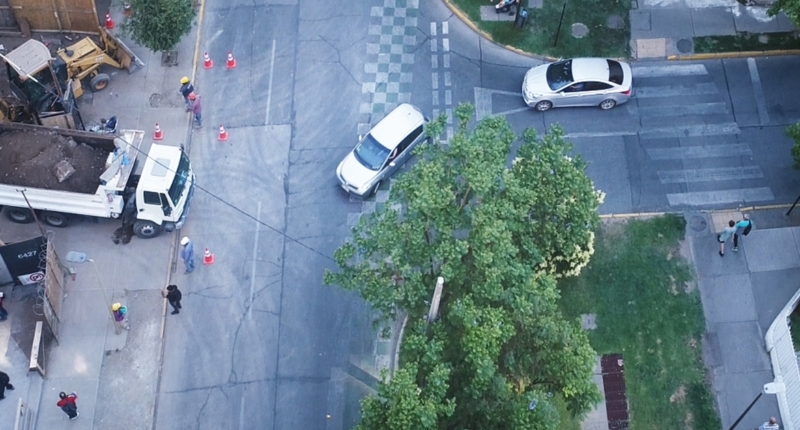
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) offer an alternative approach to systematic behavioral observation of daily activities in the street that can improve our understanding of how streets are used. Recent advancements in technology have made it possible to collect data on pedestrian behavior, but UAVs provide additional benefits such as the ability to cover larger surface areas in less time and observe people on both sides of the street simultaneously. A new study published in PLOS ONE tested the performance of UAV-based observation techniques in measuring pedestrian activity in Santiago de Chile. The study proposes a method that allows momentary time sampling to be carried out with less time differences between different parts of a study area. The study demonstrates that UAVs are a valuable tool for mapping pedestrian behavior and could be significant for understanding the relationship between the urban environment and people’s behavior on streets and in public spaces. The top five important keywords for this content are UAVs, pedestrian behavior, behavior mapping, GIS, and Santiago de Chile.
Mapping Pedestrian Street Behavior with UAVs
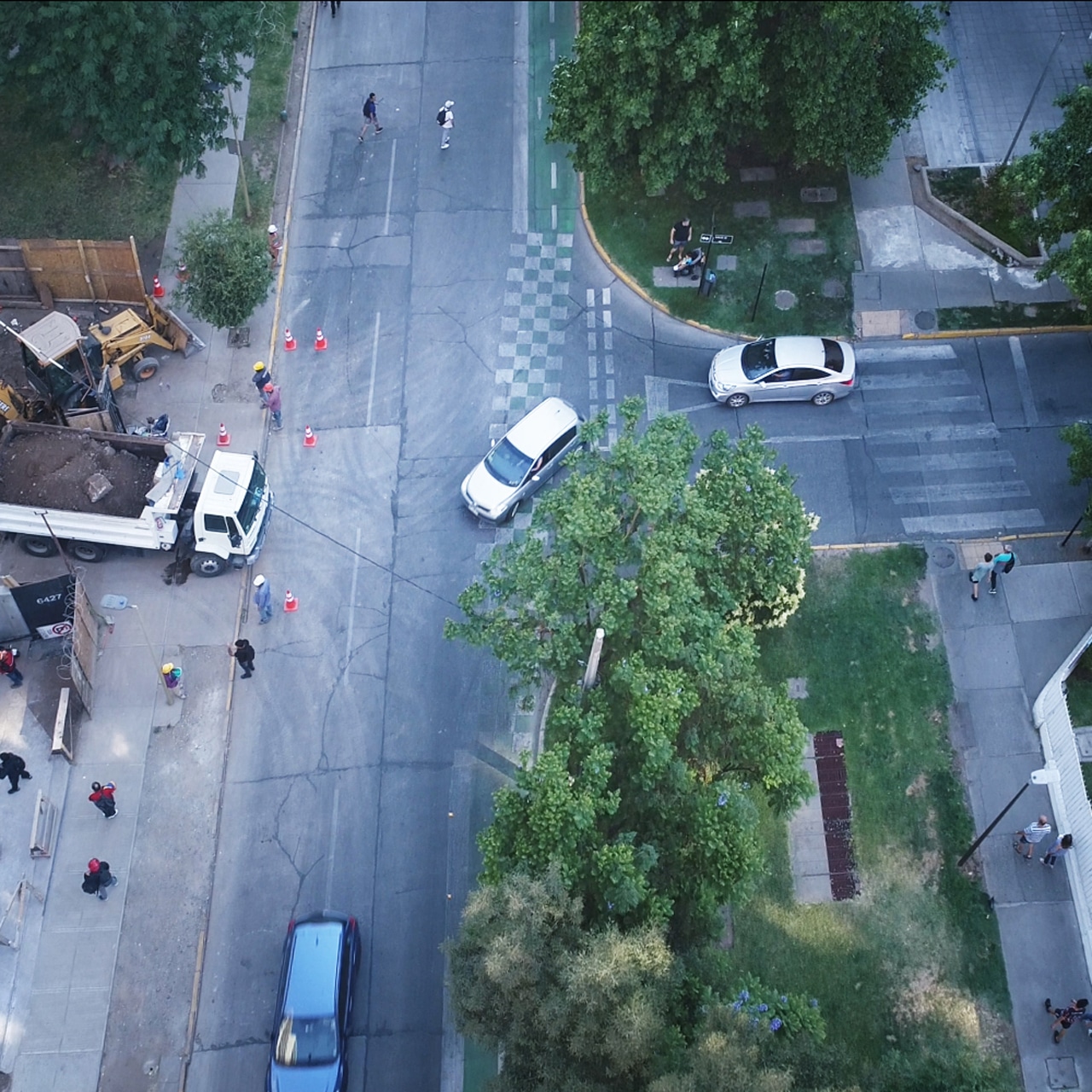

The observation of pedestrian behavior on the street has always been challenging due to the need for extensive resources to analyze pedestrian locations. The rise in walking for leisure purposes has led to the growing interest in studying the relationship between urban environments and people’s behavior on the streets and public spaces. Recent technological advancements have made it possible to collect data on pedestrian behavior through GPS, WiFi signal detection sensors, and computer vision. However, these technologies alone do not provide sufficient information on individuals’ specific activities and behaviors.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have gained popularity as a means of collecting data on pedestrian behavior due to their ability to cover larger surface areas in less time. In a recent study published in PLOS ONE, scientists used UAV-based observation techniques to measure pedestrian activity in two different settings in Santiago de Chile.
The study focused on the development of an alternative approach to systematic behavioral observation of daily activities in the street using UAVs. The approach was centered on the place, based on on-site observations, and involved detailing the necessary steps in the collection of information in the place, followed by the acquisition of data. The data was then coded in a Geographic Information System (GIS).
The results of the study showed high levels of inter-rater reliability in the different categories of recorded data, indicating that the method used to map pedestrian behavior was reliable. The method took advantage of the benefits of UAVs over conventional data collection techniques, such as the elevated position of the observation point, the constant speed of UAV flight, and the backup of data with the subsequent revision that the videos acquired on the flight allowed.
In conclusion, the study demonstrated the potential of UAVs in mapping pedestrian street behavior, providing a more objective observation of pedestrian behavior in urban environments. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that UAVs will become increasingly important in the study of pedestrian behavior on the streets and public spaces.
UAVs: A Valuable Tool for Pedestrian Behavior Mapping
A recent study published in PLOS ONE suggests that the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) can greatly improve our understanding of how streets are used, expanding the register of the volume of pedestrians with additional information that can help to understand spatial patterns or in different geospatial analyses that Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allows.
The study shows that UAVs have several advantages, such as the ability to simultaneously observe people on both sides of the street and even the activity that occurs on the road. Additionally, UAVs can travel at higher speeds than other techniques, resulting in significant resource savings.
Furthermore, the study proposes a method that allows for momentary time sampling to be carried out with less time differences between the different parts that make up a study area. This is in contrast to studies carried out on foot, where differences of several minutes or even hours often occur between the start and the end of the same observation route.
Overall, the study demonstrates that UAVs are a valuable tool for mapping pedestrian behavior, providing additional information on specific activities of people and their interactions with objects, animals, or other people. The benefits of using UAVs for behavior mapping could be significant for understanding the relationship between the urban environment and people’s behavior on streets and in public spaces.
Journal Reference:
- Daniel Parra-Ovalle, Carme Miralles-Guasch et al. Pedestrian street behavior mapping using unmanned aerial vehicles. A case study in Santiago de Chile. PLoS ONE 18(3): e0282024. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282024
Don’t miss interesting posts on Famousbio