Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar - Father of Research Laboratories, Timeline and Personal Life
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's Personal Details
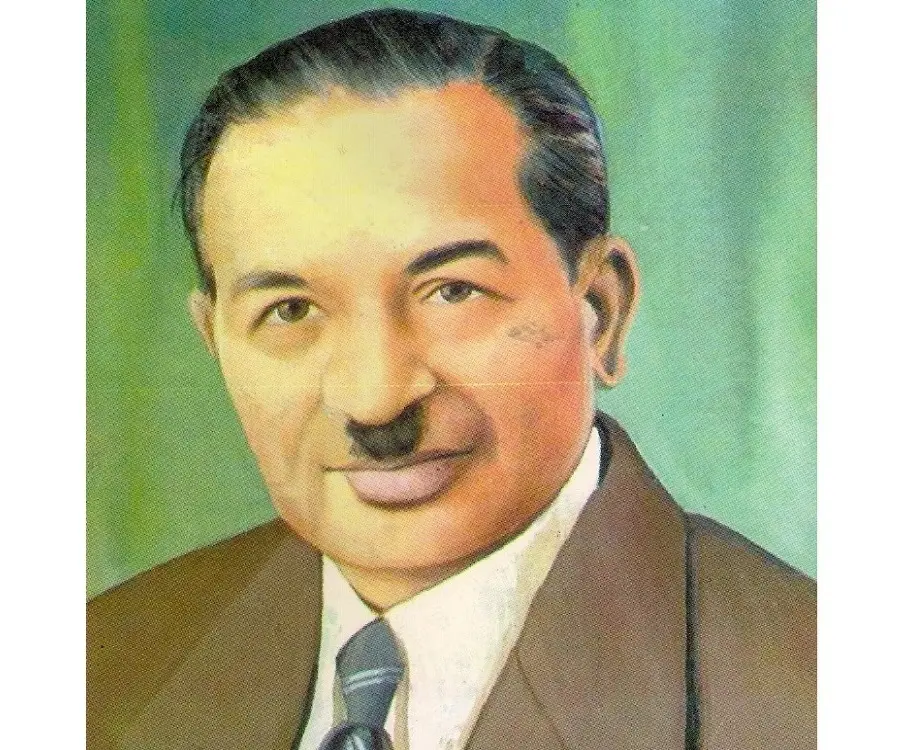
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was an Indian scientist, famously dubbed as the ‘Father of research laboratories’
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | February 21, 1894 |
| Died on | January 1, 1955 |
| Nationality | Indian |
| Famous | University College London, Scientists, Chemists, Physical Chemists, Father of Research Laboratories |
| Spouses | Lajwanti |
| Known as | Sir Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar |
| Universities |
|
| Notable Alumnis |
|
| Founder / Co-Founder |
|
| Birth Place | Bhera |
| Religion | Hinduism |
| Gender | Male |
| Father | Parmeshwari Sahai Bhatnagar |
| Sun Sign | Pisces |
| Born in | Bhera |
| Famous as | Father of research laboratories |
| Died at Age | 60 |
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's photo
Who is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was an Indian scientist, famously dubbed as the ‘Father of research laboratories’. He was the first director-general of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and a professor of chemistry for over 19 years. If chemical industry is an important part of Indian economy, a lot of its credit goes to this pioneer for his sincere efforts and conviction. Though his areas of interest included emulsions, colloids, and industrial chemistry, but his primary contributions were in the spheres of magnetochemistry. He also made a melodious “kulgeet” i.e. University song for Banaras Hindu University, which is still sung with great pride before any function in the University. During his college years, he also wrote an Urdu play for which he was awarded a prize and a medal. He was, in a way, a bridge between two cultures and two eras. He greeted science with a mission and also valued literature as much as he loved science and engineering. Under his directorship, twelve laboratories were established all over the country for scientific research in multiple areas, including the ones for food processing, metallurgy and chemical research. He could be perfectly described as a unique persona, an exceptional amalgamation of science, engineering and literature.
// Famous Physical Chemists
Willard Libby
Willard Frank Libby was an American physical chemist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Prize’ in Chemistry in 1960. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, research, achievements and timeline.
Ilya Prigogine
Ilya Prigogine was a Russian-born Belgian physical chemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1977. This biography of Ilya Prigogine provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Fritz Haber
Fritz Haber was a German chemist who won the 1918 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the synthesis of ammonia from its elements. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
He was born on February 21, 1894 in Bhera, Shahpur District, British India to Parmeshwari Sahai Bhatnagar, a school master, and his wife.
When his father died, his mother returned to her father’s house in Sikandarabad, U.P where he spent most of his childhood.
His maternal grandfather was an engineer and gradually he also developed an interest in science and engineering. He was also drawn towards poetry through various literary works he encountered in his grandfather’s house.
He received his early education from the DAV High School, Sikandarabad. Then, he attended the Dayal Singh College, Lahore and became an active member of Saraswati Stage Society.
In 1913, he cleared the Intermediate Examination of the Punjab University in first class. Then he got enrolled in the Forman Christian College and completed graduation with major in physics in 1916, and MSc in chemistry in 1919.
After completing his masters, he was awarded a scholarship by the Dayal Singh College Trust to study abroad and he left for England. In 1921, he earned his D.Sc. degree from the London University under the guidance of chemistry professor Frederick G. Donnan.
Career
In 1921, after his return to India, he joined Banaras Hindu University (BHU) as a professor of chemistry. He served at BHU for the next three years and also wrote the University song ‘Kulgeet’ for BHU.
Later, he moved to the University of the Punjab, Lahore where he was appointed the Professor of Physical Chemistry and Director of University Chemical Laboratories. It was the most active period of his scientific career.
He became involved in solving industrial problems of different organizations such as Delhi Cloth Mills, J.K. Mills Ltd. of Kanpur, Ganesh Flour Mills Ltd. of Layallapur, Tata Oil Mills Ltd. of Bombay, and Steel Brothers & Co. Ltd. of London.
In 1940, the Board of Scientific and Industrial Research (BSIR) was formed for a period of two years and he was appointed as its Director. In 1941, he persuaded the government to set up an Industrial Research Utilisation Committee (IRUC) for further investment into industrial research.
In 1942, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) was formed and the BSIR and IRUC became its advisory bodies. In 1943, CSIR approved his proposal to establish five national laboratories.
Post-independence, he was made the chairman of the CSIR and he became the first director general of the council. He established many laboratories and mentored many great minds during his tenure as the head of the CSIR.
He was appointed as the Secretary of the Ministry of Education and Educational Adviser to government. He played a significant role both in the constitution and deliberations of the Scientific Manpower Committee Report of 1948.
He was also instrumental in the establishment of the National Research Development Corporation (NRDC) of India and for the initiation of the Industrial Research Association movement in the country.
Major Works
His major innovation was improving the procedure for drilling crude oil.
His research contributions in the areas of magnetochemistry and physical chemistry of emulsion were widely recognized. He also did considerable work in applied chemistry.
He is largely celebrated for establishing various chemical laboratories in India such as Central Food Processing Technological Institute, Mysore; National Chemical Laboratory, Pune; the National Physical Laboratory, New Delhi; the National Metallurgical Laboratory, Jamshedpur and the Central Fuel Institute, Dhanbad.
Awards & Achievements
In 1936 New Year Honors List, he was appointed an Officer of the Order of the British Empire for his excellent contributions to pure and applied chemistry.
In 1941, he was knighted by the British government for his contributions to science.
In 1943, he was elected a member of Royal Society of the United Kingdom.
In 1954, he was honored with the Padma Bhushan, the third highest civilian award in the Republic of India.
The ‘Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology’, named in his honor, is awarded to outstanding scientists who made significant contributions in various branches of science since 1958.
Personal Life & Legacy
He was married to Lajwanti who died in 1946.
He died of a heart attack on January 1, 1955 in New Delhi, India.
Trivia
He was the first Chairman of the University Grants Commission.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's awards
| Year | Name | Award |
|---|---|---|
Other | ||
| 0 | Padma Bhushan (1954) | |
| 0 | Knighthood (1941) | |
| 0 | OBE (1936) | |
| 0 | Fellow of the Royal Society (1943) | |
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar biography timelines
- // 21st Feb 1894He was born on February 21, 1894 in Bhera, Shahpur District, British India to Parmeshwari Sahai Bhatnagar, a school master, and his wife.
- // 1913 To 1919In 1913, he cleared the Intermediate Examination of the Punjab University in first class. Then he got enrolled in the Forman Christian College and completed graduation with major in physics in 1916, and MSc in chemistry in 1919.
- // 1921After completing his masters, he was awarded a scholarship by the Dayal Singh College Trust to study abroad and he left for England. In 1921, he earned his D.Sc. degree from the London University under the guidance of chemistry professor Frederick G. Donnan.
- // 1921In 1921, after his return to India, he joined Banaras Hindu University (BHU) as a professor of chemistry. He served at BHU for the next three years and also wrote the University song ‘Kulgeet’ for BHU.
- // 1936In 1936 New Year Honors List, he was appointed an Officer of the Order of the British Empire for his excellent contributions to pure and applied chemistry.
- // 1940 To 1941In 1940, the Board of Scientific and Industrial Research (BSIR) was formed for a period of two years and he was appointed as its Director. In 1941, he persuaded the government to set up an Industrial Research Utilisation Committee (IRUC) for further investment into industrial research.
- // 1941In 1941, he was knighted by the British government for his contributions to science.
- // 1942In 1942, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) was formed and the BSIR and IRUC became its advisory bodies. In 1943, CSIR approved his proposal to establish five national laboratories.
- // 1943In 1943, he was elected a member of Royal Society of the United Kingdom.
- // 1946He was married to Lajwanti who died in 1946.
- // 1948He was appointed as the Secretary of the Ministry of Education and Educational Adviser to government. He played a significant role both in the constitution and deliberations of the Scientific Manpower Committee Report of 1948.
- // 1954In 1954, he was honored with the Padma Bhushan, the third highest civilian award in the Republic of India.
- // 1st Jan 1955He died of a heart attack on January 1, 1955 in New Delhi, India.
- // 1958The ‘Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology’, named in his honor, is awarded to outstanding scientists who made significant contributions in various branches of science since 1958.
// Famous University College London
Pietro Boselli
Pietro Boselli is an Italian model, engineer, teacher, and fitness athlete who became famous as the ‘world’s sexiest math teacher’. Check out this biography to know about his birthday, childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
David Attenborough
Sir David Attenborough is an English broadcaster and naturalist. This biography offers detailed information about his childhood, life, works, achievements, trivia and timeline.
Robert Browning
Robert Browning was a famous English poet and playwright. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and other facts about his life.
Mulk Raj Anand
Mulk Raj Anand was one of the first Indian writers in English to gain international fame. This biography of Mulk Raj Anand provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Joseph Lister
Joseph Lister was a British surgeon who was the founder of antiseptic medicine. This biography of Joseph Lister provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Adrian Smith
Adrian Smith is an English guitarist, who has played for various bands. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, life, music career, achievements, works & timeline.
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's FAQ
What is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar birthday?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was born at 1894-02-21
When was Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar died?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was died at 1955-01-01
Where was Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar died?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was died in New Delhi
Which age was Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar died?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was died at age 60
Where is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's birth place?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was born in Bhera
What is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar nationalities?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's nationalities is Indian
Who is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar spouses?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's spouses is Lajwanti
What was Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar universities?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar studied at University College London, University of London, University of the Punjab, University College London, Banaras Hindu University
What was Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar notable alumnis?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's notable alumnis is University College London
Which company or organization was founded by Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar was the founder/co-founder of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research
What is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's religion?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's religion is Hinduism
Who is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's father?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's father is Parmeshwari Sahai Bhatnagar
What is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar's sun sign?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar is Pisces
How famous is Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar?
Shanti Swaroop Bhatnagar is famouse as Father of research laboratories













