Albrecht von Haller - Anatomist, Family and Childhood
Albrecht von Haller's Personal Details
Albrecht von Haller was a renowned botanist of the 18th century and also regarded as the Father of modern physiology
| Information | Detail |
|---|---|
| Birthday | October 16, 1708 |
| Died on | December 12, 1777 |
| Nationality | Swiss |
| Famous | Child Prodigies, Scientists, Botanists, Physiologists, Anatomist |
| Known as | Victor Albrecht von Haller |
| Universities |
|
| Birth Place | Bern |
| Gender | Male |
| Sun Sign | Libra |
| Born in | Bern |
| Famous as | Anatomist |
| Died at Age | 69 |
// Famous Anatomist
Henry Gray
Henry Gray was an English anatomist, who authored the famous book ‘Gray’s Anatomy’. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and other facts related to his life.
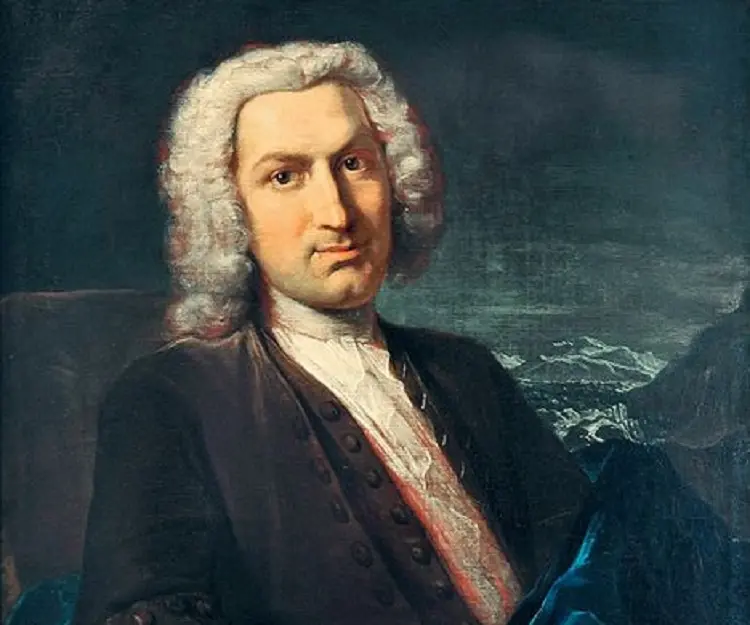
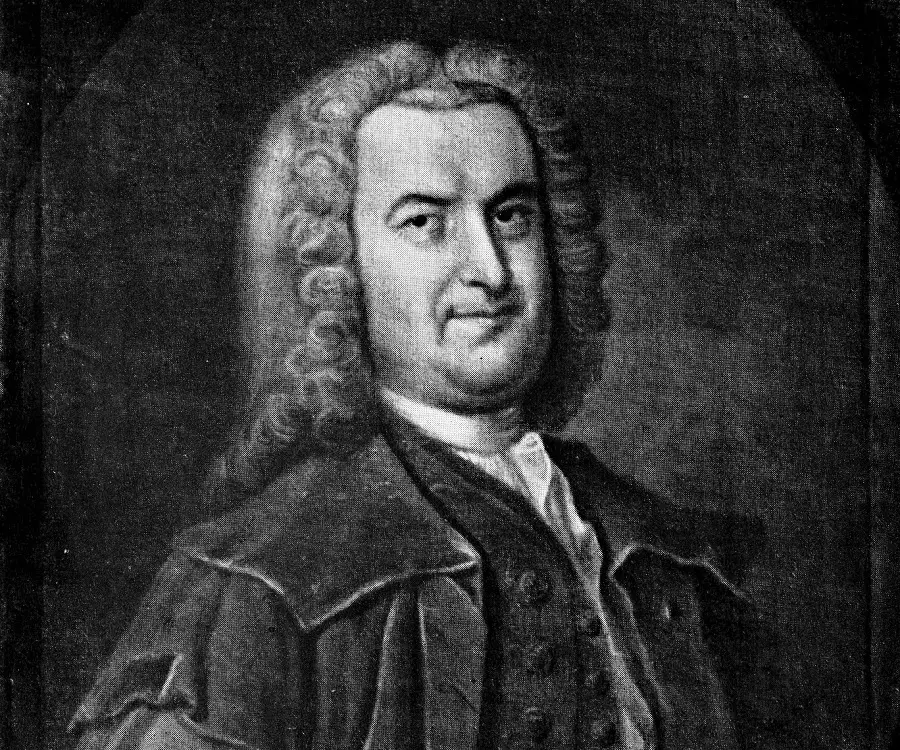
Albrecht von Haller's photo
Who is Albrecht von Haller?
Among the various contributions he has made to the world, Albrecht von Haller is most renowned for his observations related to the nervous system and respiratory process. He did not belong to a well-to-do family and even lost his parents at an early age. However, he had an innate understanding of languages and in his childhood he made a compilation of several biographies. He later decided to pursue a career as a physician and travelled to several places gaining knowledge on medicine from different exponents in the profession. One of his mentors was the renowned physician Herman Boerhaave who guided him during his days at the university. He also cultivated an interest in the subject of botany and starting from collection of different species of flowers, he went on to be a renowned botanist of the eighteenth century. He also had a knack for poetry and even when he carried on his research works in botany, he penned much poetry revolving around diverse themes. He was one among the superlative anatomists that the world had known, and is credited with heralding the era of modern day neurology and physiology. One of the most prominent observations made by him was the autonomous function of the heart. Read on to know about other valuable contributions which Haller has made to natural science.
// Famous Botanists
Carl Linnaeus
Carolus Linnaeus was a renowned Swedish biologist popularly known as the ‘Father of Modern Taxonomy’ who founded the binomial nomenclature. Read on to know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline
Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin was one of the most influential figures in human history. Go through this biography to get details about his life, profile and timeline.
Birbal Sahni
Birbal Sahni was an Indian palaeobotanist who founded the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeobotany in Lucknow. This biography of Birbal Sahni provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Childhood & Early Life
Albrecht von Haller was born to Niklaus Emanuel Haller and Anna Maria Engel, on 16th October, 1708, in Bern, Switzerland. He had five siblings and after the death of his mother, his father remarried Salome Neuhaus.
He was initially taught by a former pastor and later attended a school in Bern. Albrecht frequently suffered from illness and as a result could not participate in outdoor activities much. He developed an interest for languages and had innate talent in the discipline, and dabbled with languages such as Hebrew, Greek and Chaldee.
He had also created a compilation of about two thousand biographies of notable historical figure, in his early childhood.
During the time 1722-23, he stayed at his step-uncle’s house in Beil. His uncle Johann Rudolf Neuhaus was a physician and gave Albrecht lessons in philosophy, and various other subjects. However, he was not interested in philosophy, and determined to embark on a career as a physician. He also wrote poetry during the same time.
In December 1723, he enrolled at the ‘University of Tübingen’ where he studied medicine under the tutelage of Johann Duvernoy and Elias Rudolph Camerarius Jr.
In 1725, he joined the ‘Leiden University’ and had the opportunity to be under the guidance of renowned and remarkable people like Boerhaave and Albinus.
In 1727, he completed his graduation from the university by defending his thesis before a reviewing academic committee, that the salivary duct was only a blood-vessel and nothing else.
He travelled to London, where he was introduced to physicians and scientists such as James Douglas, Sir Hans Sloane, John Prijgle and William Chesselden among many other notable scientists.
He then went to Paris and pursued studies with Jacob Winslow and Henri François Le Dran as his teachers.
He moved to Basel in 1728, and carried on further studies under the tutelage of John Bernoulli in mathematics. Albrecht was drawn towards the subject of botany during this time and while he travelled through places like Baden, Savoy and some of the Cantons of Switzerland, he collected different plant species which later became the elementary part of his work involving flora of Switzerland.
Career
Von Haller was also engaged in literary pursuits during the same time and penned the poem ‘Die Alpen’ in 1729, which was based on his journey through the mountainous region of Alps. The same year, he travelled back to Bern and was engaged in the profession of a physician in the city.
In 1732, his book ‘Gedichte’ was published and the poem ‘Die Alpen’ was first printed in this book.
In 1736, he moved to Germany and joined the ‘University of Göttingen’ as the chairperson of the botany, medicine, surgery and anatomy department of the institute.
In 1743, this eminent physician was made a Fellow of the Royal Society. During his stay at Göttingen, he was included in the cantonal council of Bern.
Albrecht was inducted into the ‘Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences’ in 1747 as a foreign member, and two years later, he was promoted to a noble rank.
In 1753, he resigned from his post of chairman at the ‘University of Göttingen’ and relocated to his hometown Bern. There he was elected to the office of Rathausammann, and was engaged in political affairs of the region. During the same time he also carried on his botanical research work as well as penned poetry.
In 1755, his book ‘Onomatologia medica completa’ was published which was co-written by Johann Peter Eberhard.
He penned the book ‘Historia stirpium indigenarum Helvetiae inchoata’ in 1768, and this was followed by the publication of his book ‘Ode sur les Alpes’.
In between 1771-72, he inked his work on botany named ‘Bibliotheca botanica’ and his researches and observations mentioned in this book, hold good till date.
During the period 1771-74, the philosophical works which he wrote include ‘Usong’, Alfred’ and ‘Fabius and Cato’, and in these he discusses despotism, aristocratic republican and limited monarchy.
His book ‘Bibliotheca anatomica qua scripta ad anatomen et physiologiam’, which appeared in two volumes was published between the years 1774-77.
Major Works
This anatomist has made many contributions to the world but one of his most important works is his observation of the activities of the muscle as well as the nervous system. These observations by this learned physiologist, led to the foundation of modern day neurology.
Haller is also credited with observing and understanding the respiratory process and the independent functioning of the heart.
Personal Life & Legacy
He married thrice and was the father of eight children. Two of his sons named Gottlieb Emanuel and Albrecht, also embarked on a career as a botanist.
By 1773, his health started deteriorating and he took to opium in order to relieve himself of suffering. The use of this drug, apparently, brought him an early death than his illness.
On 12th December, 1777, this exceptional anatomist breathed his last in Bern. His works ‘Materia medica oder Geschichte der Arzneyen des Pflanzenreichs’ and ‘Histoire des Plantes suisses ou Matiere médicale et de l'Usage économique des Plantes par M. Alb. de Haller ... Traduit du Latin’ were published posthumously.
Trivia
The botanist Carl Linnaeus has named a shrub as ‘Halleria’ in the honour of Albrecht von Haller.
// Famous Physiologists
Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann was a German physiologist who discovered the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. This biography of Theodor Schwann provides detailed information about his childhood, life, achievements, works & timeline.
Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Wundt was a renowned doctor who conducted pioneering studies on experimental psychology. To know more about his childhood, career, profile and timeline read on
Charles Best
Charles Best was a great scientist and a renowned physiologist who is remembered for being the co-discoverer of insulin. Read this biography to learn about his profile, childhood, life and timeline.
Albrecht von Haller biography timelines
- // 16th Oct 1708Albrecht von Haller was born to Niklaus Emanuel Haller and Anna Maria Engel, on 16th October, 1708, in Bern, Switzerland. He had five siblings and after the death of his mother, his father remarried Salome Neuhaus.
- // 1722 To 1723During the time 1722-23, he stayed at his step-uncle’s house in Beil. His uncle Johann Rudolf Neuhaus was a physician and gave Albrecht lessons in philosophy, and various other subjects. However, he was not interested in philosophy, and determined to embark on a career as a physician. He also wrote poetry during the same time.
- // Dec 1723In December 1723, he enrolled at the ‘University of Tübingen’ where he studied medicine under the tutelage of Johann Duvernoy and Elias Rudolph Camerarius Jr.
- // 1725In 1725, he joined the ‘Leiden University’ and had the opportunity to be under the guidance of renowned and remarkable people like Boerhaave and Albinus.
- // 1727In 1727, he completed his graduation from the university by defending his thesis before a reviewing academic committee, that the salivary duct was only a blood-vessel and nothing else.
- // 1728He moved to Basel in 1728, and carried on further studies under the tutelage of John Bernoulli in mathematics. Albrecht was drawn towards the subject of botany during this time and while he travelled through places like Baden, Savoy and some of the Cantons of Switzerland, he collected different plant species which later became the elementary part of his work involving flora of Switzerland.
- // 1729Von Haller was also engaged in literary pursuits during the same time and penned the poem ‘Die Alpen’ in 1729, which was based on his journey through the mountainous region of Alps. The same year, he travelled back to Bern and was engaged in the profession of a physician in the city.
- // 1732In 1732, his book ‘Gedichte’ was published and the poem ‘Die Alpen’ was first printed in this book.
- // 1736In 1736, he moved to Germany and joined the ‘University of Göttingen’ as the chairperson of the botany, medicine, surgery and anatomy department of the institute.
- // 1743In 1743, this eminent physician was made a Fellow of the Royal Society. During his stay at Göttingen, he was included in the cantonal council of Bern.
- // 1747Albrecht was inducted into the ‘Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences’ in 1747 as a foreign member, and two years later, he was promoted to a noble rank.
- // 1753In 1753, he resigned from his post of chairman at the ‘University of Göttingen’ and relocated to his hometown Bern. There he was elected to the office of Rathausammann, and was engaged in political affairs of the region. During the same time he also carried on his botanical research work as well as penned poetry.
- // 1755In 1755, his book ‘Onomatologia medica completa’ was published which was co-written by Johann Peter Eberhard.
- // 1768He penned the book ‘Historia stirpium indigenarum Helvetiae inchoata’ in 1768, and this was followed by the publication of his book ‘Ode sur les Alpes’.
- // 1771 To 1772In between 1771-72, he inked his work on botany named ‘Bibliotheca botanica’ and his researches and observations mentioned in this book, hold good till date.
- // 1771 To 1774During the period 1771-74, the philosophical works which he wrote include ‘Usong’, Alfred’ and ‘Fabius and Cato’, and in these he discusses despotism, aristocratic republican and limited monarchy.
- // 1773By 1773, his health started deteriorating and he took to opium in order to relieve himself of suffering. The use of this drug, apparently, brought him an early death than his illness.
- // 1774 To 1777His book ‘Bibliotheca anatomica qua scripta ad anatomen et physiologiam’, which appeared in two volumes was published between the years 1774-77.
- // 12th Dec 1777On 12th December, 1777, this exceptional anatomist breathed his last in Bern. His works ‘Materia medica oder Geschichte der Arzneyen des Pflanzenreichs’ and ‘Histoire des Plantes suisses ou Matiere médicale et de l'Usage économique des Plantes par M. Alb. de Haller ... Traduit du Latin’ were published posthumously.
// Famous Scientists
Juliane Koepcke
Juliane Koepcke is a German-Peruvian biologist, who was the lone survivor among the 92 passengers and crew of the ill-fated LANSA Flight 508 that crashed in the Peruvian rainforest on 24 December 1971. Know more about her life in this biography.
Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish was a theoretical chemist and physicist, renowned for discovery of hydrogen and calculation of the mass of earth. To know more about his childhood, profile, timeline and career read on
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky was a Russian rocket scientist and a pioneer of astronautics. This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, achievements, etc.
Gabe Newell
Gabe Newell is an American computer programmer and businessman, best known as the co-founder of ‘Valve Corporation.’ This biography provides detailed information about his childhood, family, personal life, career, etc.
Grigori Perelman
Grigori Perelman is a Russian mathematician who is best known for his contributions to Riemannian geometry and geometric topology. Check out this biography to know about his childhood, family life, achievements and fun facts about him.
Eduardo Saverin
Eduardo Luiz Saverin is a Brazilian internet entrepreneur and investor. This biography profiles his childhood, life, career, achievements, and timeline
Albrecht von Haller's FAQ
What is Albrecht von Haller birthday?
Albrecht von Haller was born at 1708-10-16
When was Albrecht von Haller died?
Albrecht von Haller was died at 1777-12-12
Where was Albrecht von Haller died?
Albrecht von Haller was died in Bern
Which age was Albrecht von Haller died?
Albrecht von Haller was died at age 69
Where is Albrecht von Haller's birth place?
Albrecht von Haller was born in Bern
What is Albrecht von Haller nationalities?
Albrecht von Haller's nationalities is Swiss
What was Albrecht von Haller universities?
Albrecht von Haller studied at University of Tübingen, Leiden University
What is Albrecht von Haller's sun sign?
Albrecht von Haller is Libra
How famous is Albrecht von Haller?
Albrecht von Haller is famouse as Anatomist