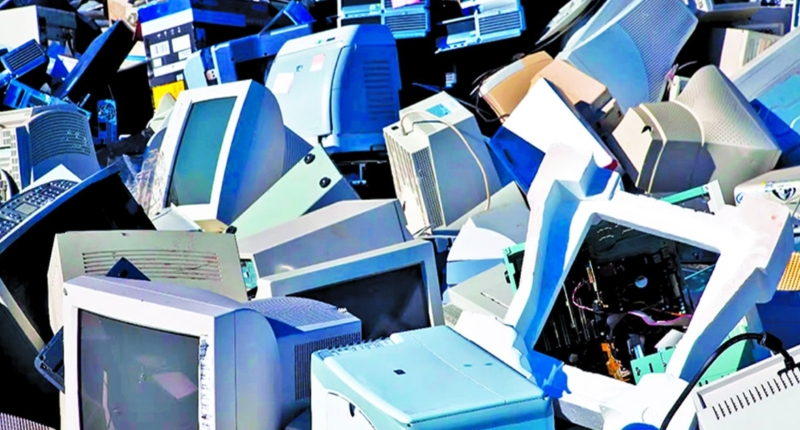
E-waste is a significant environmental issue globally, and its impact on human health and the environment is severe. The constant launch of new electronic devices has led to a growing amount of e-waste. India is the third-largest e-waste producer worldwide, and e-waste is the fastest-growing waste stream in the world.
Several solutions at the individual level can reduce e-waste, including repairing electronics instead of buying new ones, donating old devices, and educating high-school students. Adopting new technologies such as cloud computing and the internet of things can aid in dematerialization. In India, several e-waste recycling startups have emerged to conserve resources, including Cashify, Attero Recycling, and Namo E-waste.
These startups use cost-efficient and environmentally friendly technologies to transform e-waste into raw materials such as metals, plastics, and glass. Recycling old smartphones is also crucial, and small changes at the individual level can make significant impacts.
The Impact of Electronic Waste on Our Planet’s Health
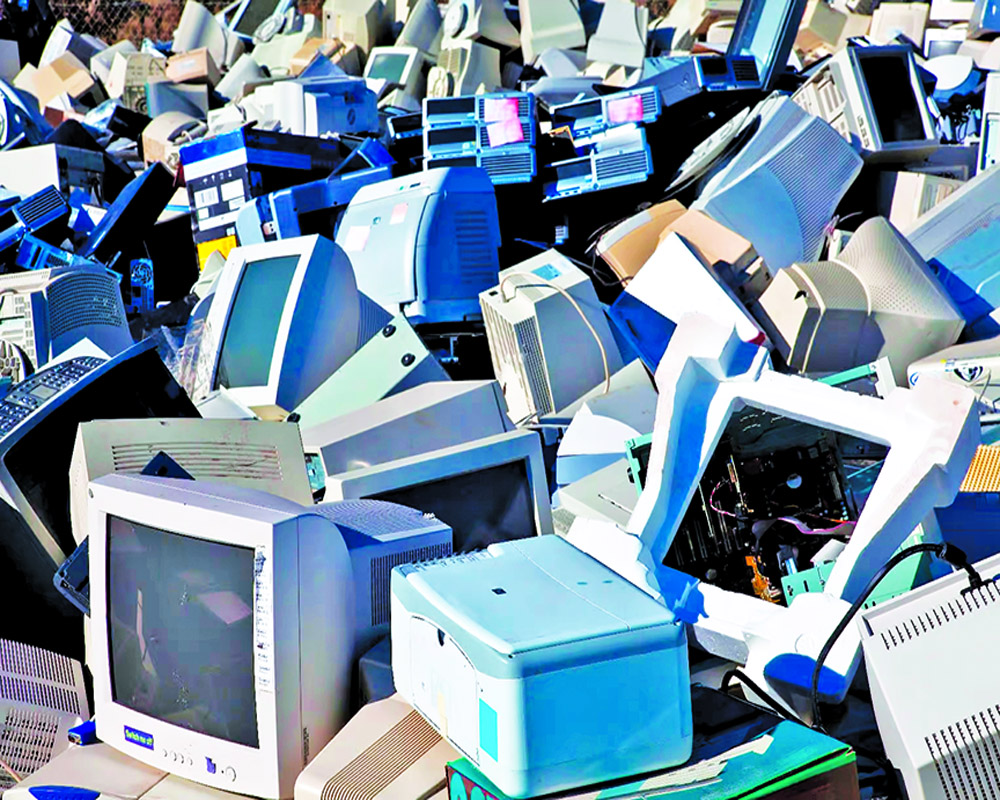

Electronic waste or e-waste is a major concern worldwide, including India. The constant launch of new gadgets and devices leads to our desire to own the latest technology, contributing to the ever-growing e-waste problem.
Addicted to Technology
Technology has transformed our lives, and today it plays a role in almost every aspect, including education, medicine, transport, socialization, food, healthcare, and productivity. However, we fail to realize that our constant use of these devices leads to the generation of e-waste, which has severe impacts on our planet’s health.
Growing E-Waste Stream

Big tech companies release new versions of their devices every year, causing the market to shift to its updated version, and people to replace their old gadgets with new ones, leading to a significant amount of e-waste. Currently, there are almost 10 billion smartphones, and without proper access to repair, these devices will add to the enormous amount of e-waste that already exists. India is the third-largest e-waste producer globally, after China and the USA, and e-waste is the fastest-growing waste stream in the world.
Types of E-Waste
E-waste includes discarded electronic devices such as mobile phones, tablets, notepads, computers, radios, and televisions, with computer devices accounting for nearly 70% of e-waste, followed by the telecom sector, medical equipment, and electrical equipment.
Environmental Impacts
E-waste ends up in landfills, where it releases hazardous gases into the atmosphere, affecting human health in terms of skin irritation, lung infections, kidney problems, nausea, and others. It also contributes to soil contamination, polluting the environment, and posing a significant threat to wildlife. According to a recent study, 5.3 billion phones are thrown away every year, and e-waste has grown by 21% over the past five years, expected to reach 74.2 MT by 2030.
Recycling as a Solution
To combat the e-waste problem, proper disposal and recycling of electronic devices are essential. Heavy metals in e-waste emit toxic substances, which cause serious environmental concern if not recycled or disposed of properly. Companies should take responsibility for their products and implement measures for sustainable e-waste management.
Conclusion
The ever-increasing demand for the latest technology leads to a rise in e-waste, posing severe impacts on our planet’s health. It is crucial to understand the importance of proper disposal and recycling of electronic devices and take necessary measures to ensure sustainable e-waste management. As Christian Lous Lange said, “technology is an effective servant but a dangerous master,” and we should use it wisely, considering its environmental impacts.
Solutions for Reducing E-Waste
E-waste is a growing concern worldwide, and there are several solutions at the individual level that can help reduce it. Repairing smartphones instead of buying new ones or donating old devices to schools or charitable organizations are some examples. Educating high-school students about the harmful effects of e-waste can also make a significant impact.
Adopting new technologies such as cloud computing and the internet of things can aid in dematerialization. In India, several e-waste recycling startups such as Cashify, Attero Recycling, Namo E-waste, Binbag, and many more have emerged to conserve resources by adopting economical and responsible disposal techniques.
These startups use simple, cost-efficient, and environmentally friendly technologies suitable for Indian conditions to transfer waste into socially and industrially beneficial raw materials such as valuable metals, plastics, and glass. As climate change effects grow, it becomes the responsibility of citizens to help the planet and prevent e-waste issues.
With the 5G revolution, it is imperative to recycle old smartphones. It is important to understand that a difference can only be made at the individual level, and small changes can lead to significant impacts.
Don’t miss interesting posts on Famousbio