic hands, arms, legs and feet. Huxley and Hodgkin explained how an electrical impulse travels from one end of the nerve cell to the other while Eccles described how the impulse was transferred from one cell to the adjacent one. They were able to solve an age old mystery where an Italian physicist made a dead frog’s leg twitch by touching it with electrical current. They used a nerve cell from a squid known as a ‘giant axion’ which is the largest nerve cell found in any type of living creature. They successfully inserted micro electrodes into the nerve cell and recorded the change in potential between the two ends when an electric current was passed through it.
// Famous Physiologists
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Wundt was a renowned doctor who conducted pioneering studies on experimental psychology. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Charles Best
Charles Best was a great scientist and a renowned physiologist who is remembered for being the co-discoverer of insulin. Read this biography to learn about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Sir Andrew Huxley was born in Hampstead, north London on November 22, 1917. His father, Leonard Huxley, was a writer and editor while his mother was Rosalind Bruce.
He was the younger of the two sons born to Leonard and Rosalind. His elder brother was David.
Julian Huxley, a scientist on animal behavior, and the novelist Aldous Huxley were his half-brothers from his father’s first marriage.
Both his half-brothers were older than him and had very little influence on his work. When Andrew was born, Aldous was 23-year-old and Julian was 30.
His parents had presented him a lathe when he was 14 as he was technically quite proficient from a young age. He kept the lathe intact and used it to build a large number of equipment for his experiments later.
After his father died when he was 15, his mother encouraged him to study physics as he had a talent for all mechanical things.
He did his initial schooling at the ‘University College School’ from 1925 to 1930 and then at the ‘Westminster School’ from 1930 to 1935. He won a scholarship for higher studies from here.
He joined the ‘Trinity College’ under the Cambridge University to study engineering and physics in 1935 but changed over to physiology which he had taken as an elective subject.
He studied anatomy from 1937 to 1938 hoping to qualify in medicine.
He received his bachelor’s degree in physiology in 1938 and his master’s degree in 1945.
Career
In the summer of 1939 he started working with Professor Alan Hodgkin on squid axon at the ‘Marine Biological Laboratory in Plymouth, England.
When the Second World War broke out in September 1939 with the German invasion of Poland, he had to abandon his experiments and join the war effort.
He was recruited by the ‘British Anti-Aircraft Command’ to work on the development of radar that would be able to control antiaircraft guns.
Later he was transferred to the Admiralty where he did the same work for anti-aircraft guns mounted on warships. He helped Hodgkin design a new gun-sight during this period.
In 1946, after the war had ended, he resumed his research with Professor Alan Hodgkin and carried out a teaching job at the ‘Department of Physiology’ even though he had been awarded a research fellowship by the ‘Trinity College’ in 1941.
He carried out his research work with Hodgkin from 1946 to 1951.
Huxley and Hodgkin published their findings in 1952.
His later researches from 1952 onwards were on the conduction of electric current in muscles.
From 1950 to 1957 he acted as the editor for the ‘Journal of Physiology’ and the ‘Journal of Molecular Biology’.
In 1953 he worked at the ‘Woods Hole’ in Massachusetts, USA.
In 1959 he gave lectures at the ‘John Hopkins Medical School’
He was appointed as professor and head of the department of physiology at the ‘University College’ in London in 1960 after being selected as a ‘Jordell Professor’. He remained in that post till 1983.
In 1961 he took part in an exchange scheme involving Russian and British professors and gave lectures on Neurophysiology at the Kiev University’.
In 1964 he gave lectures at the ‘Columbia University’.
In 1969 he got an appointment at the ‘Department of Physiology’ at the ‘University College London’ as a ‘Royal Society Research Professor’.
He was the President of the ‘British Association for the Advancement of Science’ from 1976 to 1977.
In 1983 he defended the decision made by the ‘Royal Society’ to elect Margaret Thatcher as a fellow against the opposition of 44 who protested against it.
He was made the master of the Trinity College in 1984 and held the post up to 1990.
He served as the President of the ‘Royal Society’ from 1980 to 1985.
He was the President of the ‘International Union of Physiological Sciences’ from 1986 to 1993.
Awards & Achievements
Sir Andrew Huxley was named a ‘Fellow of the Royal Society’ in 1955.
He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1963.
He was honored with the knighthood in 1974.
He was awarded with an ‘Order of Merit’ in 1983.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married Jocelyn Richenda Gammell Pease in 1947 and had a son, Stewart, and five daughters, Janet, Camilla, Eleanor, Henrietta and Clare from the marriage.
Sir Andrew Huxley died of cancer on May 30, 2012.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Andrew Huxley's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Knight Bachelor (1974) | |
| 0 | Order of Merit (1983) | |
| 0 | FRS (1955) | |
| 0 | Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1963) | |
| 0 | Copley Medal (1973) | |
Andrew Huxley biography timelines
- // 22nd Nov 1917Sir Andrew Huxley was born in Hampstead, north London on November 22, 1917. His father, Leonard Huxley, was a writer and editor while his mother was Rosalind Bruce.
- // 1935He joined the ‘Trinity College’ under the Cambridge University to study engineering and physics in 1935 but changed over to physiology which he had taken as an elective subject.
- // 1937 To 1938He studied anatomy from 1937 to 1938 hoping to qualify in medicine.
- // 1938 To 1945He received his bachelor’s degree in physiology in 1938 and his master’s degree in 1945.
- // 1939In the summer of 1939 he started working with Professor Alan Hodgkin on squid axon at the ‘Marine Biological Laboratory in Plymouth, England.
- // Sep 1939When the Second World War broke out in September 1939 with the German invasion of Poland, he had to abandon his experiments and join the war effort.
- // 1941 To 1946In 1946, after the war had ended, he resumed his research with Professor Alan Hodgkin and carried out a teaching job at the ‘Department of Physiology’ even though he had been awarded a research fellowship by the ‘Trinity College’ in 1941.
- // 1946 To 1951He carried out his research work with Hodgkin from 1946 to 1951.
- // 1947He married Jocelyn Richenda Gammell Pease in 1947 and had a son, Stewart, and five daughters, Janet, Camilla, Eleanor, Henrietta and Clare from the marriage.
- // 1950 To 1957From 1950 to 1957 he acted as the editor for the ‘Journal of Physiology’ and the ‘Journal of Molecular Biology’.
- // 1952Huxley and Hodgkin published their findings in 1952.
- // 1952His later researches from 1952 onwards were on the conduction of electric current in muscles.
- // 1953In 1953 he worked at the ‘Woods Hole’ in Massachusetts, USA.
- // 1955Sir Andrew Huxley was named a ‘Fellow of the Royal Society’ in 1955.
- // 1959In 1959 he gave lectures at the ‘John Hopkins Medical School’
- // 1960 To 1983He was appointed as professor and head of the department of physiology at the ‘University College’ in London in 1960 after being selected as a ‘Jordell Professor’. He remained in that post till 1983.
- // 1961In 1961 he took part in an exchange scheme involving Russian and British professors and gave lectures on Neurophysiology at the Kiev University’.
- // 1963He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1963.
- // 1964In 1964 he gave lectures at the ‘Columbia University’.
- // 1969In 1969 he got an appointment at the ‘Department of Physiology’ at the ‘University College London’ as a ‘Royal Society Research Professor’.
- // 1974He was honored with the knighthood in 1974.
- // 1976 To 1977He was the President of the ‘British Association for the Advancement of Science’ from 1976 to 1977.
- // 1980 To 1985He served as the President of the ‘Royal Society’ from 1980 to 1985.
- // 1983In 1983 he defended the decision made by the ‘Royal Society’ to elect Margaret Thatcher as a fellow against the opposition of 44 who protested against it.
- // 1983He was awarded with an ‘Order of Merit’ in 1983.
- // 1984 To 1990He was made the master of the Trinity College in 1984 and held the post up to 1990.
- // 1986 To 1993He was the President of the ‘International Union of Physiological Sciences’ from 1986 to 1993.
- // 30th May 2012Sir Andrew Huxley died of cancer on May 30, 2012.
// Famous Biophysicists
James Watson
James Watson is an American molecular biologist and geneticist who played a crucial role in the discovery of the molecular structure of D.N.A. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline
Francis Crick
Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist and neuroscientist, who received the Nobel Prize for Medicine. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements and timeline.
Alan Lloyd Hodgkin
Sir Alan Lloyd Hodgkin was an English biophysicist and a physiologist who received the Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1963. This biography profiles his childhood, life, research, achievements and timeline.
Archibald Hill
Archibald Vivian Hill was a Nobel Laureate English physiologist who is credited for discovering the production of heat in muscles. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Sir Bernard Katz
Sir Bernard Katz was a German born biophysicist who is known for his remarkable work on nerve biochemistry. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Jagadish Chandra Bose
Jagadish Chandra Bose was a polymath, physicist, botanist and considered to be one of the fathers of radio science. This biography of Jagadish Chandra Bose provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Andrew Huxley's FAQ
What is Andrew Huxley birthday?
Andrew Huxley was born at 1917-11-22
When was Andrew Huxley died?
Andrew Huxley was died at 2012-05-30
Where was Andrew Huxley died?
Andrew Huxley was died in Cambridge, Cambridgeshire, England
Which age was Andrew Huxley died?
Andrew Huxley was died at age 94
Where is Andrew Huxley's birth place?
Andrew Huxley was born in Hampstead, London, England
What is Andrew Huxley nationalities?
Andrew Huxley's nationalities is British
Who is Andrew Huxley spouses?
Andrew Huxley's spouses is Richenda Gammell
Who is Andrew Huxley childrens?
Andrew Huxley's childrens is Camilla, Clare, Eleanor, Henrietta, Janet, Stewart
What was Andrew Huxley universities?
Andrew Huxley studied at Trinity College, Cambridge
What was Andrew Huxley notable alumnis?
Andrew Huxley's notable alumnis is Trinity College, Cambridge
Who is Andrew Huxley's father?
Andrew Huxley's father is Leonard Huxley
Who is Andrew Huxley's mother?
Andrew Huxley's mother is Rosalind Bruce
What is Andrew Huxley's sun sign?
Andrew Huxley is Scorpio
How famous is Andrew Huxley?
Andrew Huxley is famouse as Physiologist & Biophysicist