A research team has developed a high-performance AI semiconductor device using indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO), an oxide semiconductor widely used in OLED displays. The new device has proven to be excellent in terms of performance and power efficiency. The researchers used the newly developed synaptic device to train and classify handwritten data, achieving a high accuracy of over 98%, verifying its potential application in high-accuracy AI systems in the future. They also utilized the ultra-thin film insulators inside the transistors to control the current, making them suitable for large-scale AI. Linear and symmetrical programming characteristics were obtained through a new structure using two transistors as one synaptic device. The successful development and application of this new AI semiconductor technology using IGZO materials shows great potential to improve the efficiency and accuracy of AI.
AI “Brain” Developed from Core Materials for OLED TVs
A joint research team from POSTECH has developed semiconductor devices for high-performance AI operations by applying indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) materials widely used in OLED displays. The team, led by Professor Yoonyoung Chung, Professor Seyoung Kim, and Ph.D. candidate Seongmin Park, sought IGZO as a key material for AI computations that could be mass-produced and provide uniformity, durability, and computing accuracy.
Traditional digital computer systems’ von Neumann architecture separates the storage and computation of information, resulting in increased power consumption and significant delays in AI computations. This issue is resolved with efficient AI operations, such as those of ChatGPT, which require computations to occur within the memory responsible for storing information.
Previous AI semiconductor technologies were limited in meeting all the requirements, such as linear and symmetric programming and uniformity, to improve AI accuracy. The new IGZO-based semiconductor device developed by the POSTECH team has proven to be excellent in terms of performance and power efficiency.
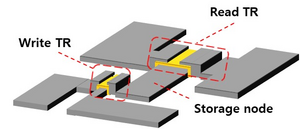
IGZO comprises four atoms in a fixed ratio of indium, gallium, zinc, and oxygen and has excellent electron mobility and leakage current properties, which have made it a backplane of the OLED display. The proposed AI synaptic device features two oxide semiconductor transistors, one for writing and the other for reading. The research team’s new semiconductor technology for AI applications utilizes IGZO materials to address the challenge of increased power consumption and significant delays in AI computations due to von Neumann architecture.
This breakthrough in AI technology has implications for various tasks, including paper writing, translation, coding, and more, all through question-and-answer-based interactions. The AI system relies on deep learning, which requires extensive training to minimize errors, resulting in frequent data transfers between memory and processors. The POSTECH team’s IGZO-based semiconductor technology for AI operations offers a promising solution to optimize performance and power efficiency for AI computations.
Researchers Develop Novel Synapse Device for High-Performance AI
A research team has developed a novel synapse device composed of two transistors interconnected through a storage node using indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) materials. The researchers utilized the ultra-thin film insulators inside the transistors to control the current, making them suitable for large-scale AI. The precise control of the charging and discharging speed of the storage node has enabled the AI semiconductor to meet the diverse performance metrics required for high-level performance.
The researchers achieved a high accuracy of over 98% when training and classifying handwritten data using the newly developed synaptic device, verifying its potential application in high-accuracy AI systems in the future.
Professor Chung explained that the successful development and application of this new AI semiconductor technology using IGZO materials shows great potential to improve the efficiency and accuracy of AI. The study was published last week on the inside back cover of Advanced Electronic Materials and was supported by the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea.
Don’t miss interesting posts on Famousbio