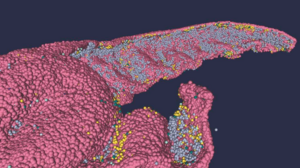
Researchers from the Institute of Biophysics of the Italian National Research Council and University of Modena e Reggio Emilia have developed a full-scale 3D structural model of the human hippocampus CA1 region. This single-cell resolution model replicates the structure, architecture, and connectivity of the neurons of the hippocampus. They have also developed an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating dendritic and axonal shapes. The researchers have compared the density of neurons in their 3D model with existing literature and found it matches experimental observations, validating the model. They will share the dataset and the extraction methodology on the EBRAINS platform, and they are using the same approach to model other brain regions. The study was published in Nature Computational Science on March 23, 2023.
Researchers from the Institute of Biophysics of the Italian National Research Council (CNR-IBF) and University of Modena e Reggio Emilia (UNIMORE), part of the Human Brain Project, have developed a new high resolution model of the CA1 region of the human hippocampus. This single-cell resolution model, which replicates the structure and architecture of the area along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons, was created from a full-scale dataset of high-resolution images. The dataset is available in the BigBrain Atlas and will soon be available on EBRAINS.
The study, published in the journal Nature Computational Science, revealed that the same methodology could be applied to generate full-scale models of other human brain areas and integrated into a co-simulation environment such as The Virtual Brain. The researchers used a customized image processing algorithm to obtain a realistic distribution of neuronal positioning and generate neuronal connectivity by approximating dendritic and axonal shapes.
The researchers performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons was derived from a detailed analysis of these images. “The amount of data on individual neurons of the human brain is very limited, both in terms of relative 3D coordinates and in terms of connectivity among neurons,” explains Michele Migliore from CNR-IBF, Palermo.
The algorithm analyzes high-resolution images and, after the creation of specific geometrical shapes associated with morphological properties, calculates the probability that two neurons are connected. The method provides not only the 3D positioning of neurons but also their connectivity. “Dendrites and axons can be classified into categories depending on the general shape of their extensions. Our algorithm approximates these shapes and analyzes high resolution images, allowing us to calculate the probability that two neurons are connected. The method provides not only the 3D positioning of neurons but also their connectivity,” says Daniela Gandolfi from UNIMORE, lead author of the study.
In conclusion, the researchers have developed a new full-scale 3D structural model of the human hippocampus. This single-cell resolution model replicates the structure and architecture of the area along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons. The dataset is available in the BigBrain Atlas and will soon be available on EBRAINS. The researchers suggest that the same methodology could be applied to generate full-scale models of other human brain areas and integrated into a co-simulation environment such as The Virtual Brain.
The researchers behind the new 3D model of the human hippocampus have compared the density of neurons in their model with existing literature and found it matches experimental observations, validating the model. The dataset and the extraction methodology will be shared on the EBRAINS platform, and the researchers are using the same approach to model other brain regions. The study was published in Nature Computational Science on March 23, 2023.
Don’t miss interesting posts on Famousbio